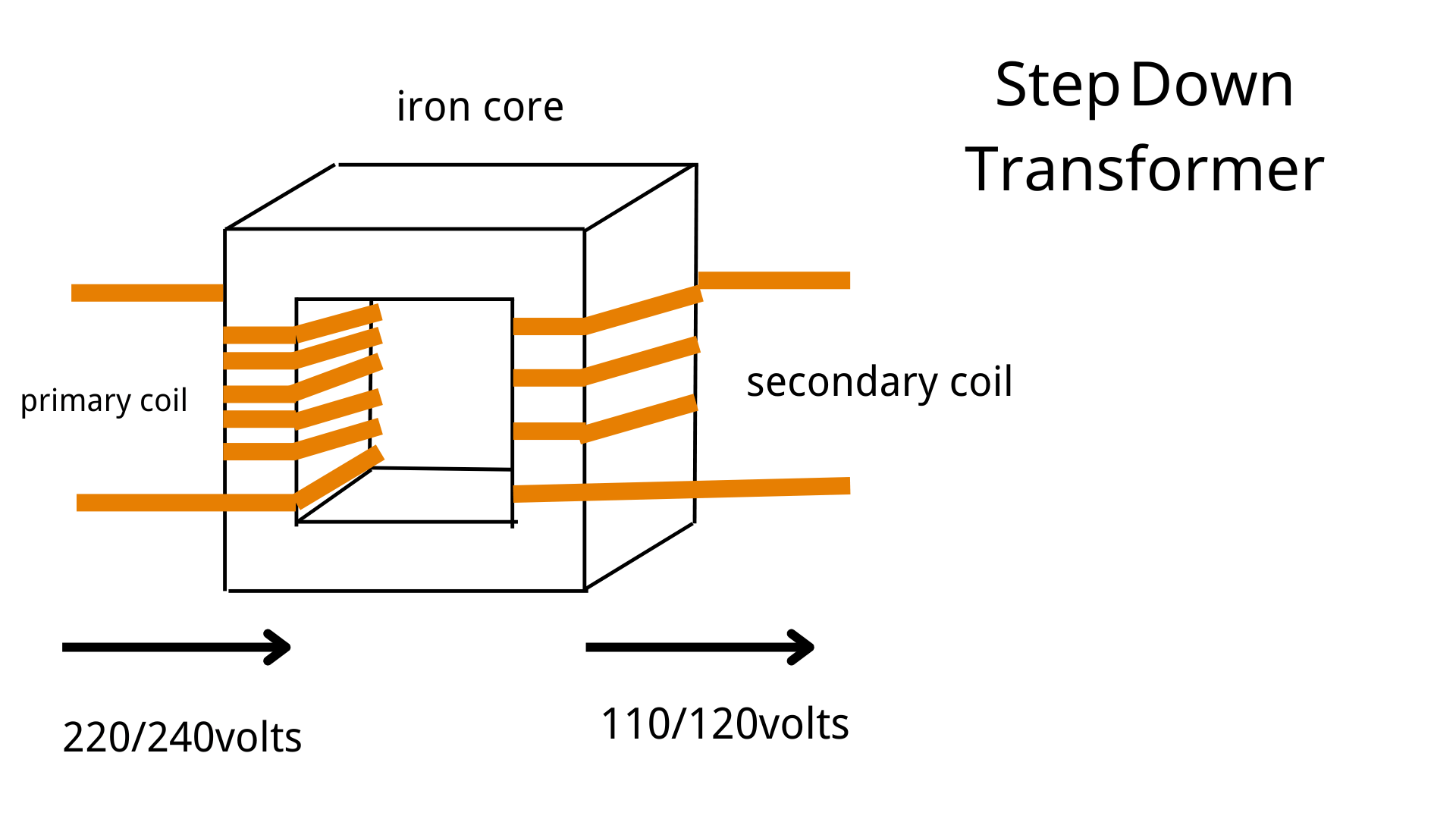
What is a Step-down Transformer?
A step-down transformer is an electrical device that converts high alternating voltage (higher voltage) into a lower alternating voltage, while keeping the power nearly constant (neglecting energy loss). It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction and is widely used in power transmission, household appliances, and industrial applications.
One of the most common uses is the step down transformer 220V to 110V, allowing appliances designed for North American voltage standards to operate safely in regions with a 220V power supply.
