How the Power Pole Transformer Works
In everyday life, we often see transformers in cities or villages, but rarely think about how electricity is transported from large power stations to the devices we use every day. A key component in this process is the pole transformer - a compact and powerful device that converts high-voltage electricity into a usable voltage.
This article explores how a pole mounted transformer functions, how it fits into the distribution network, and how it compares with other common transformer types like pad mounted transformers.
⚙️ What Is a Power Pole Transformer?
A power pole transformer (also called an electric pole transformer or pole mounted transformer) is a type of power transformer mounted on utility power poles. Its main purpose is to step down electricity from high transmission voltages to safe, low-voltage power suitable for homes and businesses.
These transformers are a crucial link in the power distribution chain, converting thousands of volts into the 120V or 240V we use every day.
⚡ Why Is Voltage Stepped Down?
Electricity is generated and transmitted at high voltages (e.g., 33kV or higher) to reduce transmission losses. However, end users cannot safely use such voltages.
Pole distribution transformers solve this by reducing transmission voltage to levels suitable for daily use, such as:
- 120/240V for residential power
- 208V, 277V, or 480V for commercial buildings
Without these electrical devices, power could not be safely delivered to end users.
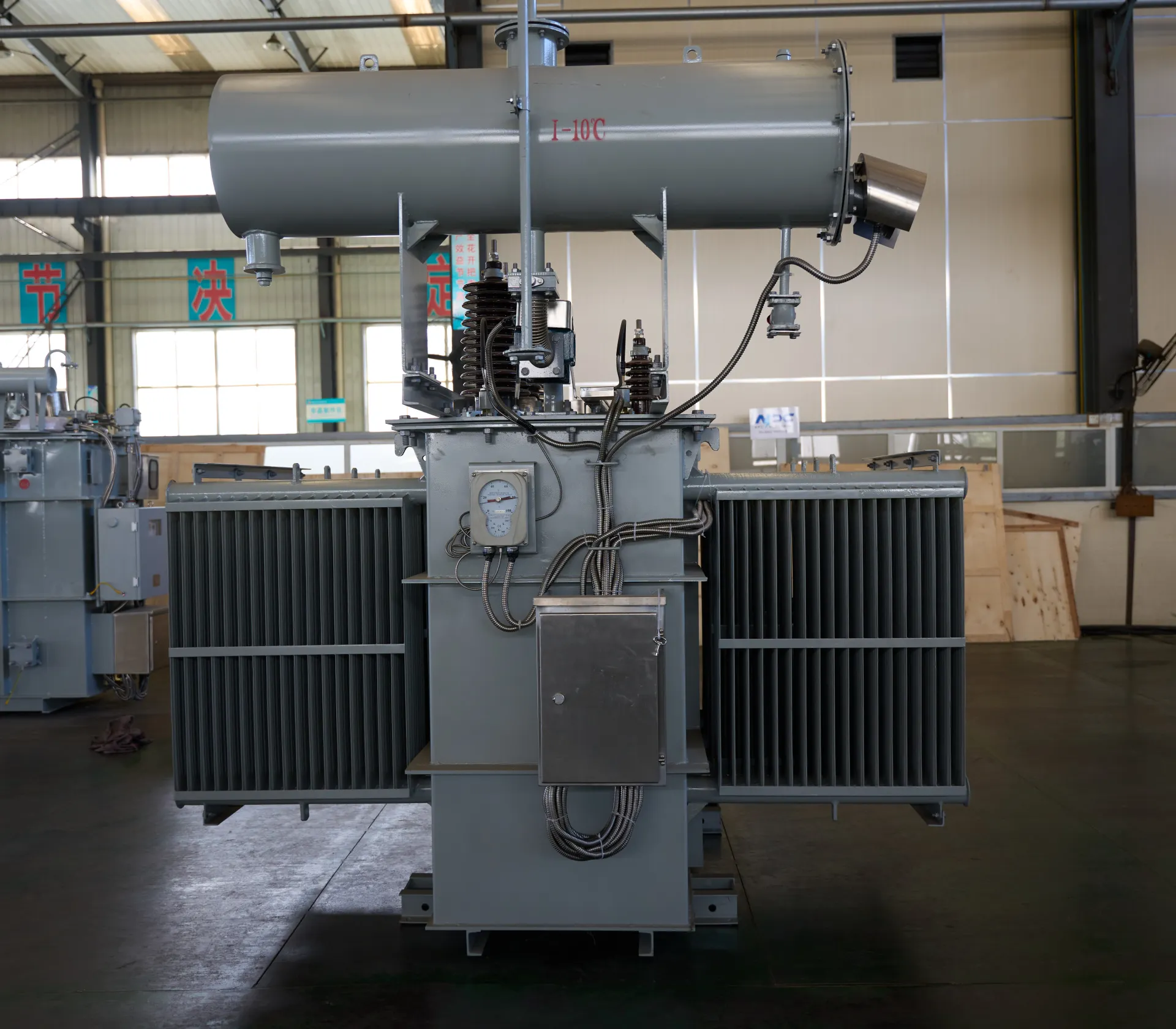
🧩 Key Components of a Power Pole Transformer
1. Core and Coil Assembly
The heart of every transformer. The magnetic core channels magnetic flux, while the windings (copper or aluminum coils) transfer energy between circuits.
