How Much Do You Know About Power Pole Transformers?
Power pole transformers are important critical components in the electrical distribution system, enabling the safe and efficient delivery of electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. Therefore, it is important for professional technicians and engineers to understand the intricacies of power pole transformers, their functionality, and their role in the power grid is essential. This article dives deep into the technical aspects of pole mounted transformers, their types, applications, and significance in modern electrical infrastructure.
What Is a Power Pole Transformer?
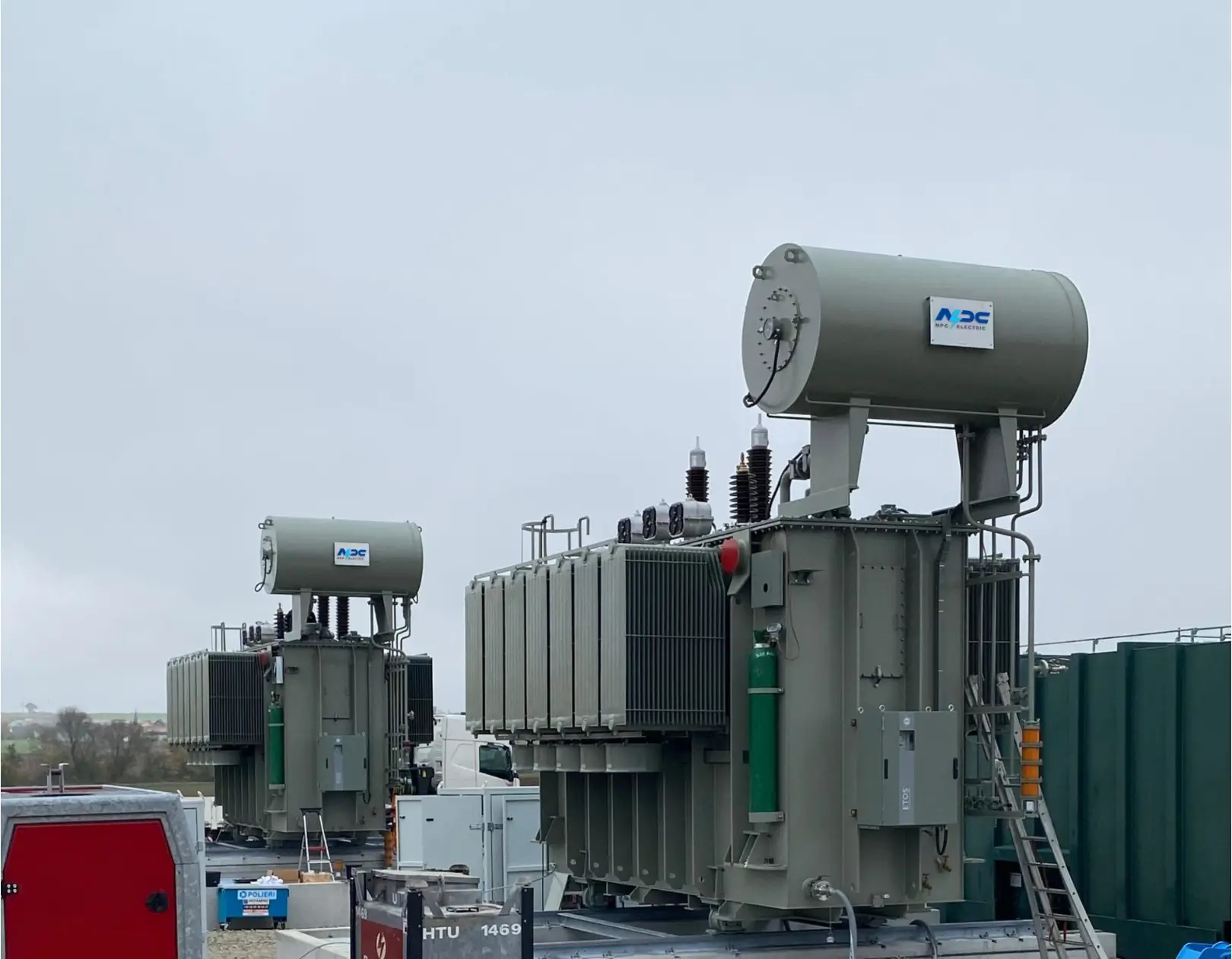
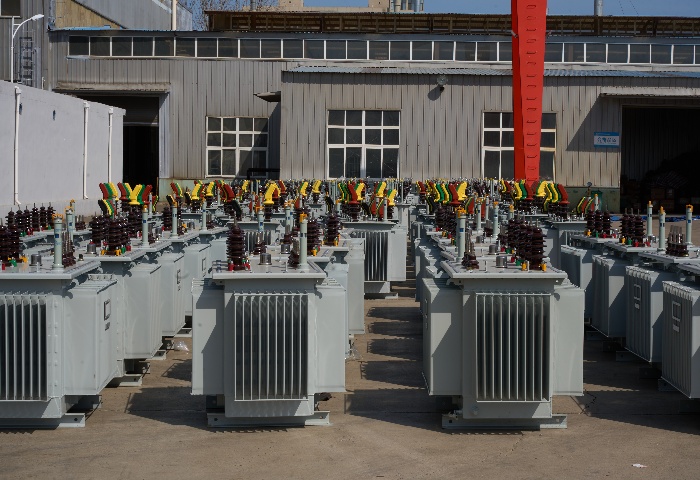
A power pole transformer, also known as a pole transformer, pole mount transformer, or distribution transformer, is a device mounted on a utility pole to step down high voltage electricity from the power grid to a lower voltage suitable for end users. These transformers are typically found in urban and rural areas, perched on power poles to facilitate electricity distribution from power stations to consumers.
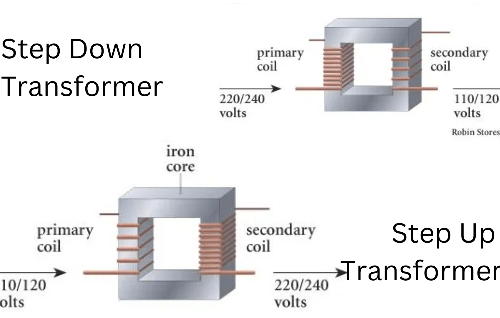
The primary function of a pole mounted transformer is to reduce voltage levels, often from 7,200–34,500 volts (medium voltage) to 120–240 volts (low voltage) for residential or commercial use. This voltage reduction ensures that electricity is safe for household appliances and industrial equipment. Transformers play a critical role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of the electrical grid.
The Role of Pole Transformers in the Power Grid