1. How a Step-down Transformer Works
A step-down transformer consists of two coils — the primary winding (connected to the input voltage) and the secondary winding (connected to the output load) — wound around a magnetic core.
The voltage ratio between primary and secondary windings depends on the number of turns in each coil:
VpVs=NpNs\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{N_p}{N_s}VsVp=NsNp
Where:
- VpV_pVp = Primary voltage
- VsV_sVs = Secondary voltage
- NpN_pNp = Number of turns in the primary winding
- NsN_sNs = Number of turns in the secondary winding
For a step-down transformer:
- Np>NsN_p > N_sNp>Ns → Output voltage is lower than input voltage.
Example: If Np:Ns=2:1N_p : N_s = 2 : 1Np:Ns=2:1 and the primary voltage is 220V, the secondary voltage will be 110V.
2. Step-down vs Step-up Transformer
It’s important to distinguish between step-down and step-up transformers:
- Step-down transformer: Converts high voltage to low voltage (e.g., 220V → 110V).
- Step-up transformer: Converts low voltage to high voltage (e.g., 110V → 220V).
- Step up and down transformer / Step up down transformer / Step up step down transformer: Multi-function transformers that can both increase and decrease voltage depending on connection configuration.
3. Transformer Types
Step-down transformers come in various types based on construction and application:
- Core-type transformer – Windings are placed around two limbs of a laminated core.
- Shell-type transformer – Windings are placed around the central limb, with magnetic flux circulating through side limbs.
- Autotransformer – Shares part of the winding between primary and secondary circuits, offering higher efficiency and compact size.
- Isolation transformer – Provides galvanic isolation between circuits for safety while stepping down voltage.
4. Applications of Step-down Transformers
- Household appliances: Operating imported electronics with different voltage requirements.
- Industrial machinery: Powering machines that require specific lower voltages.
- Power distribution systems: Reducing high transmission voltages to safe, usable levels.
- Electronics and instrumentation: Supplying stable low voltages for sensitive equipment.
5. Step Down Transformer 220V to 110V
One of the most popular practical uses of a step-down transformer is in voltage adaptation for international products. In many Asian and European countries, the mains voltage is 220–240V, while in North America it is typically 110–120V.
A step down transformer 220V to 110V safely converts the higher mains voltage to the lower voltage required by devices designed for the U.S. market, such as:
- Kitchen appliances
- Audio equipment
- Gaming consoles
- Medical devices
6. Efficiency and Energy Loss
Although step-down transformers are highly efficient (often above 95%), they are not perfect. Energy loss occurs due to:
- Copper loss (resistive heating in windings)
- Core loss (hysteresis and eddy current losses in the magnetic core)
- Leakage flux (magnetic flux that does not link both windings)
Proper design, material selection, and cooling methods help minimize these losses.
7. Step Up and Step Down Transformers in Power Transmission
In large-scale power transmission networks, step-up transformers are used at generation plants to increase voltage for long-distance transmission (reducing current and line losses), while step-down transformers are used at distribution points to lower the voltage for safe household and industrial use.
For example:
- Generation station: Step up from 11kV to 220kV
- Distribution substation: Step down from 220kV to 33kV, then further down to 400V or 230V for end users.
8. Key Considerations When Choosing a Step-down Transformer
When selecting a transformer, consider:
- Primary and secondary voltage ratings – Match with your power source and load requirements.
- Power rating (VA or kVA) – Ensure the transformer can handle the load without overheating.
- Frequency – Most transformers are designed for 50Hz or 60Hz. Using the wrong frequency can cause performance issues.
- Type – Choose between autotransformer, isolation transformer, or other designs based on safety and application needs.
- Build quality and safety certifications – Especially important for imported consumer products.
9. Summary
A step-down transformer is an essential voltage transformer that converts high voltage to low voltage through electromagnetic induction, making it possible to operate electrical equipment safely and efficiently. From the simple step-down transformer 220V to 110V for household use to large-scale transformers in power transmission systems, these devices play a crucial role in modern life.
By understanding transformer types, the relationship between primary voltage, secondary voltage, and the number of turns, as well as energy loss mechanisms, users can make informed decisions about selecting and using transformers for various applications.













2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)