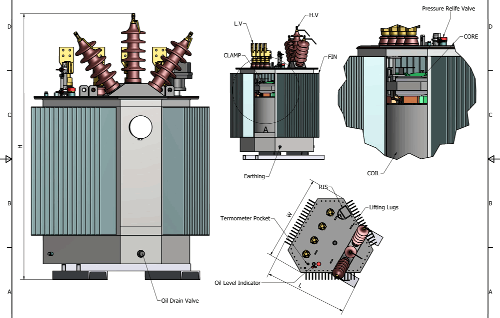
Power Transformers for Renewable Energy: Solar & Wind Integration Guide 2026
As the global energy system accelerates its low-carbon transition, renewable energy—represented by solar and wind power—has become the fastest-growing energy source in the global power generation sector. According to data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) in 2025, renewable energy will account for more than 70% of new power generation capacity, and is projected to surpass traditional fossil fuels by 2030. However, effectively integrating these variable and distributed energy sources into the existing power grid faces numerous technical challenges, requiring highly reliable electrical equipment as support. Among these, power transformers play a central role in voltage conversion, grid stability, and real-time power flow management, making them the backbone of renewable energy projects.
Modern renewable energy projects operate under unique conditions: output power fluctuates dramatically due to weather changes (e.g., solar power drops sharply at dusk, wind power varies with wind speed), voltage changes rapidly (PV inverters output 400-1500V, wind power needs to be stepped up to 33kV-220kV), power generation points are widely distributed (distributed PV, offshore wind farms), and power electronic interfaces (such as inverters and converters) are widely used. These factors place unprecedented demands on the technical performance of transformers, including higher insulation withstand voltage (such as BIL up to 550kV), efficient cooling systems (ONAN to OFAF), fault-tolerant design to cope with short-circuit impacts, and advanced online monitoring technology to detect oil-gas decomposition or partial discharge in real time. This article, based on practical engineering experience and the latest industry standards (such as IEC 60076-16 and IEEE C57.116) up to 2025, delves into the design principles, selection strategies, and specific application scenarios of power transformers in solar and wind power generation systems. It aims to provide developers, engineers, and EPC contractors with rigorous and scientific guidance to ensure that renewable energy projects achieve the optimal balance between stability, economics, and sustainability.
2. Why Transformers Are Essential for Renewable Energy Integration
Renewable energy systems generate electricity at voltages incompatible with transmission and distribution networks. Key functions of renewable-energy transformers include:
2.1 Voltage Step-Up for Grid Transmission
Solar farms typically generate electricity at 600–1500 V, while wind turbines generate 400–690 V.
Transformers step voltage up to 33 kV, 66 kV, 110 kV, or higher, enabling long-distance, low-loss transmission.
2.2 Grid Stability and Power Quality
Wind and solar outputs change rapidly due to environmental conditions. Transformers must handle:
-
Voltage fluctuations
-
Harmonics generated by inverters
-
Rapid switching and transient overvoltages
-
Real-time power flow reversals
Thus, electrical transformers for renewable systems require enhanced thermal endurance, low-loss cores, and optimized winding configurations.
2.3 Protection and Isolation
Transformers provide galvanic isolation between renewable sources and public grids, preventing grid disturbances and improving operational safety.
3. Types of Transformers for Renewable Energy Projects
Different renewable project configurations require specialized transformer designs—especially for solar farms, wind farms, and hybrid solar-wind systems.
3.1 Solar Transformers
Solar transformers are used between photovoltaic inverters and transmission grids. Their key features include:
-
Handling high harmonic distortion
-
Robust insulation against switching transients
-
Compatibility with central, string, or modular inverters
-
High-efficiency cores to reduce operational losses
Many solar farms employ dry-type or liquid-immersed designs depending on environmental requirements.
3.2 Wind Turbine Transformers
Wind turbines typically use a one or two-stage voltage transformation:
-
Turbine step-up transformers (inside nacelles)
-
Pad-mounted transformers (at tower bases)
-
Substation main transformers (grid connection)
Transformers inside nacelles must endure vibration, temperature variation, and limited space. Manufacturers, therefore, focus on high mechanical strength and compact geometry.
