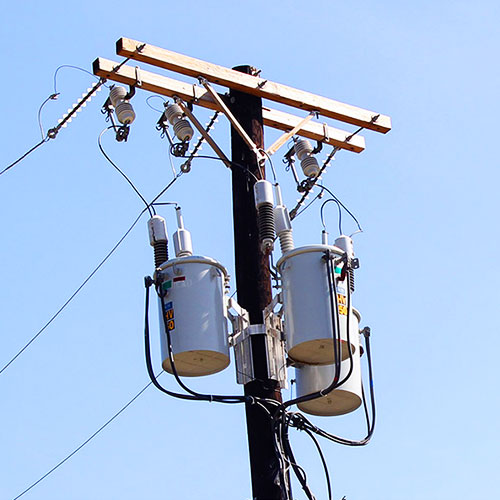
What is a Pole Mounted Transformer? An In-Depth Explanation
As an engineer working in the power distribution network for many years, I've noticed in my daily work that pole-mounted transformers are among the most overlooked critical transformers. These compact devices, often called pole-mounted transformers or power pole transformers, are mounted directly on utility poles. They play a vital role in safely and efficiently transmitting electricity from high-voltage transmission lines to the everyday devices in our homes and industries.
Unlike pad-mounted transformers, which are enclosed at ground level and frequently used in urban or underground systems, pole-mounted transformers are designed to be suspended above ground, making them both accessible for maintenance and ideal for rural or suburban distribution. Their compact design, cost-effectiveness, and reliability explain why pole-mounted transformers remain one of the most widely used distribution transformers globally.
The Role of Pole Mounted Transformers in Power Distribution
The journey of electricity is not as simple as moving electrons from a power plant to a light bulb. Electrical energy is generated at power stations and transmitted over long distances at extremely high voltages to reduce losses. However, end users cannot use this high voltage directly—it must be stepped down. This is where pole mount transformers enter the picture.
By stepping down electricity from the primary voltage of transmission lines to the secondary voltage required for consumer use, pole-mounted transformers act as the bridge between generation and consumption. Without them, the power distribution network would fail to deliver electricity safely and efficiently to residential, commercial, and industrial customers.

Types of a Pole Mounted Transformer
From an engineering perspective, there are several types of pole-mounted transformers, each designed for specific requirements:
- Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformer – This is the most common type for rural areas and residential neighborhoods. A single-phase pole-mounted transformer typically supports lighting, household appliances, and small commercial loads. It offers simplicity, low cost, and reliability.
- 3 Phase Pole Mounted Transformer – In industrial zones, commercial centers, or urban districts, demand is much higher. A 3 phase pole mounted transformer is required to power heavy machinery, HVAC systems, and larger electrical infrastructure.
- Conventional Type Pole Mounted Transformer – These rely on external protection equipment such as fuses and lightning arresters. While they are effective, they require more external installation components.
- Completely Self-Protected (CSP) Pole Mounted Transformer – This modern design integrates protective devices directly into the transformer. With internal fuses, breakers, and surge arresters, CSP transformers reduce maintenance needs and enhance safety.
Together, these phase transformers and design variants ensure that electricity delivery can be tailored to meet the needs of different environments and customer demands.
Construction and Technical Features
At its core, a pole-mounted transformer contains primary and secondary windings that facilitate voltage conversion. The primary winding connects to the incoming high-voltage transmission line, while the secondary winding delivers lower, usable voltage to consumers.
These transformers are generally oil-immersed, meaning insulating oil surrounds the windings to both cool the unit and improve dielectric strength. The tank is made of corrosion-resistant steel and designed to withstand outdoor conditions for decades. Accessories may include bushings, pressure relief valves, and mounting brackets.
The elevated design offers several practical benefits:
- Reduced the risk of accidental contact by the public.
- Faster visual inspection and maintenance by line crews.
- Lower installation cost compared to pad-mounted transformers.
Pole Mounted vs. Pad Mounted Transformers
While both fall under the category of distribution transformers, their differences are worth noting:
- Pole-mounted transformers are installed on poles for overhead systems, usually in rural or semi-urban areas. They are smaller, cheaper, and easier to maintain.
- Pad-mounted transformers are ground-mounted, enclosed in lockable steel cabinets, and used where underground distribution is preferred, such as in cities or housing developments where aesthetics and safety are priorities.
The choice between the two depends largely on specific requirements such as grid design, safety codes, load density, and maintenance accessibility.
Applications and Benefits
Pole-mounted transformers are used worldwide for:
- Rural electrification projects.
- Supplying homes, farms, and small businesses.
- Industrial areas require 3-phase pole-mounted transformers.
- Temporary power solutions at construction sites.
Key benefits include:
- Cost efficiency – lower installation and operating costs.
- Flexibility – suitable for both small and large loads.
- Safety – elevated installation reduces tampering risks.
- Durability – built to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Choosing and Purchasing a Pole Mounted Transformer
When planning to purchase a pole-mounted transformer, several factors should be considered:
- Load demand – Whether a single-phase or 3-phase transformer is needed.
- Protection level – Conventional vs. CSP designs.
- Efficiency – High-efficiency transformers reduce energy losses.
- Compliance – Ensure adherence to international and regional safety standards.
- Manufacturer reputation – Trustworthy pole-mounted transformer manufacturers provide not just reliable equipment but also long-term service and support.
A transformer must be matched to the specific requirements of the distribution system to ensure longevity, reliability, and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are pole-mounted transformers safe?
Yes. They are designed with robust insulation, oil cooling, and are mounted out of public reach. CSP models add extra safety through built-in fuses and arresters.
Q2: What is the difference between pole-mounted and pad-mounted transformers?
Pole-mounted transformers are suspended on poles for overhead systems, while pad-mounted transformers are ground-based, enclosed, and better suited for underground systems.
Q3: When should I choose a single-phase vs. a 3-phase pole-mounted transformer?
Single-phase transformers are ideal for residential and rural loads, while 3-phase transformers are required for industrial and urban networks with higher demand.
Q4: How long does a pole-mounted transformer last?
With proper maintenance, most units last 25–40 years, depending on environmental conditions and load cycles.
Q5: What factors matter most when purchasing a pole-mounted transformer?
Key considerations include load capacity, phase requirements, protection features, energy efficiency, and trusted pole-mounted transformer manufacturers.
Final Thoughts
From the standpoint of an engineer, pole-mounted transformers are indispensable to modern power systems. Whether it’s a single-phase pole-mounted transformer supplying a rural community or a 3-phase pole-mounted transformer driving industrial equipment, these compact devices are the backbone of safe and reliable electricity distribution. By understanding their types, applications, and technical features, stakeholders can make informed choices that ensure efficient power delivery across diverse environments.













2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)