Power Transformer Installation: Common Cable Types and Selection Guide
Why Cable Selection Matters in Transformer Installation
Power transformer installation is a critical phase in any electrical infrastructure project, directly affecting system reliability, operational safety, and long-term lifecycle costs. For EPC contractors, utility companies, industrial facility owners, and renewable energy developers, transformer installation is not merely a technical operation—it is a strategic investment decision.
Cables form the physical and electrical link between the electrical transformer and the wider electrical system. Improper cable selection can result in overheating, insulation failure, electric shocks, unexpected downtime, and even regulatory non-compliance. From real-world engineering experience, many transformer failures are not caused by the transformer itself, but by incorrect cable types, undersized conductors, or unsuitable insulation materials.
Who This Guide Is For
This article is designed for professionals involved in transformer projects, including:
- EPC contractors and project engineers
- Power utility companies and grid operators
- Industrial facility managers and plant engineers
- Renewable energy developers (solar and wind projects)
- Electrical distributors and procurement teams
The focus is on real installation conditions, not theoretical assumptions.
Understanding Cable Requirements in Power Transformer Installation
In power transformer installation, cables must safely transmit electrical energy while withstanding mechanical, thermal, and environmental stresses. Key design considerations include:
- Voltage level (low, medium, or high voltage)
- Current-carrying capacity
- Insulation performance
- Installation method (underground, overhead, tray, conduit)
- Environmental exposure
- Compliance with electrical standards
Both copper and aluminum conductors are widely used in transformer installations. Copper offers superior conductivity and compact sizing, while aluminum provides cost efficiency and lighter weight—often preferred in large-scale electrical systems.
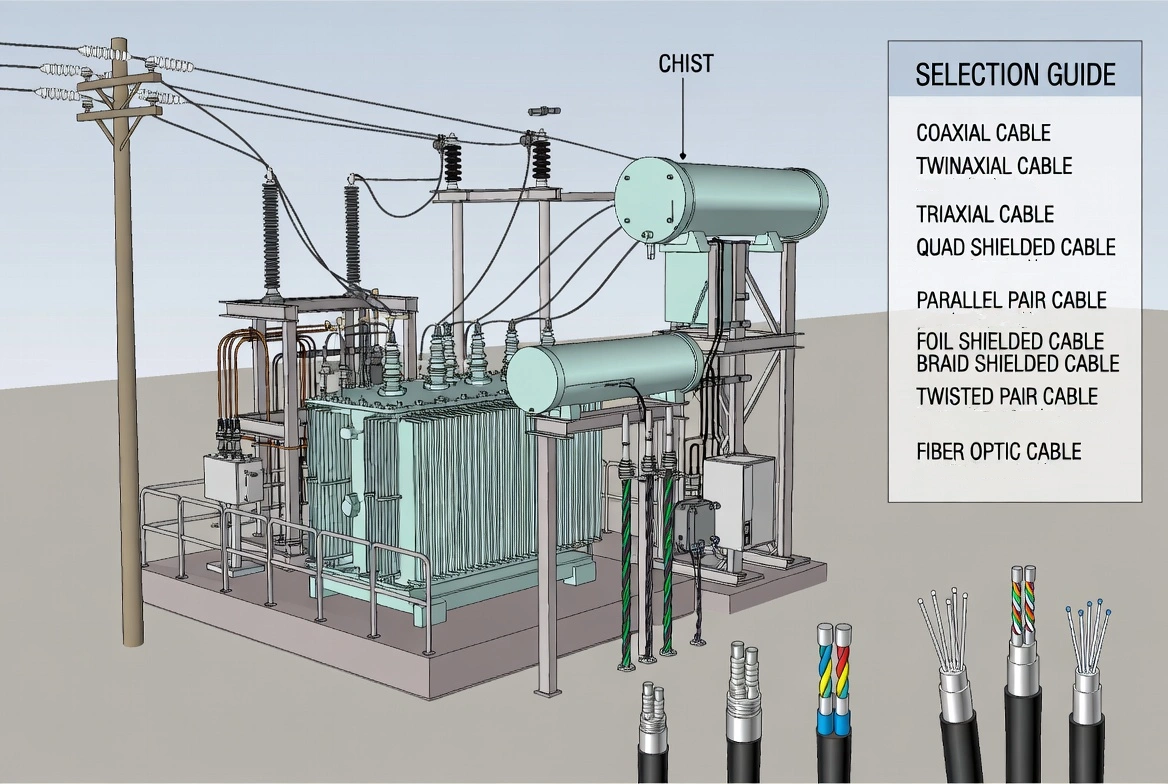
Common Cable Types Used in Transformer Installation
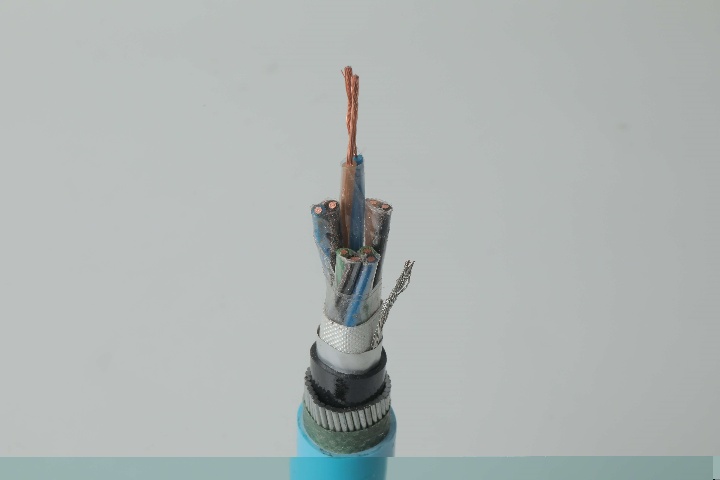
1. XLPE Cable (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
XLPE cable is the most widely used option in modern power transformer installation due to its excellent thermal and electrical properties.
Key advantages from field experience:
- Higher operating temperature rating compared to PVC cable
- Lower dielectric losses in medium- and high-voltage systems
- Strong resistance to moisture and chemical exposure
- Reduced long-term maintenance requirements
XLPE cables are commonly used on transformer primary and secondary sides, especially in medium-voltage and high-voltage applications.