The power grid is a complex network that generates, transmits, and distributes electricity across vast distances. Power transformers at power stations step up voltage for long-distance transmission, minimizing energy losses. At the distribution level, pole transformers step down this high voltage for local consumption.
Pole mounted transformers are strategically placed on utility poles to serve specific neighborhoods or facilities. They ensure that electricity is delivered at the correct voltage, protecting equipment and preventing electrical hazards. Without these transformers, the high voltage electricity transmitted over long distances would be unusable for most applications.
Key Components of a Pole Mount Transformer
A pole mount transformer consists of several critical components:
- Core: Typically made of laminated silicon steel, the core minimizes energy losses during magnetic flux transfer.
- Windings: Copper or aluminum coils that carry electrical current, with primary windings handling high voltage and secondary windings delivering low voltage.
- Insulating Oil: Used in oil-filled transformers to cool and insulate internal components, preventing overheating and electrical faults.
- Bushings: Insulated connectors that link the transformer to external high- and low-voltage lines.
- Tank: A sealed enclosure that houses the core, windings, and insulating oil, protecting them from environmental factors.
These components work together to ensure efficient voltage transformation and reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Types of Pole Transformers
There are several types of transformers used as pole mounted transformers, each designed for specific applications. Understanding these variations is crucial for technicians selecting the right equipment for a given distribution network.
