Three Phase Transformer Guide: How It Works and Why It Matters in Modern Power Systems
Three-phase transformers are an indispensable component of modern power systems, demonstrating their high efficiency in power conversion, especially in high-power applications. Compared to single-phase transformers, three-phase transformers provide more stable power output, making them suitable for large-scale power transmission and distribution. Whether providing a stable power supply to heavy machinery in industrial plants or distributing power in urban power grids, three-phase transformers operate efficiently with minimal energy loss.
Furthermore, three-phase transformers play a crucial role in renewable energy systems, helping to convert and effectively transmit electricity from sources such as wind or solar power to the grid. By optimizing power flow and reducing energy losses during transmission, three-phase transformers ensure system stability and long-term reliability. With the increasing global demand for clean energy, the high efficiency and reliability of three-phase transformers are leading to their increasingly widespread application in modern power systems.
What is a Three Phase Transformer?
A three-phase transformer is a type of electrical transformer designed to work with a three-phase electrical system. It converts three-phase power from one voltage level to another—either stepping it up or stepping it down. This transformation is essential for the efficient distribution and transmission of electrical power over long distances.
In a three-phase system, three separate voltage waveforms are generated 120 degrees apart. A three-phase transformer consists of three primary windings and three secondary windings, each connected in either wye (star) or delta configuration. This setup provides a continuous power supply, which is more stable and efficient than a single-phase transformer, particularly for high-power applications like industrial machinery and large power grids.

How Does a Three Phase Transformer Work?
The principle behind a three-phase transformer is based on electromagnetic induction, just like other transformers. The transformer consists of three windings:
-
Primary Windings: These are connected to the source of power, typically the high-voltage side of a distribution system.
-
Secondary Windings: These deliver the transformed voltage to the load side of the system.
When three-phase power enters the primary side, the current flows through the windings, creating a rotating magnetic field in the transformer’s core. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary windings. The resulting secondary voltages are then used to power equipment or to further distribute the power to other systems.
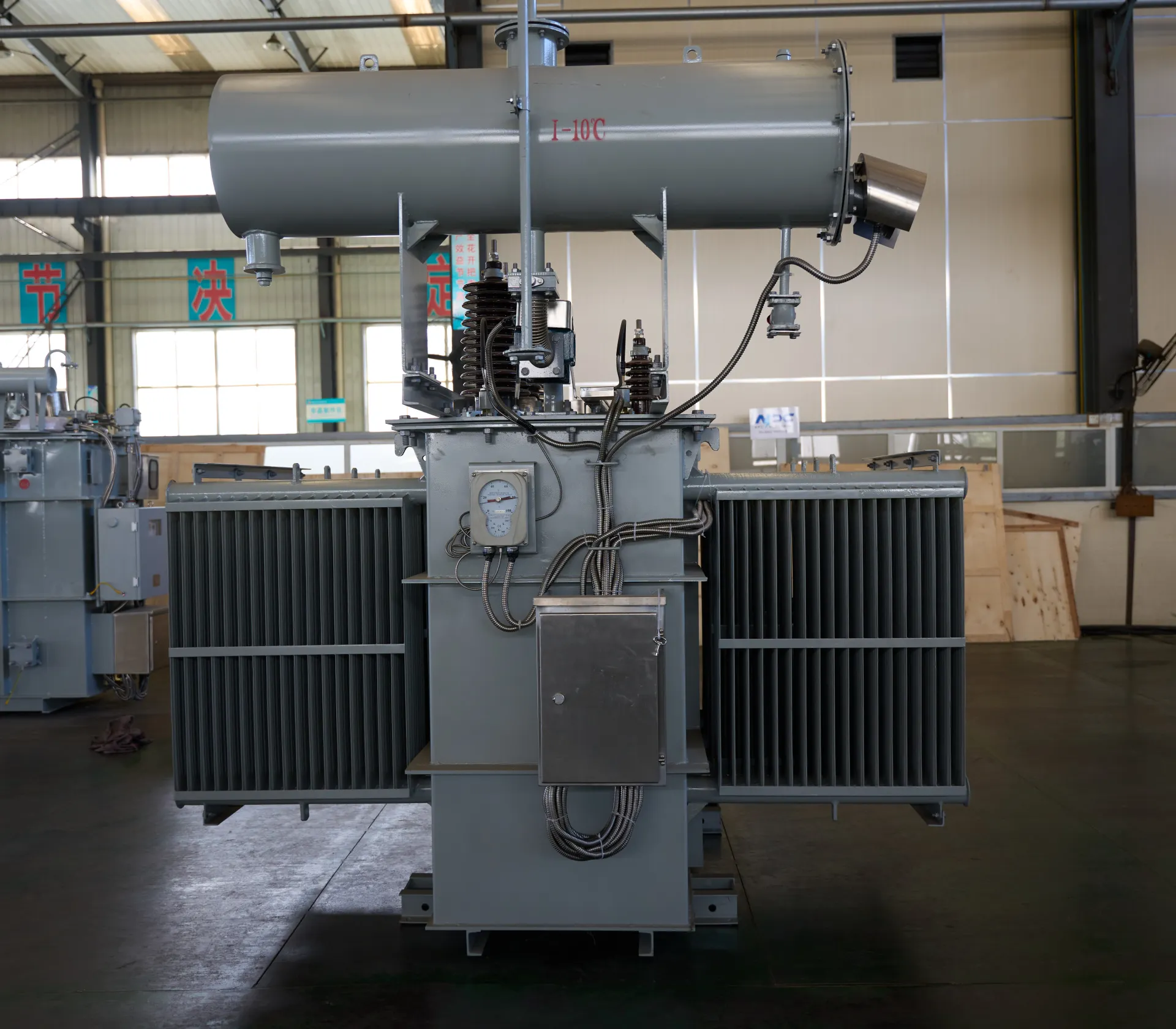
Key Components of a Three Phase Transformer
- Primary and Secondary Windings: The core components that determine the voltage conversion ratio. The windings are typically made of copper or aluminum, wound around a core of steel sheets to provide efficient magnetic flux paths.