2. PVC Cable
PVC cable remains common in low-voltage transformer connections and auxiliary circuits.
Practical considerations:
- Lower material cost
- Suitable for controlled indoor environments
- Limited thermal performance compared to XLPE cable
PVC cable is frequently used where operating temperatures and load fluctuations are predictable.
3. Flexible Cable
Flexible cable is typically applied in control circuits, temporary connections, and locations requiring vibration resistance.
Advantages:
- Excellent bending performance
- Reduced risk of conductor fatigue
- Improved job performance during installation
4. Armored Power Cables
Armored cables provide mechanical protection for transformer installations in underground or industrial environments.
Real-world benefits:
- Protection against physical damage
- Reduced the risk of cable failure during civil works
- Enhanced safety in harsh operating conditions
Cable Selection Table for Power Transformer Installation
|
Application Area |
Recommended Cable Type |
Insulation |
Business & Engineering Benefit |
|
Transformer Primary (MV) |
XLPE Cable |
XLPE |
Long service life, low electrical losses |
|
Transformer Secondary (LV) |
PVC or XLPE Cable |
PVC / XLPE |
Cost flexibility, stable performance |
|
Underground Installations |
XLPE Armored Cable |
XLPE |
Mechanical protection, reduced failures |
|
Industrial Electrical Systems |
XLPE Cable |
XLPE |
High thermal stability, low downtime |
|
Utility Distribution Networks |
Aluminum XLPE Cable |
XLPE |
Cost-effective for large-scale projects |
Key Cable Selection Criteria from Engineering Practice
Voltage Rating
Selecting a cable with an insufficient voltage rating increases electrical stress and insulation degradation, potentially leading to system failure and compliance violations.
Current-Carrying Capacity
Undersized cables result in excessive heating, energy losses, and reduced transformer lifespan—raising the total cost of ownership.
Insulation Type
- XLPE cable is preferred for high-load and outdoor environments.
- PVC cable is suitable for controlled, low-voltage installations.
Installation Environment
Environmental factors such as humidity, soil conditions, chemical exposure, and ambient temperature must be considered during cable selection.
Common Costly Mistakes in Transformer Cable Selection
Based on real installation projects, frequent mistakes include:
- Using PVC cable where XLPE cable is required for thermal performance
- Ignoring future load expansion when sizing cables
- Underestimating mechanical stress in underground installations
- Selecting non-certified wires and cables that fail electrical standards
These errors often lead to project delays, rework costs, and unexpected operational failures.
