Choosing the Right Power Transformer: A Complete Guide to Types and Applications
Power transformers are one of the core pieces of equipment in modern power systems, playing a crucial role in power transmission and distribution. By stepping up or down voltage from high voltage to a suitable level, power transformers ensure minimal energy loss during long-distance power transmission while guaranteeing voltage stability at the user end. Especially in high-voltage transmission and low-voltage distribution systems, the performance of power transformers directly impacts the operational efficiency and safety of the power system. Different types of transformers are suitable for different application environments; for example, single-phase transformers are suitable for residential and small commercial facilities, while three-phase transformers are suitable for large industrial facilities and high-load power systems. Choosing the right power transformer not only improves system efficiency but also extends equipment lifespan and reduces the risk of failure. Furthermore, with increasing demands for energy efficiency and environmental protection, modern transformers must also meet environmental standards, such as low noise, low loss, and high efficiency design requirements. Therefore, whether for new projects or equipment replacement, selecting the right power transformer is a key factor in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the power system.
1. What are Power Transformers?
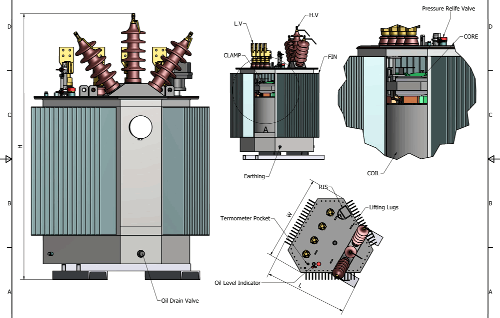
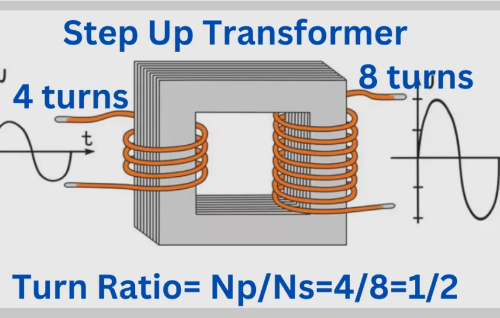
Power transformers are electrical devices used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits, modifying the voltage level as required for different parts of the electrical system. They are designed to operate at high voltages and are commonly used in power distribution networks to ensure that electricity is transmitted efficiently over long distances.
Power transformers are typically categorized based on their voltage ratings and the type of current they handle. Most commonly, they are used in high-voltage transmission lines, substations, and distribution systems to step up or step down the voltage according to the needs of the electrical grid.
2. Types of Power Transformers
a. Single-Phase Power Transformer
A single-phase power transformer is a type of transformer that uses a single-phase electrical system to distribute power. These transformers are primarily used in residential areas or small businesses where the power demand is relatively low and only a single phase of power is needed.
Key Features of Single-Phase Power Transformers:
- Voltage Conversion: Converts high voltage into usable lower voltage for household or small business use.
- Cost-Effective: Ideal for low-power applications due to their lower cost and simplicity.
