What Is The Bare Copper Wire?
In the world of wire and cable, bare copper wire is one of the most basic and reliable materials. Whether you are working on residential wiring, industrial power systems, or grounding applications, bare copper wire is an integral part of countless electrical systems due to its superior conductivity, durability, and versatility.
NPC ELECTRIC provides a comprehensive, easy-to-understand explanation of what bare copper wire is, its types, common specifications like 4 bare copper wire and 6 bare copper wire, and how it compares to other wire types, such as tinned copper wire. By the end, you’ll understand why bare copper remains a top choice for electrical conductors.
What Is Bare Copper Wire?
Bare copper wire refers to copper conductors that are not coated with any insulation or protective jacket. In its purest form, it is simply copper—exposed, untreated, and unshielded. Despite its simplicity, it plays a critical role in electricity transmission, especially in grounding and bonding applications.
Thanks to copper's superior electrical conductivity—second only to silver—bare copper wire efficiently transmits electricity with minimal resistance and heat buildup. It's widely used where insulation isn’t necessary, such as grounding or where the wire will later be insulated manually or placed inside a protective conduit.

Types of Bare Copper Wire
Not all bare copper wires are the same. They come in several types, each designed for specific use cases and flexibility needs.
1. Soft Drawn Bare Copper
Also known as soft-drawn bare copper wire, this type is heat-annealed after being drawn through dies, making it more flexible. It’s ideal for installations that require bending and shaping, such as in building wiring or flexible grounding setups.
2. Solid vs. Stranded Bare Copper
- Solid bare copper wire is a single, continuous piece of copper. It offers better conductivity and is easier to produce, making it ideal for permanent or low-flex applications.
- Stranded bare copper wire consists of multiple thin copper strands twisted together. This provides greater flexibility, making it suitable for dynamic environments like industrial machinery or where vibration is a concern.
Stranded bare copper wire is often chosen when wire must be repeatedly moved or flexed during its lifetime.
3. Tinned Copper Wire
Although technically not "bare," tinned copper wire is worth mentioning. It’s copper wire coated with a thin layer of tin to enhance corrosion resistance. This type of wire is commonly used in marine and high-moisture environments, offering longevity and reliability.
Tinned wire is part of the broader category of copper wire, including specialized variants for harsh conditions.
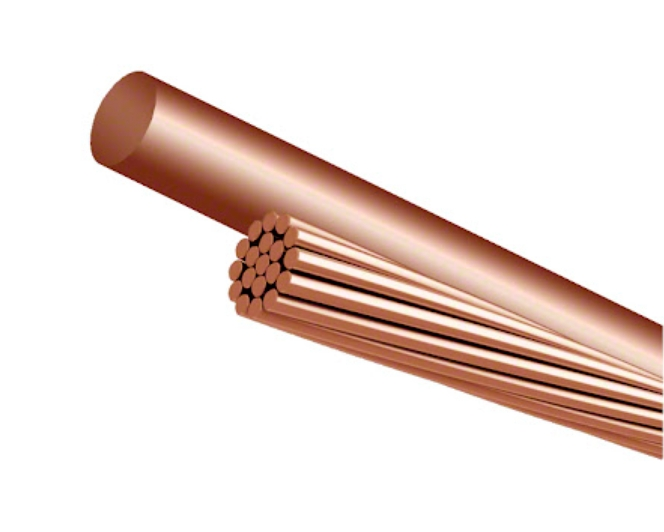
Common Sizes: 4 Bare Copper Wire and 6 Bare Copper Wire
Two of the most commonly used sizes in the U.S. for grounding and power distribution are 4 AWG and 6 AWG bare copper wire.
|
Wire Size |
Approx. Diameter |
Ampacity (in conduit) |
Common Uses |
|
4 AWG |
5.19 mm |
~85 Amps |
Grounding for service panels, large equipment |
|
6 AWG |
4.11 mm |
~65 Amps |
Residential grounding, bonding, and solar arrays |
These sizes are particularly important for grounding systems where a reliable grounding wire is essential for safety and code compliance.
Key Applications of Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire is found across a wide range of industries and use cases. Below are some of its most common applications:
1. Grounding Systems
One of the most critical roles of bare copper wire is in grounding. Whether in residential homes, commercial buildings, or utility substations, grounding wires help safely dissipate excess electricity into the earth during surges, lightning strikes, or faults.
Bare copper is preferred in this context due to its high conductivity, durability, and cost-efficiency.
2. Electrical Panel Bonding and Bus Bars
Bare copper wires are used to connect panels and bus bars in electrical systems. These copper conductors ensure stable current flow and low resistance between system components.
3. Residential and Commercial Building Wiring
In many cases, bare copper wire is used inside conduit or in places where insulation is not necessary. It is commonly used for neutral or ground connections and bonding applications.
4. Utility and Industrial Power Distribution
In outdoor utility systems, bare copper is often used for overhead power lines or grounding grids. Its robustness against weather and temperature extremes makes it ideal for industrial environments.
Benefits of Bare Copper Wire
Choosing high-quality bare copper wire comes with a range of advantages:
- ✅ Excellent Conductivity
Copper has one of the highest electrical conductivity levels among metals, ensuring efficient power transmission. - ✅ Durability
Bare copper resists environmental wear and tear, offering a long service life, especially in dry or controlled environments. - ✅ Cost-Effective
While copper is more expensive than aluminum, it offers better long-term value due to its performance and reliability. - ✅ Environmentally Friendly
Copper is 100% recyclable, making it a sustainable choice for green building projects.
Bare Copper Wire vs. Tinned and Insulated Copper Wire
Understanding the differences between bare copper and other wire types is key to choosing the right material for your application.
|
Feature |
Bare Copper Wire |
Tinned Copper Wire |
Insulated Copper Wire |
|
Protective Coating |
None |
Tin coating |
Plastic or rubber |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
High |
High |
|
Flexibility |
Varies (solid or stranded) |
High |
Medium |
|
Typical Applications |
Grounding, bonding |
Marine, humid environments |
General-purpose wiring |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Slightly higher |
Higher |
If you are working in a corrosive or humid environment, tinned wire is a better choice. But for most standard installations, especially indoors, bare copper provides an excellent balance of performance and affordability.
Tips for Choosing the Right Bare Copper Wire
Selecting the right type and size of copper wire depends on your project’s unique requirements. Here are some general tips:
- ✅ Know the Ampacity Requirements: Choose the correct gauge (AWG) to safely carry the current load.
- ✅ Choose the Right Type: For flexibility, go with stranded bare copper; for more rigid applications, choose solid wire.
- ✅ Environment Matters: For high-moisture or outdoor areas, consider tinned copper wire instead of bare wire.
- ✅ Follow Local Codes: Always consult electrical codes for minimum grounding wire sizes and acceptable conductor types.
So, Bare copper wire is one of the most essential and versatile components in modern electrical systems. From 4 bare copper wires used in large-scale grounding to 6 bare copper wires ideal for residential panels, this simple yet powerful material continues to be the go-to conductor across industries.
Whether you’re working with soft-drawn bare copper, stranded bare copper, or comparing it with tinned copper wire, understanding its properties and applications can help you make informed, safe, and cost-effective decisions.










2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)