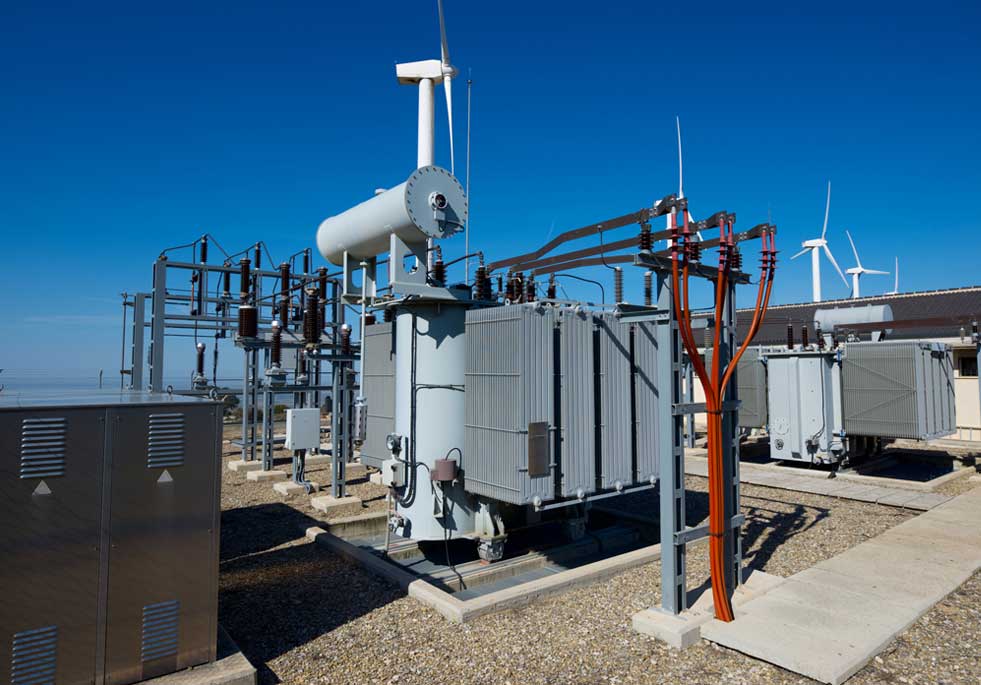
What Makes Substation Transformers So Important?
At the heart of this power journey are substation transformers, vital components that ensure electricity is safely and efficiently transmitted and distributed across vast distances. Modern life depends on the seamless flow of electrical power — from massive generation stations to the lights in your home or the machines in your workplace.
1. The Role of Transformers in the Electrical Power System
Transformers play a critical role in the electrical power infrastructure. Their primary function is to step up or step down voltage levels, enabling safe and efficient energy transfer.
- Step-up transformers increase voltage levels for long-distance power transmission.
- Step-down transformers, including distribution transformers, reduce voltage levels for safe delivery to end users.
Without transformers, the generation, transmission, and end-use of electricity would be inefficient, expensive, and potentially dangerous.

