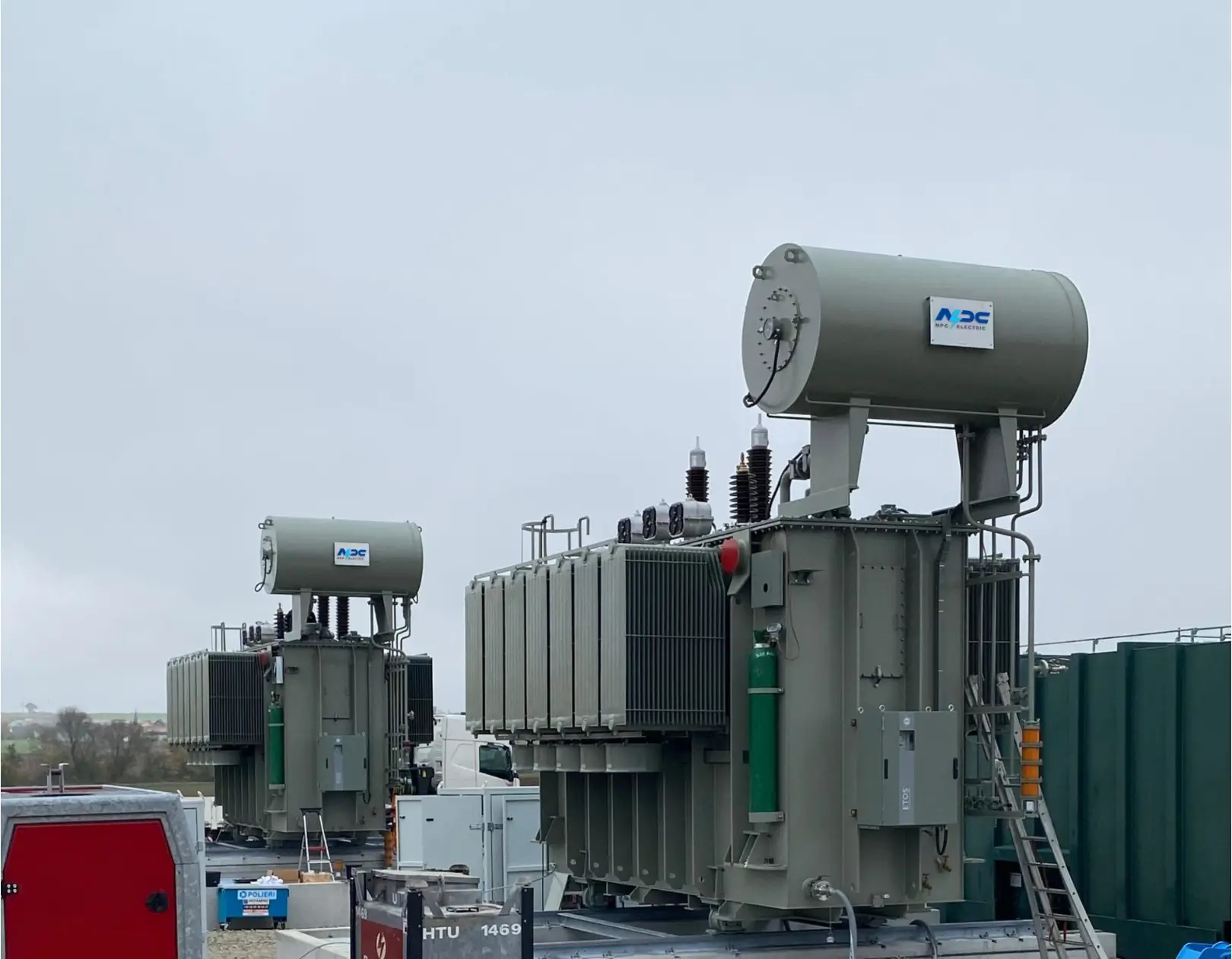
What Are the Applications of Electrical Transformers?
Electrical transformers are indispensable components in modern electrical systems, enabling the efficient transfer of electric power across various applications. From powering homes to supporting industrial operations, devices like the electric transformer, power pole transformer, and electric pole transformer play a critical role in ensuring electricity is delivered safely and reliably.

Understanding How Electrical Transformers Work
At the core of every electrical transformer is the principle of electromagnetic induction. This process allows the device to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits without direct electrical contact. An electric transformer consists of primary and secondary windings—coils of wire wrapped around a magnetic core. When alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces voltage in the secondary winding, enabling energy transfer.