-
Core: The transformer’s core is made of laminated steel sheets to reduce energy losses and ensure efficient operation. The core helps direct the magnetic flux and provides the necessary magnetic field for voltage induction.
-
Cooling System: Large transformers require efficient cooling systems to prevent overheating. This can include oil cooling systems or air-cooling methods, depending on the transformer’s size and operating conditions.
-
Taps and Connections: The transformer’s connection to the electrical system can vary. It can be connected in a delta configuration for more balanced power flow or in a wye configuration for better voltage regulation.
Why Three-Phase Transformers Matter in Modern Power Systems
Three-phase transformers are essential for the efficient transfer of high power across large distances. They allow for the generation and transmission of electricity with fewer losses and more reliable power delivery. Here’s why three-phase transformers are so critical in modern power systems:
1. Improved Power Flow and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of a three-phase transformer is its ability to handle a larger volume of power, delivering stable and continuous power flow. In industrial and utility-scale applications, this means more reliable service and less downtime. A three-phase system can handle higher currents and distribute them more evenly across the three wires, reducing the risk of overloads and improving system efficiency.
2. High-Power Distribution
For large-scale industrial systems or power distribution networks, three-phase transformers are essential because they can handle higher power capacities. Whether stepping down high-voltage power for local distribution or stepping up power for long-distance transmission, these transformers provide the high power necessary to keep systems running smoothly.
3. Flexibility and Scalability
A three-phase transformer allows for greater flexibility in terms of voltage regulation and scalability. Systems can be designed to meet the evolving demands of growing industries and expanding power grids. Additionally, three-phase pad-mounted transformers are commonly used in urban environments for underground power distribution, offering flexibility without compromising on power quality.
4. Applications in Renewable Energy
In renewable energy systems, such as wind farms or solar power plants, three-phase transformers are used to convert the generated power into a format suitable for grid integration. Whether converting the output from wind turbines or solar panels into high-voltage transmission lines, these transformers ensure that the power from renewable sources can be efficiently transferred to the grid.
5. Better Voltage Regulation
In three-phase systems, voltage regulation is more efficient compared to single-phase systems. The use of a delta configuration in three-phase transformers helps reduce the amount of voltage drop, making it ideal for applications where consistent voltage is required.
Configuration Types of Three-Phase Transformers
This table provides a detailed description of three-phase transformers, covering key factors such as configuration type, voltage level, and power rating, while also listing the actual usage scenarios of these transformers in different power applications.
|
Factor |
Description |
Application |
|
Transformer Configuration |
The arrangement of the windings, either a Wye (Star) or a Delta configuration. |
Wye (Star): Common for low voltage applications. Delta: Used for high power transfer and balanced loads. |
|
Voltage Rating |
The maximum voltage the transformer can handle. |
High-voltage applications require transformers with ratings up to 110 kV or more. |
|
Cooling System |
Method used to dissipate heat generated during operation. |
Oil-immersed or air-cooled systems for cooling, depending on transformer size and environment. |
|
Power Rating |
The amount of electrical power the transformer can handle. |
Large-scale industrial power systems often require transformers capable of handling several MVA. |
|
Phase Power |
The power is supplied by each of the three phases of the transformer. |
Optimizes electrical flow in systems requiring three-phase power for high efficiency and reduced power losses. |
|
Insulation Type |
Material used to insulate the windings, commonly XLPE or oil-paper. |
XLPE for modern systems, offering high thermal resistance and electrical strength. |
|
Applications |
Specific use cases where three-phase transformers are essential. |
Power generation, renewable energy, power distribution, and high-voltage transmission systems. |
Choosing the Right Three-Phase Transformer
When selecting a three-phase transformer, there are several factors to consider:
-
Voltage Requirements: Ensure the transformer meets the voltage ratings for your application. Different configurations (wye or delta) may be required based on the load type and voltage levels.
-
Power Requirements: Understand the total power needs of your system. For high-power applications, selecting a three-phase transformer that can handle large currents is critical.
-
Cooling Needs: Transformers can generate a lot of heat. Choose a transformer with a suitable cooling system for the expected operational conditions.
-
Installation Environment: Consider whether the transformer will be used in a harsh environment, such as outdoor installations, or require additional protection against moisture and physical damage.
Three-phase transformers are integral to the efficient and reliable operation of modern electrical systems. From power generation transmission to industrial power systems, they ensure high power transfer and smooth electrical flow. Their versatility in applications like power distribution, renewable energy integration, and industrial machinery makes them an essential part of the electrical grid.
Whether you need to transform DC to AC or step down high voltage for local use, a three-phase transformer provides the best solution for power distribution and phase power needs. By understanding how these transformers work and selecting the right configuration, you can optimize your electrical systems for efficiency and reliability.













2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)