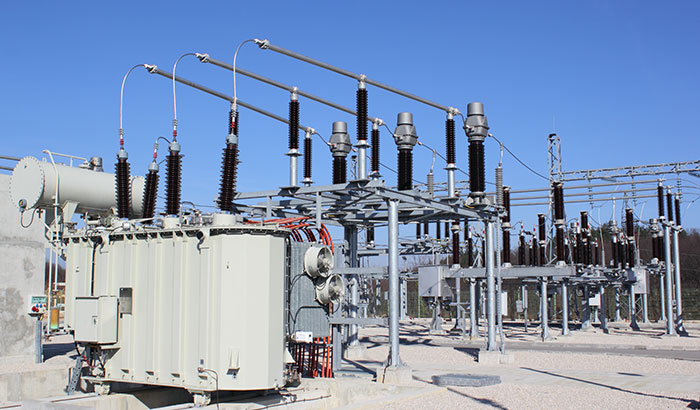
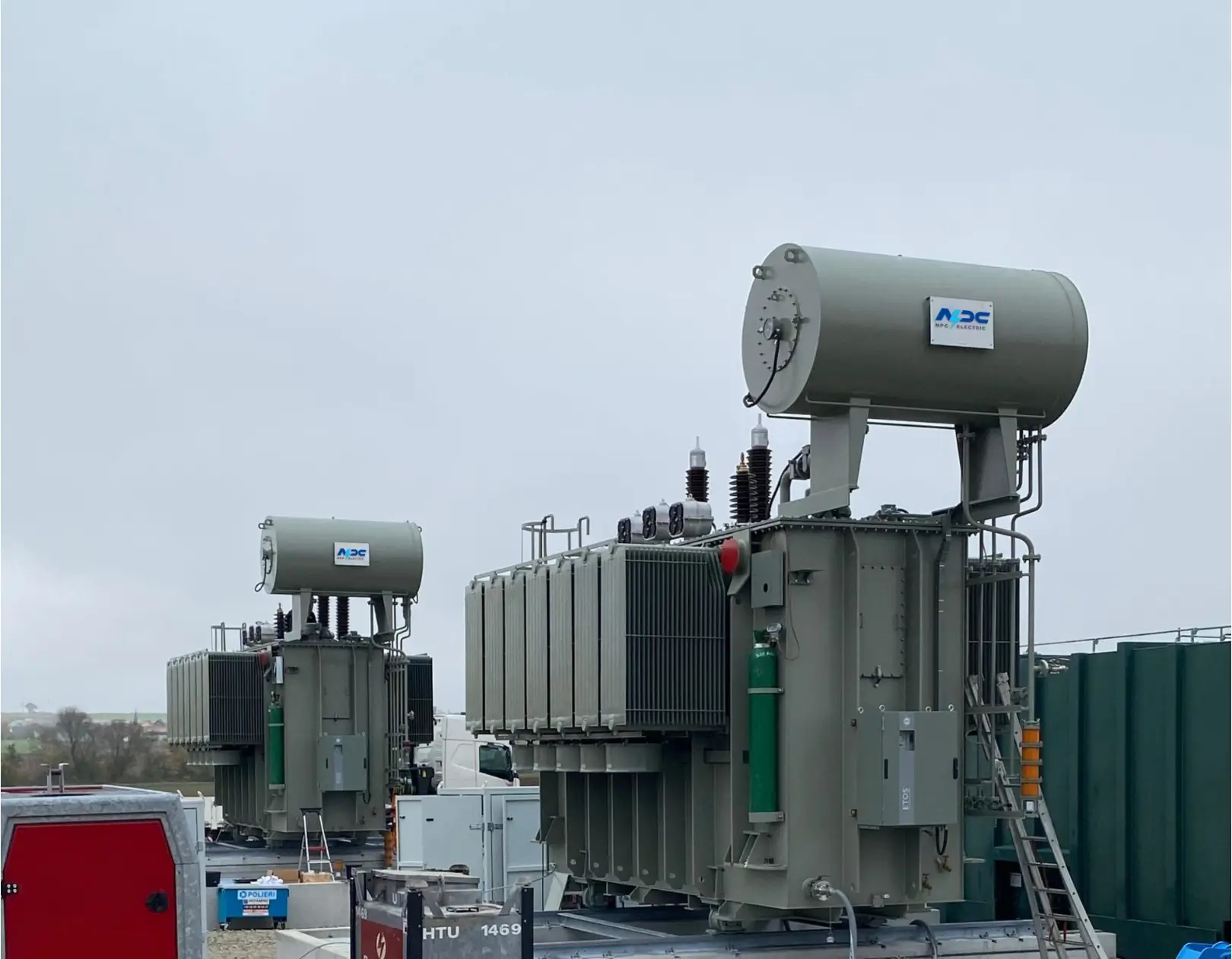
2. What Is a Substation Transformer?
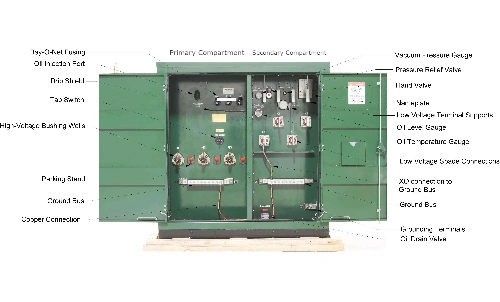
A substation transformer is a specialized type of power transformer found within electrical substations. These transformers act as the bridge between high-voltage transmission lines and the lower-voltage distribution systems that serve homes and businesses.
Depending on their position within the power system, substation transformers can function as either step-up or step-down units. In most distribution substations, they step down high transmission voltages (e.g., 110kV or higher) to levels suitable for local networks (e.g., 11kV or 33kV).
3. How Substation Transformers Work: The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
All transformers, including substation transformers, operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This principle states that a changing magnetic field within a coil of wire induces a voltage in a nearby coil.
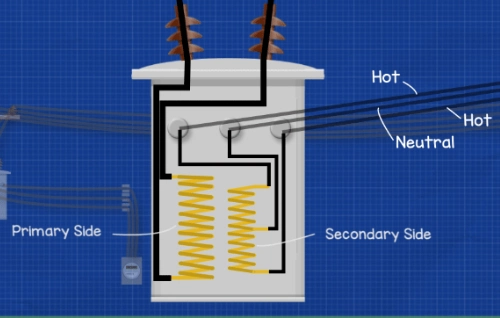
- The transformer consists of two windings: a primary winding and a secondary winding.
- As alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field.
- This changing field induces a voltage in the secondary coil, adjusting the voltage according to the winding ratio.
This core electromagnetic process allows transformers to adjust voltage levels without any moving parts, making them highly efficient and reliable over decades of service.
4. Integration with Transmission and Distribution Networks
Substation transformers are the linchpin connecting long-distance power transmission with local power distribution networks.
➤ Transmission Phase:
After power is generated, step-up transformers raise the voltage to hundreds of kilovolts for efficient transmission. This minimizes losses due to resistance in wires, which is critical when power must travel hundreds of kilometers.
➤ Substation Phase:
When power reaches a substation near the end user, a substation transformer lowers the voltage to medium levels. This makes it suitable for delivery via underground cables or overhead lines to neighborhoods and industrial facilities.
➤ Distribution Phase:
Distribution transformers then reduce the voltage further (e.g., down to 120V or 240V), making it safe for electricity to be distributed to homes and businesses.
5. Types of Substation Transformers
Depending on their application and environment, substation transformers can vary in design:
- Oil-immersed transformers: Common in outdoor applications; they use oil for insulation and cooling.
- Dry-type transformers: Used indoors or where fire safety is critical.
- Auto-transformers: Efficient for small voltage changes but not typically used where electrical isolation is needed.
Each type is selected based on safety, capacity, environmental conditions, and space requirements.
6. Why Substation Transformers Are Indispensable
Here are key reasons why substation transformers are essential in any modern electrical system:
✅ Voltage Regulation
They ensure that voltage levels remain within safe, usable ranges across the entire grid.
✅ Grid Stability
Transformers play a crucial role in balancing supply and demand, preventing overloads and blackouts.
✅ Efficiency
By enabling high-voltage transmission, they significantly reduce energy loss across distances.
✅ Scalability
Substations can be upgraded with higher-capacity transformers as demand grows in cities and industries.
✅ Safety
By stepping down voltage before electricity enters neighborhoods, substation transformers protect people and property from high-voltage hazards.
7. Future Trends and Innovations
As renewable energy sources like solar and wind are integrated into the grid, the role of substation transformers is evolving:
- Smart transformers are being developed with monitoring and self-regulation capabilities.
- Improved materials and insulation are increasing transformer lifespan and efficiency.
- Compact, modular substation transformers are becoming essential for urban applications and renewable power plants.