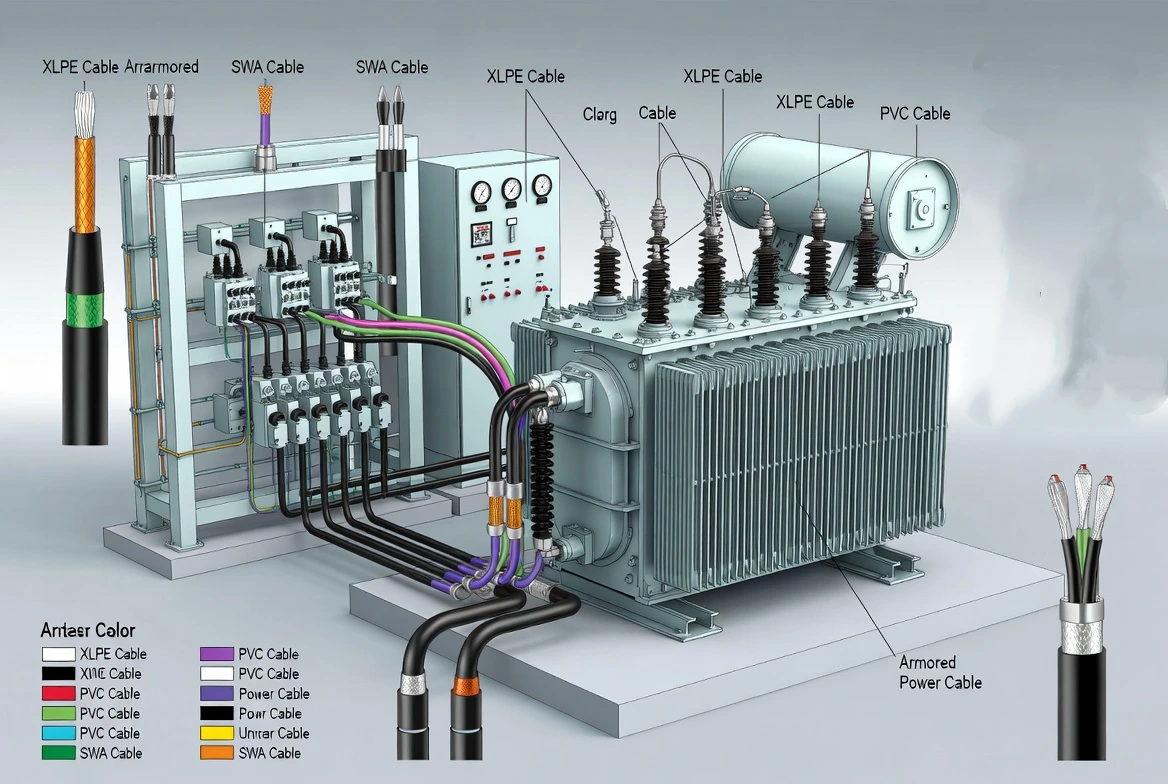
Safety Considerations and Electric Shock Prevention
Inadequate cable insulation and improper termination significantly increase the risk of electric shocks during operation and maintenance. Correct cable selection, grounding, and termination practices are essential to ensure personnel safety and regulatory compliance in electrical systems.
Compliance with Electrical Standards
Professional power transformer installation requires cables compliant with international and regional standards, such as:
- IEC 60502 (Power cables)
- IEC 60840 / IEC 62067 (High voltage cables)
- IEEE and utility-specific requirements
Working with an experienced supplier ensures proper documentation, testing records, and traceability.
Engineering Support and Cable Solutions for Transformer Projects
Selecting cables for power transformer installation requires more than catalog specifications—it demands real project experience. Whether for utility substations, industrial plants, or renewable energy installations, professional engineering support can significantly reduce technical and commercial risks.
Professional suppliers typically provide:
- Cable sizing and selection assistance
- XLPE cable and PVC cable customization
- Compliance with IEC and utility standards
- Logistics coordination for transformer projects
Contact an experienced engineering team to discuss cable solutions tailored to your transformer installation requirements.
Power transformer installation is only as reliable as the cables that connect it to the electrical system. Selecting the right cable types—whether XLPE cable, PVC cable, or armored solutions—ensures safety, efficiency, and long-term system performance. By aligning engineering principles with real installation conditions, project teams can optimize both technical reliability and lifecycle costs.