What is the Difference Between a Pole Mounted and a Pad Mounted Transformer?
In modern electrical power distribution networks, transformers are designed to step down high transmission voltages to levels suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial use. Two commonly used types of transformers in distribution systems are the pole-mounted transformer and the pad-mounted transformer. Although both serve the same fundamental purpose—voltage transformation—their design, installation, and operational environments differ significantly.
1. Overview of Pole-Mounted and Pad-Mounted Transformers
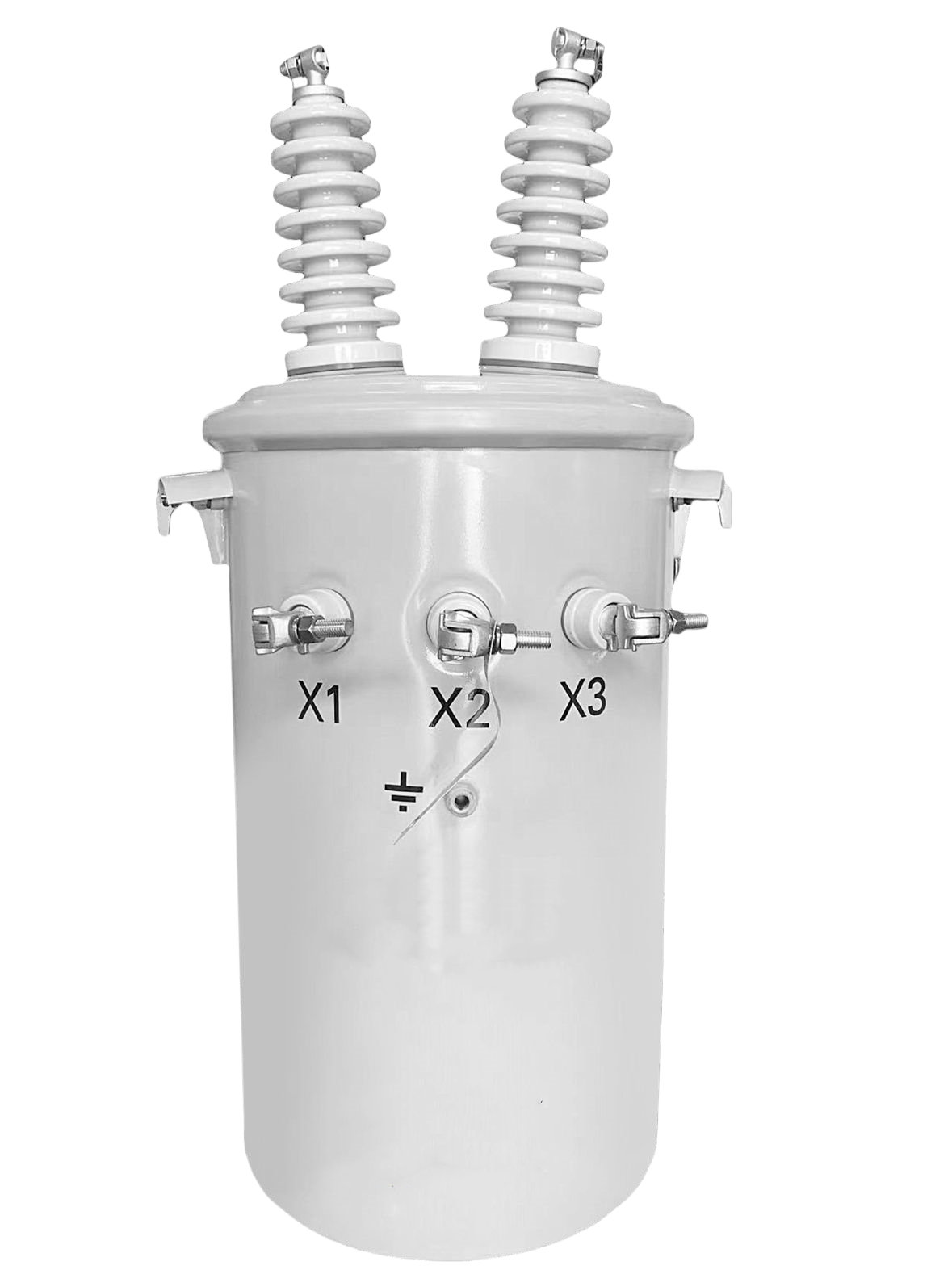
Pole-Mounted Transformer
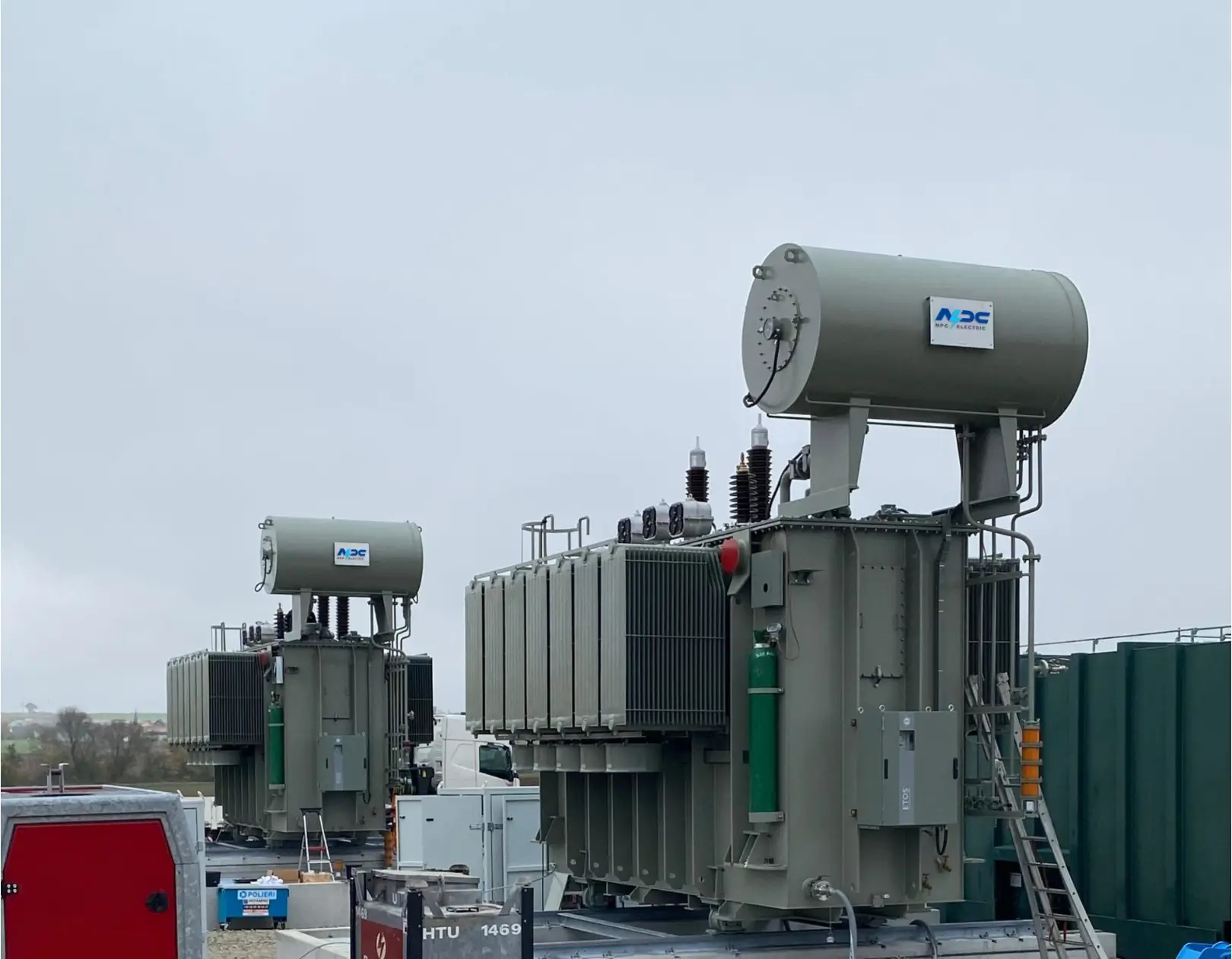
A pole-mounted transformer is typically installed on a utility pole and is a common sight in overhead distribution systems. These transformers are often used in rural or suburban areas where overhead power lines are prevalent. They are compact, cost-effective, and easy to install at elevated positions to keep them safe from physical interference.
