Step Up Transformer vs Step-Down Transformer: What’s the Difference and Which One Do You Need?
Transformers are ubiquitous in everyday life and production, and are essential components of modern power systems, ensuring efficient power distribution and voltage regulation. The most common types of transformers are step-up transformers and step-down transformers. While both are voltage transformers that change voltage levels, their functions, structures, and applications are quite different.
What is a Step-Up Transformer?
A step-up transformer is designed to increase the voltage from a lower level to a higher level. It takes input power at a primary voltage and converts it to a higher secondary voltage. This process is crucial when electricity generated at power plants needs to be transmitted over long distances.
How a Step-Up Transformer Works
- The primary windings of a step-up transformer have fewer turns compared to the secondary windings.
- When AC power flows through the primary coil, it induces a higher voltage in the secondary coil because of the greater number of turns.
- In simple terms, a step-up transformer raises voltage while lowering the current proportionally to maintain the same power (minus losses).
Key Features
- High Voltage Windings: The secondary side has high voltage windings for stepping up the voltage.
- Application: Long-distance power transmission, industrial machinery requiring high voltage input.
What is a Step-Down Transformer?
A step-down transformer does the opposite of a step-up transformer. It reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower level. This is essential for making electricity safe and usable for homes, businesses, and low-voltage equipment.
How a Step-Down Transformer Works
- The primary windings of a step-down transformer have more turns than the secondary windings.
- The induced secondary voltage is lower because of fewer turns on the secondary coil.
- This allows high-voltage transmission power to be safely reduced for end-users.
Key Features
- Low Voltage Windings: The secondary windings are designed for lower voltage output.
- Application: Power supply for residential, commercial, and electronic devices.
Primary and Secondary Windings: The Core Difference
The main structural difference between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer lies in the design of the primary and secondary windings:
- Step-Up Transformer: Primary coil has fewer turns, secondary coil has more turns.
- Step-Down Transformer: Primary coil has more turns, secondary coil has fewer turns.
This design principle determines whether the transformer raises or lowers the voltage.
Comparison Table: Step-Up vs Step-Down Transformer
|
Feature |
Step-Up Transformer |
Step-Down Transformer |
|
Function |
Increases voltage |
Decreases voltage |
|
Primary Voltage |
Low |
High |
|
Secondary Voltage |
High |
Low |
|
High Voltage Windings |
Secondary side |
Primary side |
|
Primary Winding Turns |
Fewer |
More |
|
Secondary Winding Turns |
More |
Fewer |
|
Application |
Power transmission, industrial equipment |
Residential power, low-voltage electronics |
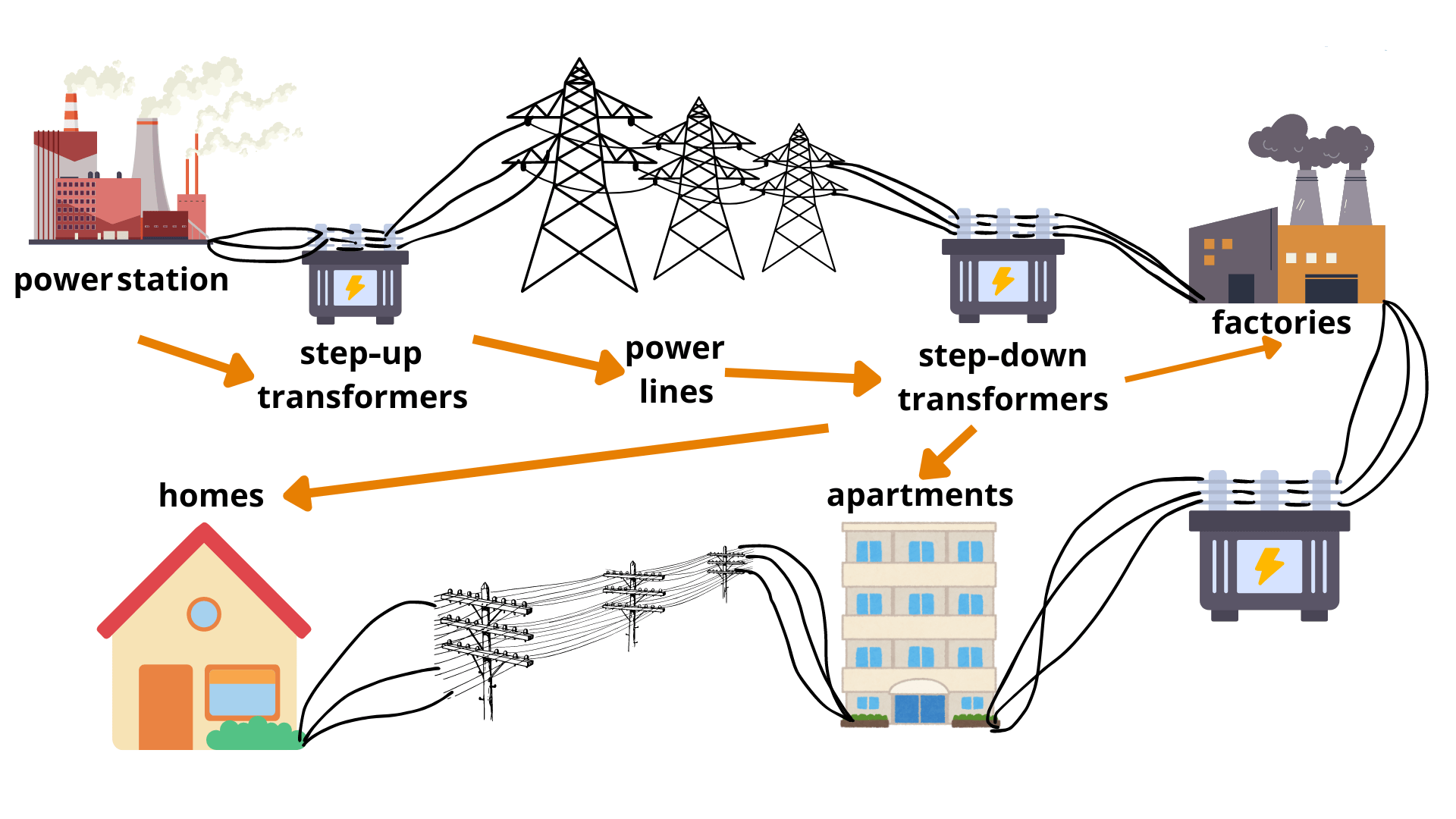
Applications in Power Systems
Both transformer types play critical roles in power systems:
