Modern Power Transformers: Efficiency, Design, and Smart Grids
In today's rapidly evolving energy landscape, power transformers play a central role in ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission and distribution. With the continued growth of global electricity demand, power systems are accelerating their transition to smart grids and large-scale integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. This makes the design, performance, and efficiency of modern power transformers more critical than ever before.
These devices are no longer simply tools for stepping up or stepping down voltage; they are essential components of the digital energy ecosystem. To meet the requirements of smart grids, next-generation transformers must minimize energy losses, achieve precise and stable operational control, and seamlessly integrate with advanced sensor, monitoring, and diagnostic technologies. This means they need to be highly resilient to voltage fluctuations and transient impacts from renewable energy sources, while supporting predictive maintenance and fault diagnosis through real-time data analysis, thereby significantly improving the grid's resilience, reliability, and operational efficiency. Therefore, continuous innovation in transformers is the fundamental guarantee for building a sustainable and efficient future power system.
1. Understanding Modern Power Transformers
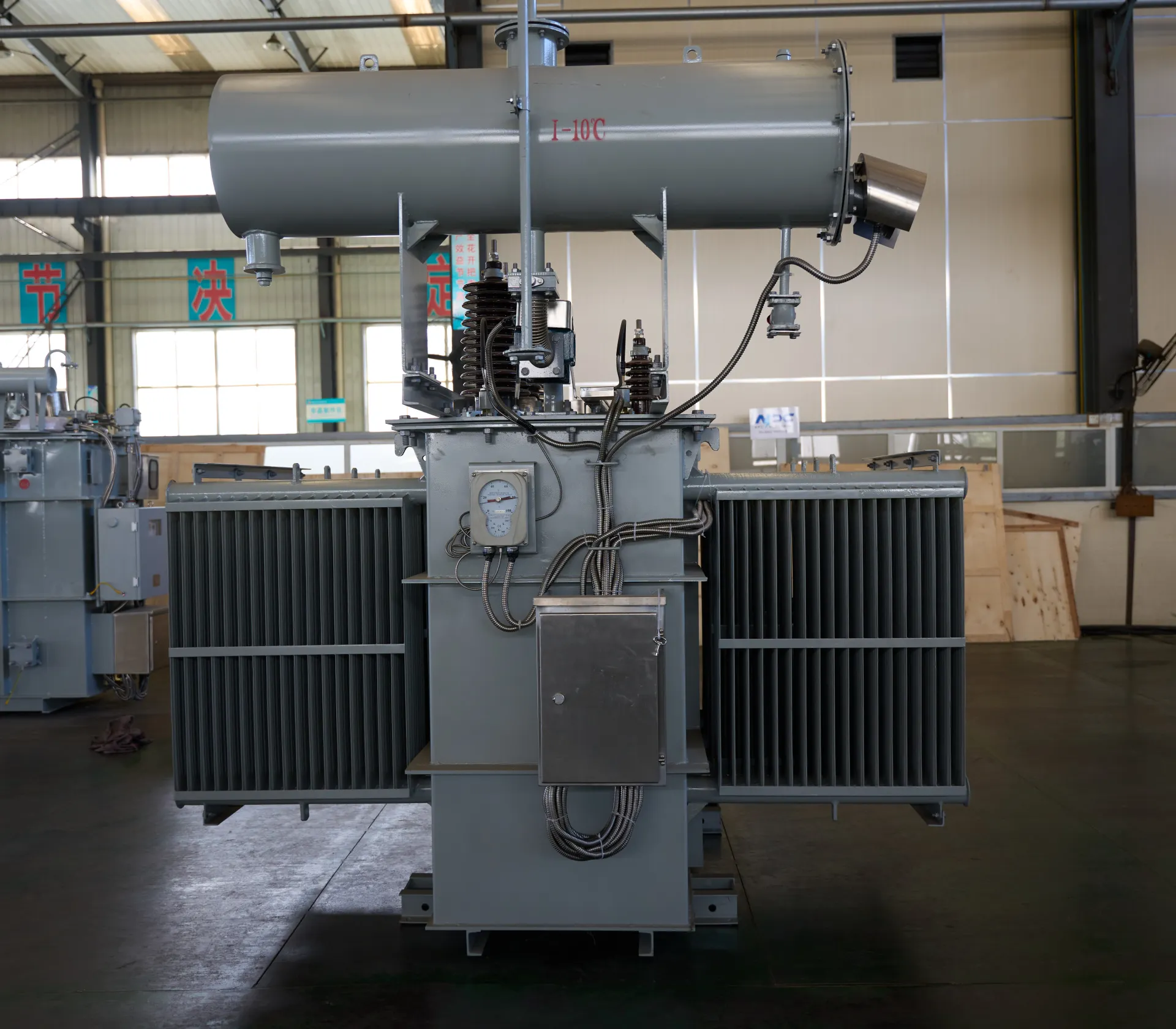
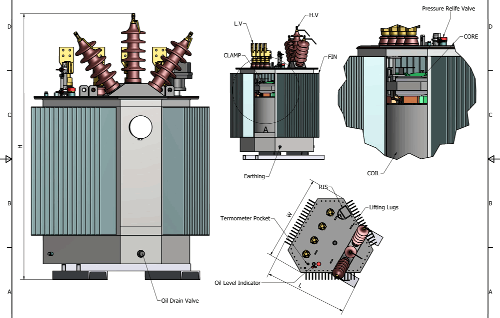
A power transformer is an electrical transformer designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Unlike smaller distribution transformers used for end-user supply, power transformers handle high-voltage transmission in large-scale networks.