2. High-Voltage and Low-Voltage Windings
- Primary winding: Connects to power lines and receives high voltage input.
- Secondary winding: Outputs low voltage to users.
The ratio between these windings determines the voltage reduction.
3. Transformer Oil
Used for insulation and cooling, transformer oil protects internal components from heat and moisture.
4. Bushing Terminals
These are the input/output connections. Insulated bushings keep the system safe from electrical discharge.
5. Tap Changer (Optional)
Adjusts voltage output based on fluctuations in load, helping to maintain grid stability.
🔄 How Does It Work?
The operation is based on electromagnetic induction:
- High voltage enters the primary winding.
- A magnetic field is created in the core.
- This field induces current in the secondary winding.
- The resulting voltage is stepped down and sent to consumers.
➡️ No moving parts are involved, making it highly reliable and low-maintenance.
🔌 Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Transformers
|
Type |
Use Case |
Description |
|
Single-phase |
Homes, light loads |
Converts 1-phase power |
|
Three-phase (phase transformer) |
Industrial, heavy loads |
Converts 3-phase power, higher efficiency |
Utilities may mount three single-phase transformers on a pole (a "bank") or use one large three-phase unit.
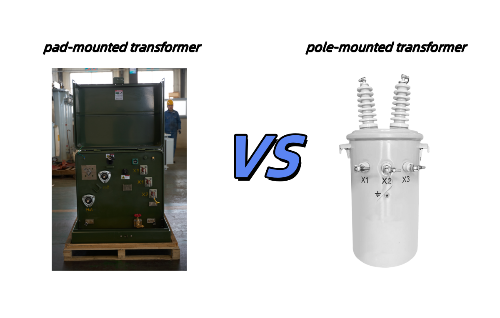
🆚 Pad Mounted Transformers vs. Pole Mounted Transformers
|
Feature |
Pole Mounted |
Pad Mounted |
|
Location |
On power poles |
On concrete pads |
|
Use |
Rural & suburban areas |
Urban or underground networks |
|
Aesthetics |
Exposed |
Enclosed, low-profile |
|
Maintenance Access |
Elevated |
Ground-level |
|
Safety |
Needs ladder/lift access |
Lockable cabinet, safer for public |
Both serve the same function: stepping down voltage for local use in the distribution network.
🔐 Safety Features
Modern power pole transformers are equipped with:
- Surge arresters
- Oil pressure relief valves
- Grounding systems
- Fuses and breakers
These ensure safe operation in all weather and load conditions.
🛠️Transformer Maintenance & Lifespan
Though highly reliable, periodic maintenance ensures optimal performance:
- Check transformer oil level and quality
- Visual inspections for rust, leaks, or damage
- Thermal imaging to detect overheating
- Electrical testing for winding resistance
🕒 Typical lifespan: 20–40 years with proper maintenance
📡 Smart Grids and the Future
Smart electrical equipment is transforming traditional power distribution systems.
Newer pole distribution transformers may include:
- Remote monitoring
- Load balancing
- Fault detection
- Grid communication
This makes the grid more responsive and efficient — ideal for renewable integration and peak demand management.
✅ Conclusion
The power pole transformer plays a foundational role in the global electric power infrastructure. As a bridge between high-voltage transmission and local power distribution, it ensures safe and efficient energy delivery.
Whether it's a single-phase transformer on a rural power pole or a phase transformer integrated into a smart grid, these silent workhorses are critical to modern life.
As urbanization and renewable energy use grow, so too will the innovation and intelligence built into these crucial electrical devices.
📞 Interested in Transformer Solutions?
NPC Electric offers a full range of:
- Pole mounted transformers
- Pad mounted transformers
- Custom power distribution equipment
🔗 Visit: https://www.npcelectric.com
📧 Email: info@npcelectric.com











2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)