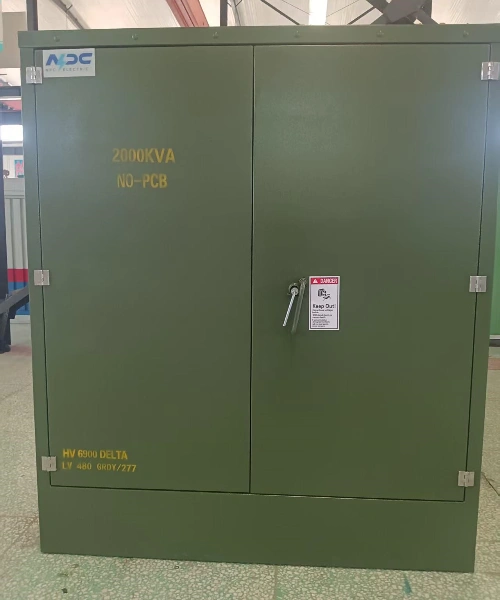
Pad-Mounted Transformer
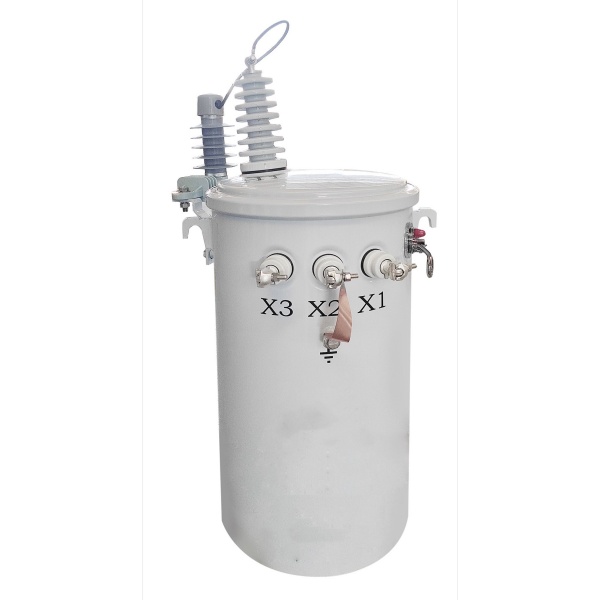
On the other hand, a pad-mounted transformer is installed on a concrete pad at ground level. These transformers are enclosed in tamper-resistant, weatherproof cabinets, making them suitable for areas with underground distribution lines. They are widely used in urban environments, industrial zones, and residential neighborhoods where aesthetics and safety standards require underground cabling.
2. Practical Differences in Real-World Applications
Case 1: Rural Overhead Distribution – Pole-Mounted Transformers
In rural areas with vast distances between loads, overhead lines are the most economical solution. A small utility cooperative in Texas, for instance, uses pole-mounted transformers to supply single-phase power to farms and homes spread over large areas. These transformers are mounted on wooden poles approximately 25 feet above ground, which protects them from accidental contact, flooding, and small animals.
Advantages in this case:
- Lower installation cost compared to underground systems.
- Quick deployment and maintenance.
- Ideal for areas where aesthetics are not a primary concern.
Case 2: Urban Residential Development – Pad-Mounted Transformers
In contrast, a new housing project in California installed pad-mounted transformers because the local code required underground distribution lines for safety and aesthetic reasons. In this case, pad-mounted transformers are installed at ground level on concrete pads, inside lockable enclosures to prevent unauthorized access.
Advantages in this case:
- Safe and accessible for maintenance without climbing poles.
- Compatible with underground systems, reducing exposure to storms and falling trees.
- Better visual appeal for urban or suburban neighborhoods.
3. Design and Configuration Differences
-
Pole-Mounted Transformers:
- Usually single-phase units.
- Mounted on poles for overhead line connection.
- Exposed to the environment, so requires regular inspection.
-
Pad-Mounted Transformers:
- Available in single-phase pad-mounted transformer and three-phase pad-mounted transformer configurations.
- Installed in a weatherproof cabinet on the ground.
- Offer enhanced safety for pedestrian areas.
Single Phase vs. Three Phase Pad-Mounted Transformers
- A single-phase pad-mounted transformer is commonly used for residential neighborhoods or light commercial loads.