- Common Use: Typically used in residential buildings, small commercial establishments, and street lighting.
These transformers are compact and easy to install, making them a common choice for small-scale applications, though they are less suitable for industrial environments with higher power demands.
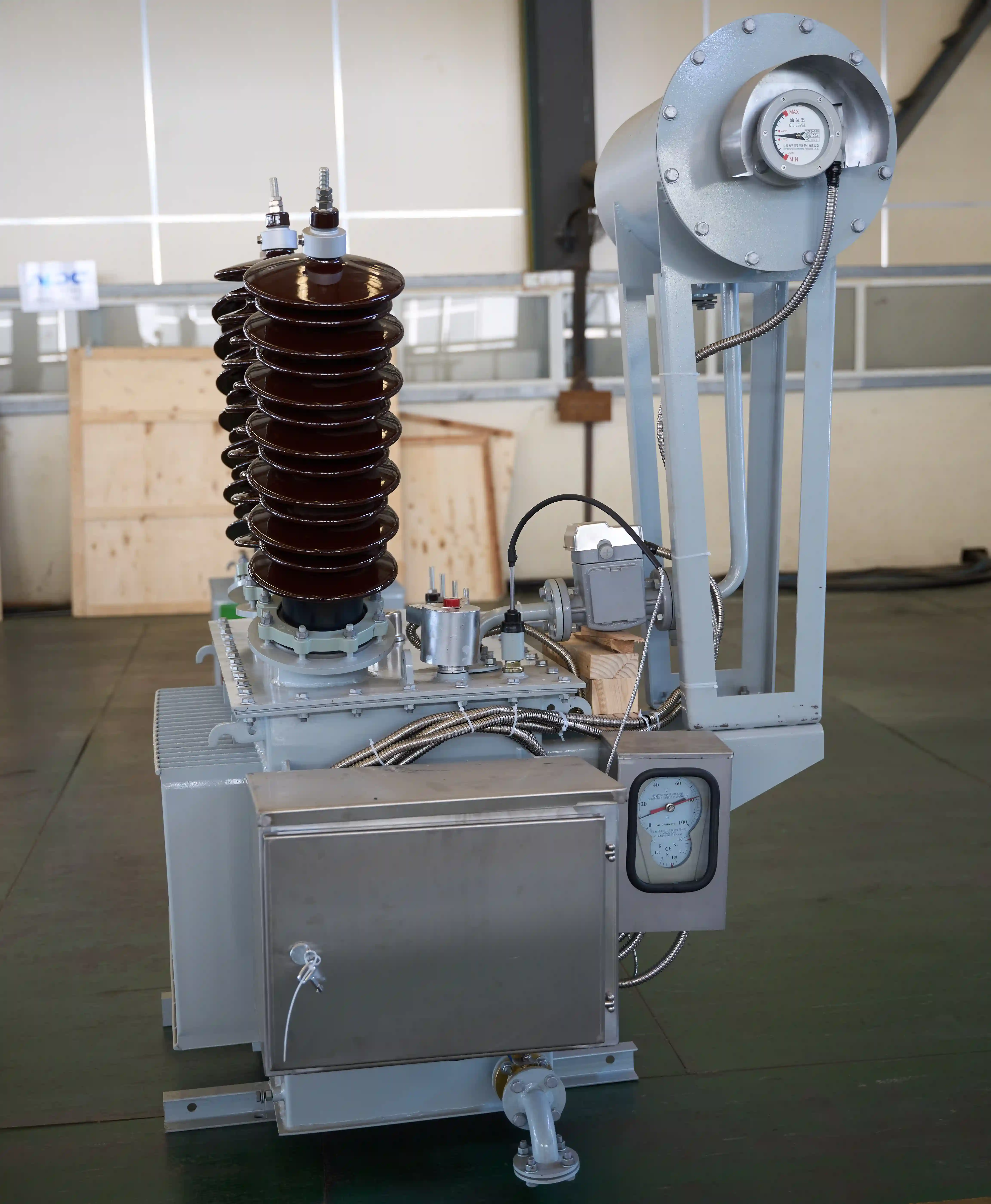

b. Step-Down Power Transformer
A step-down power transformer is used to decrease the voltage level of the electricity transmitted through the power lines to a usable level for homes, businesses, or machinery. These transformers are crucial in reducing the high voltage from transmission lines to a lower, safer voltage suitable for local distribution.
Key Features of Step-Down Power Transformers:
- Voltage Reduction: Reduces the voltage from high voltage transmission levels to the lower voltages used by appliances and industrial machines.
- Common Use: These are essential in residential and commercial power systems, often seen in substations.
- Safety: Step-down transformers ensure that electricity is at safe voltage levels when reaching homes and businesses.
For example, in a typical residential setting, a step-down transformer reduces the voltage from 11 kV to 220 V or 440 V, depending on the grid requirements.
c. Power Line Transformer
A power line transformer is a type of transformer specifically designed for use on overhead power lines. These transformers are typically installed on utility poles and are used to step-down the high voltage of the transmission lines to a level suitable for homes and businesses.
Key Features of Power Line Transformers:
- Overhead Installation: These transformers are mounted on power poles in the electrical grid, making them easy to access for maintenance.
- Voltage Conversion: Like step-down transformers, they reduce high voltage for safe distribution.
- Common Use: They are primarily used in rural areas and residential neighborhoods where the power distribution is overhead.
These transformers must be robust to withstand the outdoor environment, including weather conditions such as rain, wind, and extreme temperatures.
d. Power Pole Transformer
A power pole transformer is essentially another term for power line transformers mounted on utility poles. They serve the same purpose of stepping down high-voltage electricity to lower voltages suitable for local use.
Key Features of Power Pole Transformers:
- Outdoor Use: Mounted on utility poles to serve communities and businesses.
- Capacity: Typically used for medium voltage power supply, providing electricity to homes, small businesses, and streetlights.
- Maintenance: Easier to maintain and repair due to their accessible pole-mounted position.
Power pole transformers are vital for remote areas and locations where underground wiring is not feasible.