This mechanism makes transformers highly efficient for stepping up or stepping down high voltage levels, ensuring electricity is transmitted over long distances with minimal loss or delivered at safe voltages for end users. Whether it’s a power pole transformer mounted on utility poles or a power transformer in a substation, the basic operation remains the same.
Key Applications of Electrical Transformers
The versatility of electrical transformers makes them essential across residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Below, we explore their primary applications, focusing on the roles of electric transformers, power pole transformers, and electric pole transformers.
1. Power Distribution in Residential Areas
One of the most visible applications of electrical transformers is in residential power distribution, where power pole transformers and electric pole transformers are commonly used. These transformers are mounted on utility poles to step down high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to lower, safer voltages (typically 120/240V in the U.S.) for household use.
Power pole transformers ensure that homes receive consistent and safe electric power for lighting, appliances, and electronics. Without these electric pole transformers, the high voltage used in long-distance transmission would be hazardous for residential consumption. Their compact design and reliability make them a staple in urban and rural electrical systems.
2. Industrial Power Supply
In industrial settings, power transformers and other types of transformers are critical for managing electric power demands. Factories and manufacturing plants often require specific voltage levels to operate heavy machinery, and electrical transformers step up or step down voltages to meet these needs. For instance, a power transformer in an industrial facility might step down incoming high voltage to power equipment like motors, conveyor systems, or welding machines.
Additionally, instrument transformers are used in industrial applications to measure high voltage or current levels safely. These transformers provide accurate readings for monitoring and controlling power systems, ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
3. Long-Distance Power Transmission
Efficient long-distance power transmission relies heavily on electrical transformers. Electricity generated at power plants is typically at a relatively low voltage, but transmitting it over long distances at low voltage results in significant energy losses. Power transformers step up the voltage to high voltage levels (often 110 kV or higher) for transmission, reducing losses during transit.
Once the electricity reaches its destination, electric transformers or power pole transformers step the voltage back down for distribution. This ability to manage voltage levels makes electrical transformers a cornerstone of modern power systems, enabling electricity to travel hundreds of miles with minimal waste.
4. Renewable Energy Integration
As the world shifts toward renewable energy, electrical transformers are playing a pivotal role in integrating sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power into the grid. Renewable energy systems often generate electricity at varying voltages, and electric transformers ensure compatibility with existing power systems.
For example, a wind turbine might use a power transformer to step up its output voltage for grid connection. Similarly, solar farms rely on electrical transformers to convert and distribute power efficiently. These applications highlight the adaptability of electric transformers in supporting sustainable energy solutions.
5. Commercial and Urban Infrastructure
In commercial buildings, shopping malls, and urban infrastructure, electrical transformers ensure a stable supply of electric power. Large facilities often require custom voltage levels, and power transformers or distribution transformers are used to meet these demands. For instance, an electric transformer in a high-rise building might step down voltage for lighting, HVAC systems, and elevators.
In densely populated areas, electric pole transformers are commonly seen along streets, delivering power to businesses and public services. These transformers are designed for durability and efficiency, ensuring uninterrupted service in high-demand environments.
6. Specialized Applications: Instrument Transformers
Instrument transformers are a unique type of transformer used in power systems for measurement and protection. They include current transformers (CTs) and voltage transformers (PTs), which reduce high voltage or current to standardized levels for metering and relaying. Utilities and industries rely on these transformers to monitor electrical systems, detect faults, and ensure safety.
For example, an instrument transformer might be used in a substation to provide data for billing or to protect equipment from overloads. Their precision makes them essential for maintaining the reliability of electric power delivery.
