AAC, AAAC, ACSR, and ACAR Conductor Cable Manufacturer: High-Performance Overhead Power Transmission Solutions
In modern power infrastructure design, bare conductors play a vital role in transporting electricity from power generation stations to end users. Among these, AAC (all-aluminum conductor), AAAC (all-aluminum alloy conductor), ACSR (aluminum steel core stranded conductor), and ACAR (alloy reinforced aluminum stranded conductor) are the most widely used conductor types. Each type of conductor utilizes different materials, mechanical properties, and performance characteristics to meet the requirements of different power systems and environmental conditions.
⚙️ 1. Understanding the Function of Overhead Conductors
The primary function of an overhead conductor is to efficiently carry electrical current over long distances with minimal losses while withstanding environmental stresses such as wind, ice, and high temperatures.
These conductors must balance electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance, which directly influences their design and material composition.
🔧 2. Types of Overhead Conductors
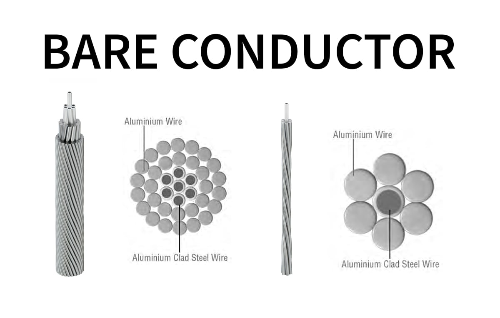
(1) AAC – All-Aluminum Conductor
AAC conductors are made entirely of electrically conductive aluminum strands.
They offer excellent conductivity and lightweight design, making them ideal for urban distribution networks where short spans and high conductivity are needed.
However, they have lower tensile strength, limiting their use in long transmission lines.
Applications:
- City distribution lines
- Short-span overhead networks
- Coastal areas (with corrosion-resistant aluminum)
(2) AAAC – All-Aluminum Alloy Conductor
AAAC conductors are composed of aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy strands.
They provide better mechanical strength and superior corrosion resistance compared to AAC, with only a small reduction in conductivity.
Applications:
- Medium-span power lines
- Coastal and industrial environments
- Regions with high humidity or chemical exposure
(3) ACSR – Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced
ACSR conductors consist of a steel core surrounded by layers of aluminum strands.
This structure combines high tensile strength (from the steel) with excellent conductivity (from the aluminum).
They are widely used for long-distance, high-voltage transmission lines.
Advantages:
- Excellent mechanical strength
- Suitable for long spans and river crossings
- Cost-effective for high-voltage systems
(4) ACAR – Aluminum Conductor Alloy Reinforced
ACAR conductors combine the advantages of ACSR and AAAC, featuring an aluminum alloy core surrounded by aluminum strands.
This design enhances both mechanical strength and current-carrying capacity, while maintaining corrosion resistance.
Applications:
- Long-span transmission lines
- Upgrading existing ACSR lines
- Environments requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio
📊 3. Comparison of AAC, AAAC, ACSR, and ACAR Conductors
|
Type |
Material Composition |
Conductivity (% IACS) |
Tensile Strength |
Corrosion Resistance |
Typical Use |
|
AAC |
Pure Aluminum |
61% |
Low |
Medium |
Urban Distribution |
|
AAAC |
Aluminum Alloy (Mg-Si) |
59% |
Medium |
High |
Coastal / Industrial Areas |
|
ACSR |
Aluminum + Steel Core |
61% |
High |
Moderate |
Long Transmission Lines |
|
ACAR |
Aluminum + Alloy Core |
59–61% |
High |
High |
Long Span & Retrofit Lines |
⚡ 4. Design and Manufacturing Process
Manufacturers of conductor cables follow rigorous standards such as ASTM B231, B232, B399, and IEC 61089.
The process includes:
- Wire drawing – reducing the aluminum rod diameter to the required gauge.
- Stranding – combining wires helically to form conductor layers.
- Core insertion – inserting steel or alloy cores for reinforcement.
- Annealing and surface treatment – improving flexibility and corrosion resistance.
- Testing – ensuring compliance with tensile, resistivity, and elongation requirements.
🌍 5. Applications in Power Systems
- Transmission lines (110kV to 800kV)
- Substation interconnections
- Distribution networks
- Renewable energy transmission (wind & solar farms)
- Utility grid reinforcement and upgrades
Modern grids rely on the right conductor selection to optimize cost, reduce energy losses, and enhance reliability.
💡 6. Choosing the Right Conductor
Selecting between AAC, AAAC, ACSR, and ACAR depends on factors such as:
- Line span and voltage level
- Environmental conditions (corrosive, coastal, or desert)
- Mechanical load requirements
- Budget and maintenance cycle
ACAR often serves as a modern replacement for traditional ACSR due to its lighter weight and similar strength.
🧭 Conclusion
AAC, AAAC, ACSR, and ACAR conductors are critical components in today’s power transmission infrastructure. Each type offers unique benefits — from conductivity and strength to corrosion resistance — allowing engineers to tailor solutions for specific network needs.
Choosing the right conductor not only ensures safe and efficient power delivery but also contributes to lower power losses and long-term system reliability.