- Step-Up Transformer: Used at power generation stations to raise voltage for efficient power transmission over long distances, reducing line losses.
- Step-Down Transformer: Installed at distribution substations to lower the voltage for safe power distribution to homes and businesses.
Without this step-up and step-down process, energy losses would be significant, and equipment could be damaged by inappropriate voltage levels.
Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers in a Single Unit
For certain applications, a step-up and down transformer (or step-up-down transformer) can serve both functions. These versatile power transformers allow switching between step-up and step-down modes, commonly used in laboratory settings or equipment that must adapt to different voltage standards.
Choosing the Right Transformer Type
When selecting a transformer type, consider:
- Voltage Requirements: Do you need to increase or decrease voltage?
- Power Rating: Ensure the transformer can handle the expected load.
- Efficiency: Look for designs that minimize losses.
- Safety Standards: Especially important in residential and commercial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between a step-up and a step-down transformer?
A step-up transformer increases voltage from a lower primary voltage to a higher secondary voltage, while a step-down transformer reduces voltage from high to low. The difference is mainly in the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings.
2. Where are step-up transformers used in a power system?
Step-up transformers are used in power generation stations to raise voltage for long-distance power transmission, which minimizes energy loss during transport.
3. Why do we need a step-down transformer?
A step-down transformer reduces high transmission voltages to safe levels for power distribution to homes, offices, and electronic devices. Without it, electrical equipment could be damaged.
4. Can a transformer work as both a step-up and a step-down?
Yes, a step-up-down transformer (also called a step-up-down transformer) can function in both modes, depending on the wiring configuration. These are commonly used in laboratories and international power adapters.
5. How do primary and secondary windings affect transformer type?
If the primary windings have more turns than the secondary, the transformer steps down the voltage. If the secondary windings have more turns, the transformer steps up the voltage.
6. Which transformer type is best for residential use?
A step-down transformer is typically used for residential and commercial applications because it lowers the high transmission voltage to a safe secondary voltage level.
Understanding the differences between step-up transformers and step-down transformers is vital for engineers, technicians, and facility managers. Step-up transformers raise voltage for efficient transmission, while step-down transformers reduce voltage for safe utilization. Both are integral to power systems and modern electrical infrastructure.
If you need a reliable step up and down transformer or a specialized voltage transformer for your application, always prioritize quality, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards.












2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)


-AL-medium-voltage-power-cable-2.jpg)