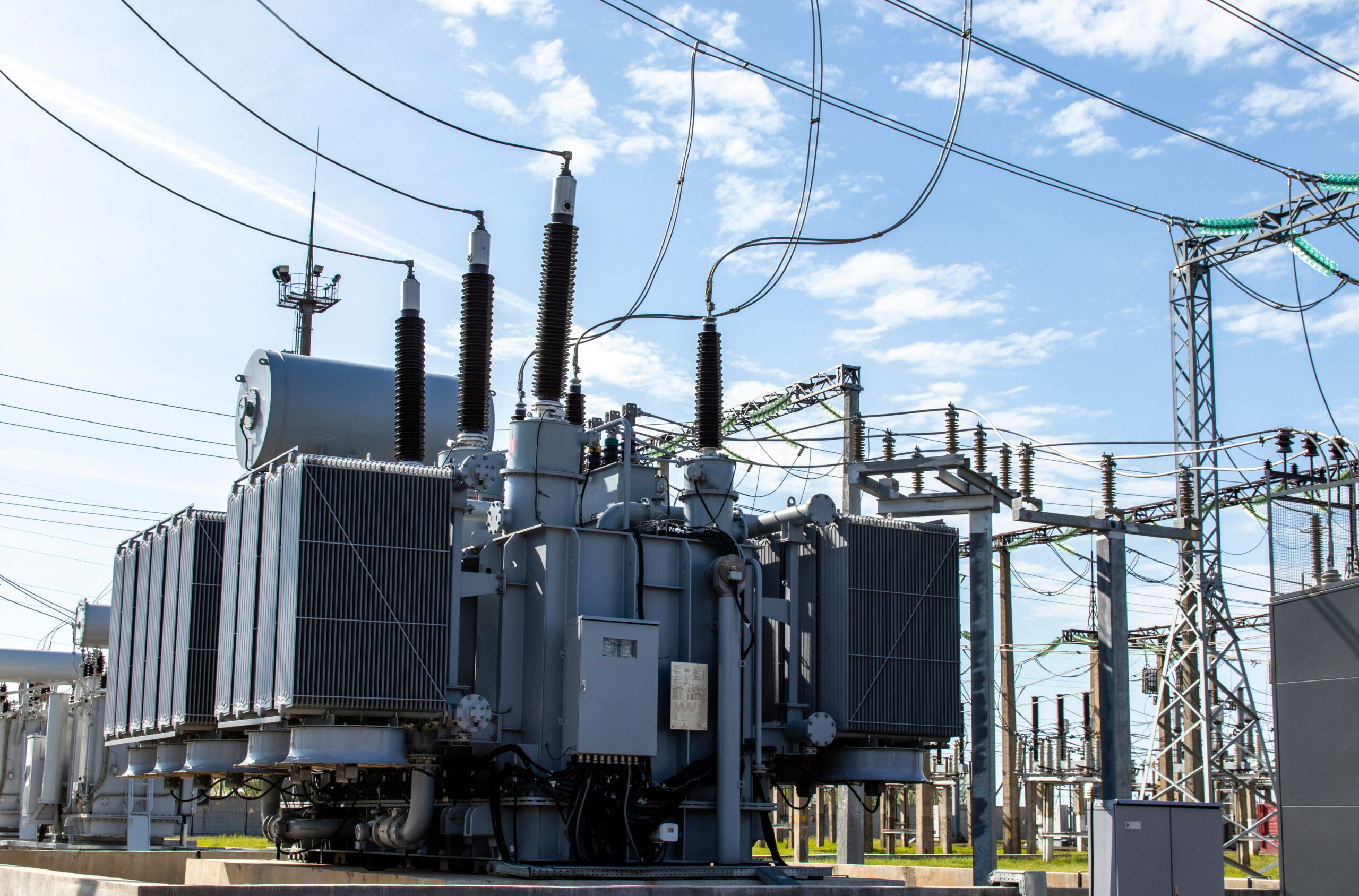

Types of Electrical Transformers and Their Roles
Different types of transformers are designed for specific applications. While power pole transformers and electric pole transformers are common in distribution, other types include:
- Power Transformers: Used in substations for high-voltage applications.
- Distribution Transformers: Step down voltage for local distribution, including power pole transformers, electric pole transformers.
- Instrument Transformers: Measure voltage or current in power systems.
- Isolation Transformers: Provide electrical isolation for safety in sensitive equipment.
- Autotransformers: Used for small voltage adjustments in specific applications.
Each type of transformer contributes uniquely to the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
The Importance of Electrical Transformers in Power Systems
The ability of electrical transformers to transfer electrical energy efficiently is what keeps modern society powered. From enabling long-distance transmission to protecting equipment and ensuring and delivering safe voltages, electric power transformers, power pole transformers, and electric pole transformers are vital to power systems. Their applications span residential, industrial, commercial, and renewable energy sectors, showcasing their versatility.
As technology evolves, electrical transformers continue to adapt, supporting smart grids, renewable energy integration, and energy-efficient solutions. By harnessing electromagnetic induction and precise engineering, these devices ensure that electric power flows reliably to every corner of our world.
In conclusion, electrical transformers are the unsung heroes of electrical systems, enabling the safe and efficient distribution of electric power across diverse applications. Whether it’s a power pole transformer lighting up a neighborhood, an electric transformer powering a factory, or an electric pole transformer supporting urban infrastructure, these devices are essential to modern life. Understanding their applications highlights their critical role in power systems and their contribution to a sustainable energy landscape.
By leveraging electromagnetic induction and advanced designs, electrical transformers continue to power our homes, industries, and future innovations, making them a cornerstone of global power systems.
















2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)