1. Single-Phase Pole Transformers
Single-phase pole transformers are commonly used in residential areas to supply power to individual homes or small businesses. They typically have a capacity of 5–100 kVA and are ideal for low-density load areas. These transformers are compact, cost-effective, and easy to install on utility poles.
2. Three-Phase Pole Transformers
Three-phase pole mount transformers are used in commercial and industrial settings where higher power demands exist. They can handle larger loads, typically ranging from 50–500 kVA, and are essential for powering heavy machinery and large facilities. These transformers are more complex and require careful installation to balance the three-phase load.
3. Dry-Type vs. Oil-Filled Transformers
- Oil-Filled Transformers: Most pole mounted transformers are oil-filled, using mineral oil for cooling and insulation. They are highly efficient but require regular maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure oil quality.
- Dry-Type Transformers: These use air or solid insulation and are less common in pole-mounted applications. They are preferred in environmentally sensitive areas due to the absence of oil but are generally more expensive.
4. Specialty Transformers
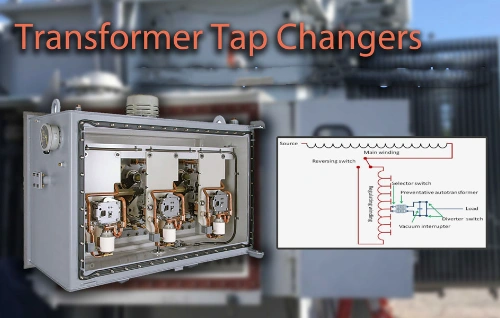
Some pole transformers are designed for specific purposes, such as voltage regulation or harmonic mitigation. These specialty units are tailored to unique grid requirements, ensuring optimal performance in challenging conditions.
Installation and Maintenance of Pole Mounted Transformers
Proper installation and maintenance of power pole transformers are critical to their longevity and performance. Technicians must adhere to strict safety protocols when working with high voltage electricity and follow industry standards for installation.
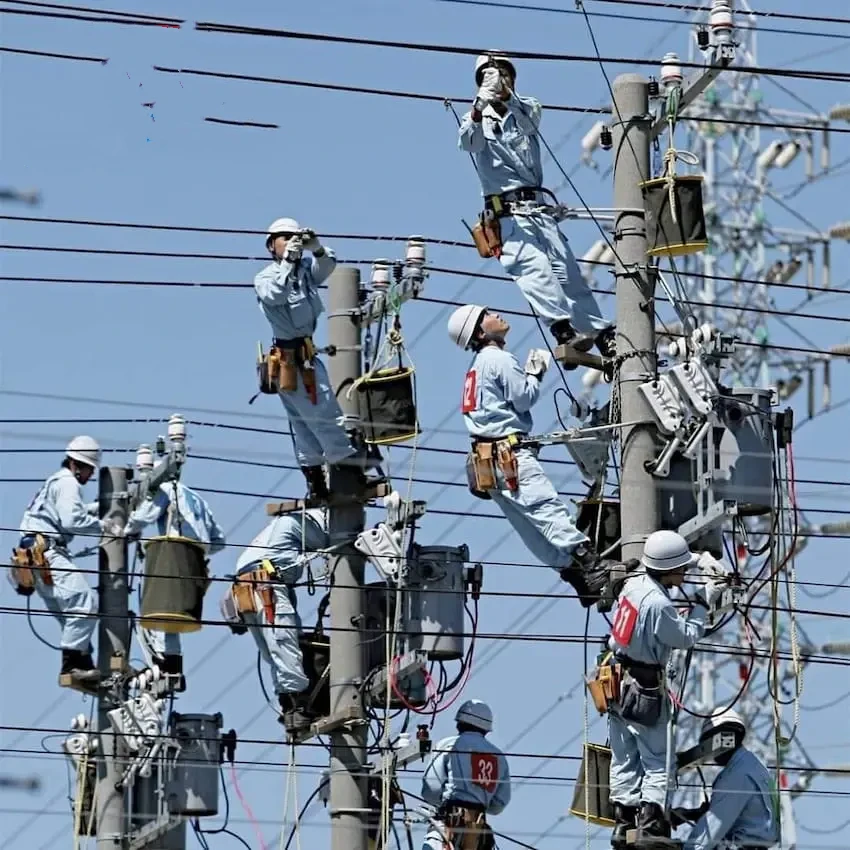

Installation Considerations
- Site Selection: The utility pole must be structurally sound and capable of supporting the transformer’s weight, which can range from 200 to 2,000 pounds.