Modern designs focus on:
-
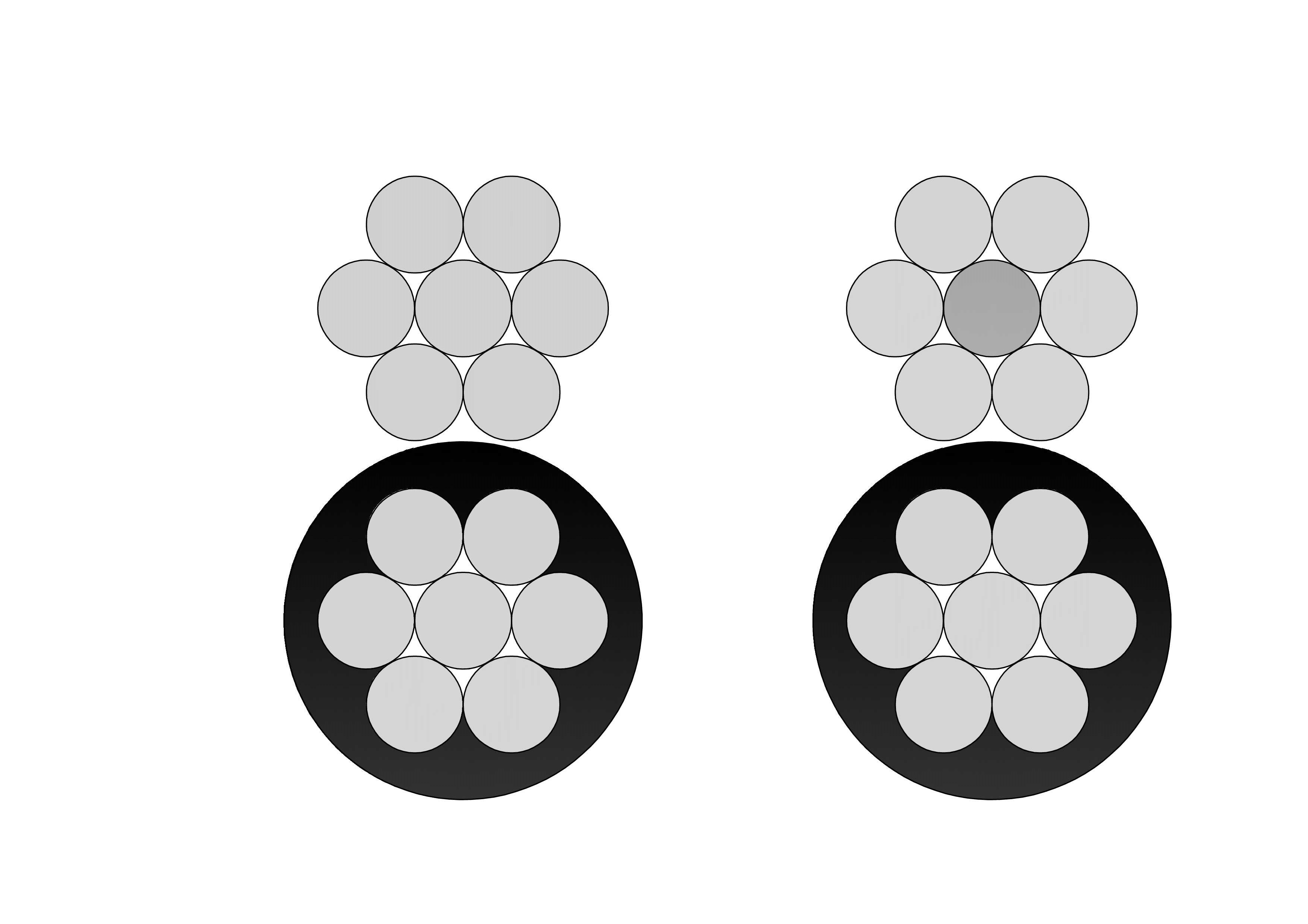
Enhanced magnetic core materials (using grain-oriented silicon steel or amorphous metal) to reduce core losses.
-
High-efficiency winding structures that minimize leakage reactance and improve thermal performance.
-
Digital monitoring systems for real-time performance diagnostics and predictive maintenance.
These advancements make modern power line transformers more efficient, compact, and environmentally friendly compared to traditional units.
2. Design Evolution and Technological Advancements
Traditional transformers were primarily mechanical and passive components. Today’s power transformers integrate advanced materials and digital technologies to meet the demands of smart grids.