3. Comparison Table: Types of Power Transformers
|
Feature |
Single-Phase Power Transformer |
Step-Down Power Transformer |
Power Line Transformer |
Power Pole Transformer |
|
Voltage Type |
Single-phase AC |
High to low voltage conversion |
High-voltage AC to low-voltage conversion |
High-voltage AC to low-voltage conversion |
|
Common Use |
Residential and small commercial applications |
Distribution networks, residential areas |
Overhead lines for local distribution |
Outdoor installations, typically on utility poles |
|
Voltage Rating |
Low to medium voltage |
Medium to high voltage |
High voltage |
Medium to high voltage |
|
Installation Location |
Indoor |
Indoor or outdoor (depending on capacity) |
Outdoor (mounted on poles) |
Mounted on utility poles, outdoor |
|
Cooling Medium |
Air (natural or forced) |
Oil or air (depending on transformer type) |
Oil or air (depending on design) |
Oil or air (depending on design) |
|
Applications |
Light-duty electrical systems |
Industrial power systems, commercial use |
Overhead power lines |
Overhead power distribution and residential power supply |
|
Efficiency |
Moderate efficiency |
High efficiency in voltage reduction |
High efficiency for large-scale distribution |
High efficiency for long-distance power transmission |
|
Maintenance |
Low maintenance |
Medium maintenance |
Regular maintenance due to environmental exposure |
Regular maintenance, especially for outdoor installations |
|
Capacity |
Low (typically up to 10 kVA) |
Medium to large capacity |
High capacity for large-scale transmission |
High capacity for outdoor areas |
|
Cost |
Low to moderate |
Moderate to high |
Moderate |
Moderate to high |
|
Fire Safety |
High (no oil involved) |
Moderate (oil-based, fire risk) |
Moderate (oil-based, fire risk) |
Moderate (oil-based, fire risk) |
Key Highlights:
- Single-Phase Power Transformer: Typically used in residential and small commercial applications. These transformers are cost-effective, have low capacity, and require minimal maintenance. They are ideal for low power needs and single-phase circuits.
- Step-Down Power Transformer: Step-down transformers are used to convert high voltage from transmission lines to low voltage for distribution. These transformers are often used in substations and distribution networks. They are highly efficient and commonly found in commercial and industrial settings.
- Power Line Transformer: These transformers are mounted on overhead power lines and are commonly found in rural or residential areas. They are used to reduce voltage from transmission lines to usable levels for homes and businesses. These transformers are robust and designed to withstand outdoor conditions.
- Power Pole Transformer: Similar to power line transformers, power pole transformers are specifically designed for installation on utility poles. These transformers are commonly used for long-distance power distribution and are often installed in outdoor locations to supply electricity to communities or businesses.
4. How to Choose the Right Transformer
Choosing the right power transformer depends on several factors, including the application, voltage requirements, installation space, and operational costs. Here are some key considerations:
a. Voltage Requirements
The primary consideration in choosing a transformer is the voltage requirements of your system. If you are stepping down high voltage from a transmission line to a usable level for local distribution, a step-down transformer is required. For small, residential applications, a single-phase transformer may be sufficient.
b. Power Capacity
Ensure that the transformer you select can handle the required load. For example, if you are installing a transformer for an industrial site with heavy machinery, a high-capacity step-down transformer or three-phase transformer may be necessary.
c. Environment and Installation
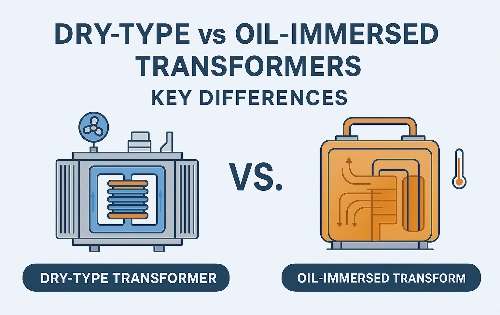
- Indoor vs Outdoor: Choose a power pole transformer for outdoor installations in areas with overhead lines, while indoor transformers, like dry-type transformers, are better for confined spaces.
- Space Considerations: Make sure you have enough space for the installation of the transformer, particularly for larger models.
d. Operational Costs and Maintenance
Consider the operational cost and maintenance requirements of the transformer. Step-down transformers typically require less maintenance, while power pole transformers may need more frequent inspections due to their exposure to environmental conditions.

5. Conclusion
When choosing the right power transformer, it is essential to consider your application’s specific voltage, capacity, and installation needs. Single-phase transformers are ideal for residential use, while step-down transformers are necessary for larger power systems. For overhead applications, power line transformers and power pole transformers provide the necessary voltage adjustments for safe, efficient power distribution.
Understanding these different types of transformers and their features will help you make an informed decision, ensuring that your power system runs efficiently and reliably.