- Electrical Connections: Proper grounding and secure connections to high- and low-voltage lines are essential to prevent faults.
- Environmental Factors: Transformers must be positioned to withstand weather conditions, such as wind, rain, and extreme temperatures.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance ensures that pole transformers operate efficiently and safely. Key tasks include:
- Inspecting for oil leaks and checking oil levels in oil-filled units.
- Testing insulation resistance to detect potential faults.
- Cleaning bushings and connections to prevent corrosion.
- Monitoring load conditions to avoid overheating or overloading.
Proactive maintenance reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of distribution transformers, which typically ranges from 20 to 30 years.
Challenges and Innovations in Pole Transformer Technology
As the demand for electricity grows and the power grid evolves, pole mounted transformers face new challenges. Aging infrastructure, increasing load demands, and the integration of renewable energy sources require innovative solutions.
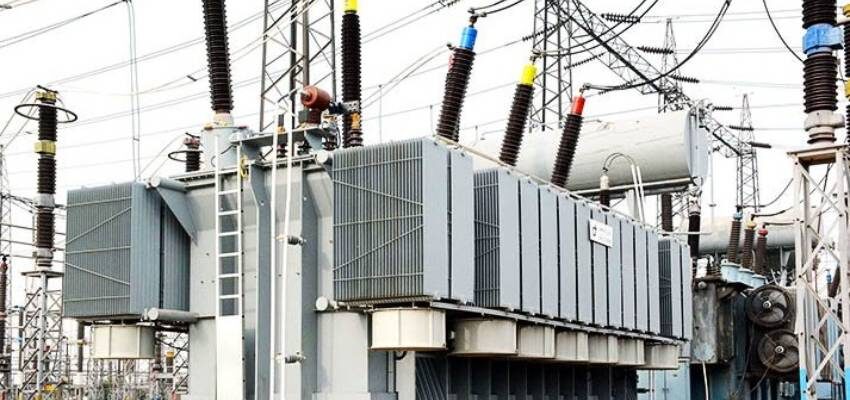

Challenges
- Overloading: Urbanization and the rise of electric vehicles can overload existing pole transformers, leading to failures.
- Environmental Impact: Oil-filled transformers pose a risk of spills, prompting stricter environmental regulations.
- Grid Modernization: The shift to smart grids requires transformers to handle bidirectional power flow from distributed energy resources like solar panels.
Innovations
- Smart Transformers: Equipped with sensors and communication modules, smart pole mount transformers monitor performance in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and load balancing.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Manufacturers are developing biodegradable insulating fluids and dry-type transformers to reduce environmental impact.
- Compact Designs: Newer distribution transformers are smaller and lighter, making them easier to install on utility poles without compromising performance.
The Importance of Transformers in Power Distribution
Transformers play an indispensable role in the electrical distribution system. Power pole transformers ensure that high voltage electricity from power stations is safely stepped down for end users, maintaining the reliability and efficiency of the power grid. For professional technicians, a deep understanding of pole mounted transformers—from their design and installation to maintenance and emerging technologies—is essential for supporting modern energy needs.
By staying informed about advancements in pole transformer technology and adhering to best practices, technicians can contribute to a more resilient and sustainable electrical infrastructure. Whether you’re working on a single-phase unit in a rural area or a three-phase system in an industrial zone, the knowledge of power pole transformers is a cornerstone of electrical engineering expertise.









3GHSSYCY-mining-cable-2.webp)




2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)