Key design improvements include:
-
High-efficiency cooling systems: Forced-air and oil-immersed cooling methods enhance heat dissipation, while dry-type designs improve fire safety.
-
Low-loss core design: Modern laminations and optimized flux paths minimize eddy current losses.
-
Smart sensors and IoT integration: Continuous data collection enables grid operators to monitor temperature, vibration, and load conditions remotely.
These technologies help extend transformer lifespan, reduce operational costs, and improve network reliability.
3. Power Transformers in Smart Grid Systems
In smart grids, transformers act as the bridge between generation, transmission, and consumption. They regulate voltage levels, balance load distribution, and enable dynamic power flow management.
Modern power distribution systems utilize digital power transformers equipped with communication modules that connect to SCADA and IoT platforms. This allows utilities to:
-
Perform remote monitoring and fault detection
-
Implement predictive maintenance strategies
-
Optimize load balancing and energy dispatch
Furthermore, single-phase power transformers are widely used in distributed renewable systems—such as solar and wind farms—where modularity and flexibility are required for grid integration.
4. Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Efficiency is a core concern in transformer design. Even a 1% efficiency gain can save millions of kilowatt-hours annually in a large utility network.
Modern electrical transformers achieve up to 99.7% efficiency through:
-
Improved insulation materials and optimized winding geometries
-
Reduced core losses via amorphous steel cores
-
Advanced cooling and oil filtration technologies
In addition, eco-friendly transformer oils, biodegradable materials, and low-noise operation make modern transformers compliant with environmental and regulatory standards.
The move toward sustainable materials and energy-efficient power systems aligns with global initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
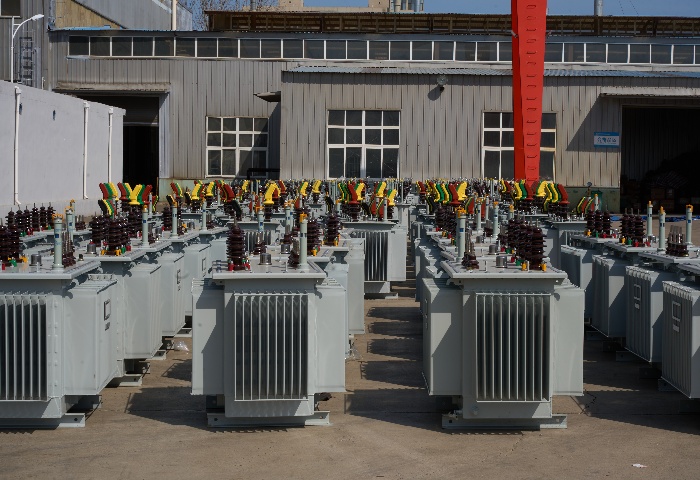
5. Real-World Applications
Modern power transformers are deployed across multiple sectors:
-
Utility power grids: For high-voltage transmission and regional distribution.
-
Industrial facilities: Supplying consistent voltage to heavy machinery and process plants.
-
Renewable energy plants: Connecting solar farms and wind turbines to the main grids.
-
Urban distribution networks: Using compact transformers to minimize space while maintaining reliability.
In renewable energy systems, power transformers enable bidirectional power flow—crucial for integrating distributed generation and energy storage systems.
6. Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Regular monitoring and maintenance ensure long transformer lifespans and optimal performance. Key maintenance activities include:
-
Oil analysis to detect dissolved gases or moisture
-
Thermal imaging to identify overheating zones
-
Partial discharge testing to assess insulation integrity
-
Digital diagnostics using online monitoring tools
Implementing these practices reduces unexpected downtime, enhances safety, and lowers lifecycle costs.

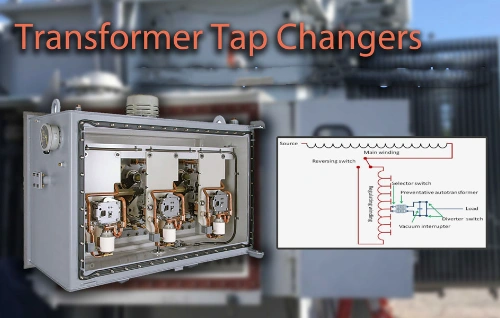
7. The Future of Power Transformers
The future of power transformers is defined by smart, sustainable, and self-optimizing technologies.
Emerging trends include:
-
Solid-state transformers (SSTs) for real-time power conversion and bidirectional flow.
-
Integration with renewable sources and energy storage systems.
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive maintenance and autonomous control.
As smart grids expand globally, modern transformers will become even more intelligent, efficient, and environmentally compatible—serving as the backbone of the next-generation power distribution system.
Modern power transformers are far more than voltage regulators—they are intelligent components essential for the stability and efficiency of future energy systems. Through advanced design, smart technologies, and sustainable materials, they ensure that the world’s power infrastructure remains reliable, safe, and ready for the challenges of tomorrow’s electrical transformation.










SSCHOU-mining-cable-2.webp)

2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)