- Three-phase pad-mounted transformer (also referred to as a 3-phase pad-mounted transformer) is typically used for industrial parks, large buildings, and shopping centers where loads demand balanced three-phase power.
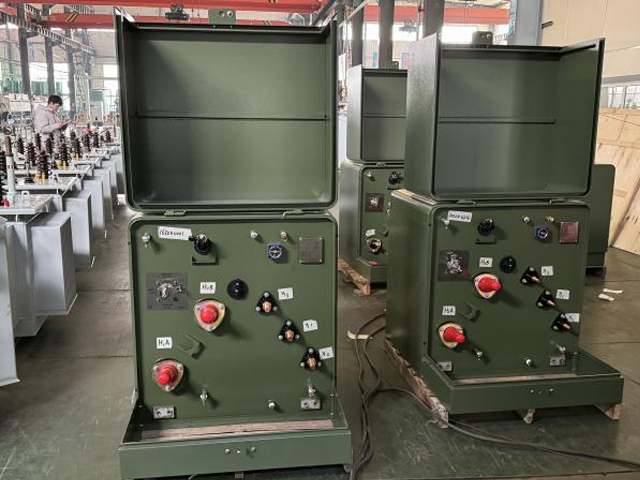
4. How Pad-Mounted Transformers Work
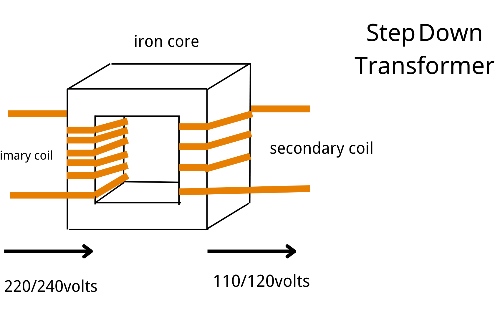
Many wonder how pad-mounted transformers work compared to their pole-mounted counterparts. Functionally, the principle is the same—reducing voltage from distribution level (e.g., 13.8 kV) to service level (e.g., 240/120 V or 480 V). However, because pad-mounted transformers are installed in secure enclosures, they have additional components like bayonet fuses, load break switches, and grounding systems for safety.
5. Safety and Maintenance Considerations
- Pole-mounted transformers: Maintenance requires linemen to climb poles or use bucket trucks. Exposure to weather can lead to corrosion or oil leaks. Wildlife interference (such as squirrels) is a common cause of outages.
- Pad-mounted transformers: Easier and safer to access for maintenance since they are at ground level. However, they require tamper-proof enclosures because they are more accessible to the public.
6. Cost and Aesthetic Factors
- Pole-mounted: Lower installation cost and faster deployment. Best for rural areas.
- Pad-mounted: Higher initial cost due to underground cabling and pad construction, but offers long-term benefits such as lower outage rates and better appearance in urban settings.
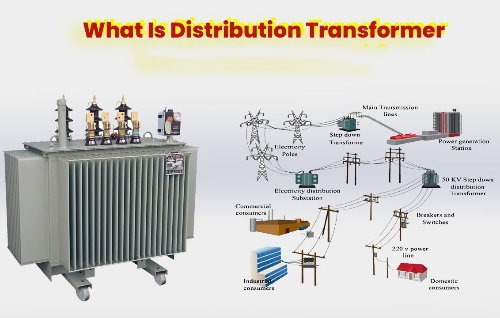
7. Types of Transformers in Distribution Systems
While pole-mounted transformers and pad-mounted transformers are common, they are part of a larger family of types of transformers, including:
- Substation transformers
- Distribution transformers
- Isolation transformers
Each type serves a unique role in the overall power delivery system.
Both pole-mounted transformers and pad-mounted transformers play critical roles in modern electrical distribution. The choice depends on factors like installation environment, load requirements, safety regulations, and aesthetics. Rural areas favor pole-mounted units for cost efficiency and simplicity, while urban and industrial settings rely on pad-mounted units for safety and reliability with underground systems.
Understanding these differences helps engineers, contractors, and utility planners make informed decisions when designing or upgrading distribution networks.


















-AL-medium-voltage-power-cable-2.jpg)