3.3 Substation Power Transformers
Utility-scale renewable parks require large grid step-up transformers, often rated between 30 MVA and 300 MVA, to integrate into regional transmission networks.
4. Technical Requirements of Transformers in Solar & Wind Applications
4.1 High Voltage Performance
Renewable projects frequently integrate with high-voltage networks, demanding:
-
Enhanced dielectric insulation
-
Higher Basic Insulation Level (BIL)
-
Capable bushings for switching and lightning impulses
4.2 Thermal Management
Solar and wind farms often operate in harsh outdoor conditions:
-
Desert solar farms: 40°C–55°C
-
Offshore wind farms: high humidity and salt fog
-
Mountain wind farms: freezing climates
Thus, transformers use:
-
Mineral oil, synthetic ester, or natural ester cooling
-
Advanced ONAN/ONAF cooling systems
-
Heat-resistant insulation grades
4.3 Mechanical Durability
Wind turbine transformers endure mechanical vibration, requiring:
-
Reinforced windings
-
High-strength clamping structures
-
Shock-resistant cores
4.4 Smart Monitoring and Digitalization
Future smart power networks rely heavily on real-time data. Renewable transformers increasingly include:
-
Thermal sensors
-
Dissolved gas analysis (DGA)
-
Online partial discharge monitoring
-
SCADA/IoT connectivity
This enables predictive maintenance and improves transformer lifespan.

5. Typical Transformer Configurations in Renewable Projects
Power transformers in renewable energy follow several wiring and configuration standards.
5.1 Solar Farm Transformer Connections
Common types:
| Configuration | Application | Advantages |
| Dyn11 | Solar inverter output | Reduces harmonics, provides neutral grounding |
| Yyn0 | Medium-voltage systems | Simple structure, easy protection coordination |
| Yd11 | Grid step-up stations | High efficiency, suitable for HV interconnection |
5.2 Wind Farm Transformer Connections
| Transformer Type | Use Case | Key Benefit |
| Pad-mounted transformer | Wind turbine base | Compact, safe, outdoor-ready |
| Nacelle transformer | Inside turbine | Vibration-resistant, space-efficient |
| Collector system transformer | Substation | High reliability, long-distance collection |
6. Key Considerations When Selecting Renewable Energy Transformers
Selecting the right electrical transformer requires an engineering-based evaluation of environmental, electrical, and operational conditions.
6.1 Renewable Energy Density and Output Variation
Solar panels and wind turbines have non-linear output profiles; transformers must support overload margins and dynamic loading.
6.2 Compatibility with Power Electronics
Solar inverters and wind converters produce harmonics. Transformers may require:
-
K-factor ratings
-
Harmonic-resistant cores
-
Amorphous steel sheets for reduced losses
6.3 Safety and Environmental Compliance
Renewable installations often specify:
-
ECO-friendly ester oil
-
Fire-safe dry-type transformers
-
Low noise levels for residential zones
6.4 Manufacturer Expertise
A reliable transformer manufacturer must demonstrate:
-
Proven renewable energy experience
-
Compliance with IEC/IEEE standards
-
Customizable designs for terrain, climate, and grid codes
7. Future Trends: Transformers for Smart Renewable Networks
The next decade will see rapid evolution in transformer technologies:
7.1 Integration With Smart Grids
Transformers will support:
-
Real-time energy flow adjustment
-
Automated voltage regulation
-
AI-driven predictive maintenance
7.2 Hybrid Solar-Wind Storage Transformers
Battery systems require bi-directional power flow and advanced protection schemes.
7.3 Ultra-High Voltage for Renewable Corridors
Countries are building UHV transmission channels for long-distance renewable power transport.
Power transformers remain the backbone of modern renewable power systems. Whether for solar farms, wind farms, or hybrid installations, transformer technology continues to evolve to meet challenges in power quality, grid compatibility, environmental safety, and smart control. As renewable energy capacity expands globally, advanced transformer solutions will be essential for ensuring stable, efficient, and future-ready power networks.