In conclusion, Substation transformers are much more than passive electrical devices — they are essential for the safe, stable, and efficient operation of the entire power system. From enabling long-distance power transmission to supporting the final distribution to homes and businesses, their role is foundational to modern life.
Understanding their function — grounded in the principle of electromagnetic induction — reveals just how critical they are in turning generated electricity into usable power across the globe. Whether you’re a utility provider, engineer, or simply a curious homeowner, recognizing the value of substation transformers helps deepen appreciation for the technology powering our world.



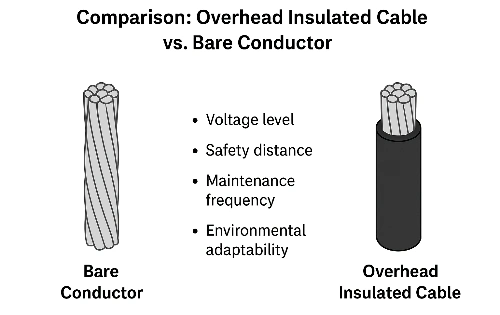


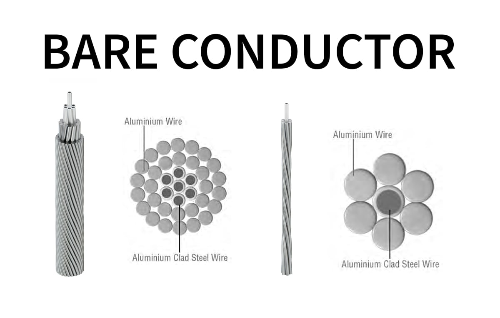

2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)





SHOUOJ-mining-cable-2.webp)