Underground Power Cables: Enhancing Safety and Reliability in Urban Areas
1. The Role of Underground Power Cables in Modern Cities
In modern urban environments, the power system plays a vital role, providing uninterrupted power to millions of residents and businesses. Ensuring a reliable power supply is not only the cornerstone of comfortable living but also crucial for the normal functioning of the urban economy and society. For a long time, overhead cables have been the primary means of power transmission, crisscrossing the city and forming the backbone of the power grid. However, with the acceleration of urbanization and the continuous expansion of urban scale, the limitations of overhead cables have become increasingly apparent.
Overhead cables are not only susceptible to severe weather (such as strong winds and snow) and natural disasters (such as lightning strikes and fallen trees), leading to power outages, but their exposed nature also presents potential safety hazards, such as the risk of electric shock. Furthermore, the dense overhead lines visually impact the urban landscape and require regular tree felling to prevent interference, increasing maintenance costs and workload.
It is against this backdrop that underground cables, as a more advanced and reliable method of power transmission, are becoming increasingly prevalent. Buried underground, they effectively mitigate the aforementioned risks, enhance the resilience of the power grid and the safety of the city, while also beautifying the urban environment and reducing the complexity of long-term maintenance.
Underground cables offer a solution to many of the challenges faced by overhead power lines, including vulnerability to weather conditions, aesthetic concerns, and safety risks. By burying power cables underground, cities can improve the reliability of their electrical infrastructure and reduce the impact of environmental and human factors on the system.
2. Key Benefits of Underground Power Cables
The transition from overhead cables to underground power cables provides several advantages that contribute to the overall safety and reliability of the power distribution system in urban areas:
a. Enhanced Safety
One of the primary benefits of underground power cables is the reduced risk of electrical hazards. Overhead power lines are more susceptible to damage from severe weather events, such as thunderstorms, ice storms, or high winds, which can lead to short circuits, fires, or power outages. Underground cables, on the other hand, are shielded from these environmental factors, which significantly reduces the risk of accidents and electrical fires.
In addition, underground power cables are not as easily accessible as overhead lines, preventing accidental contact by people, animals, or vehicles. This is especially important in urban areas where the risk of contact with power lines is higher.
b. Reliability in Harsh Weather Conditions
Underground power cables provide increased resilience during extreme weather conditions. Overhead cables are vulnerable to damage from storms, fallen trees, or high winds. In contrast, underground systems are protected from these issues, maintaining a continuous power supply during adverse weather. This reliability is especially vital for essential services like hospitals, emergency response centers, and data centers.
c. Aesthetic and Urban Planning Benefits
Overhead power lines can be unsightly and disrupt the visual appeal of urban landscapes. Underground power cables are ideal for aesthetic reasons, as they free up space in cities, providing more flexibility for urban planning, landscaping, and the development of new infrastructure.
Moreover, burying power cables underground reduces the potential for power outages caused by fallen trees, debris, or even human interference, creating a safer and more organized environment for urban residents and businesses.
3. How Underground Power Cables Work
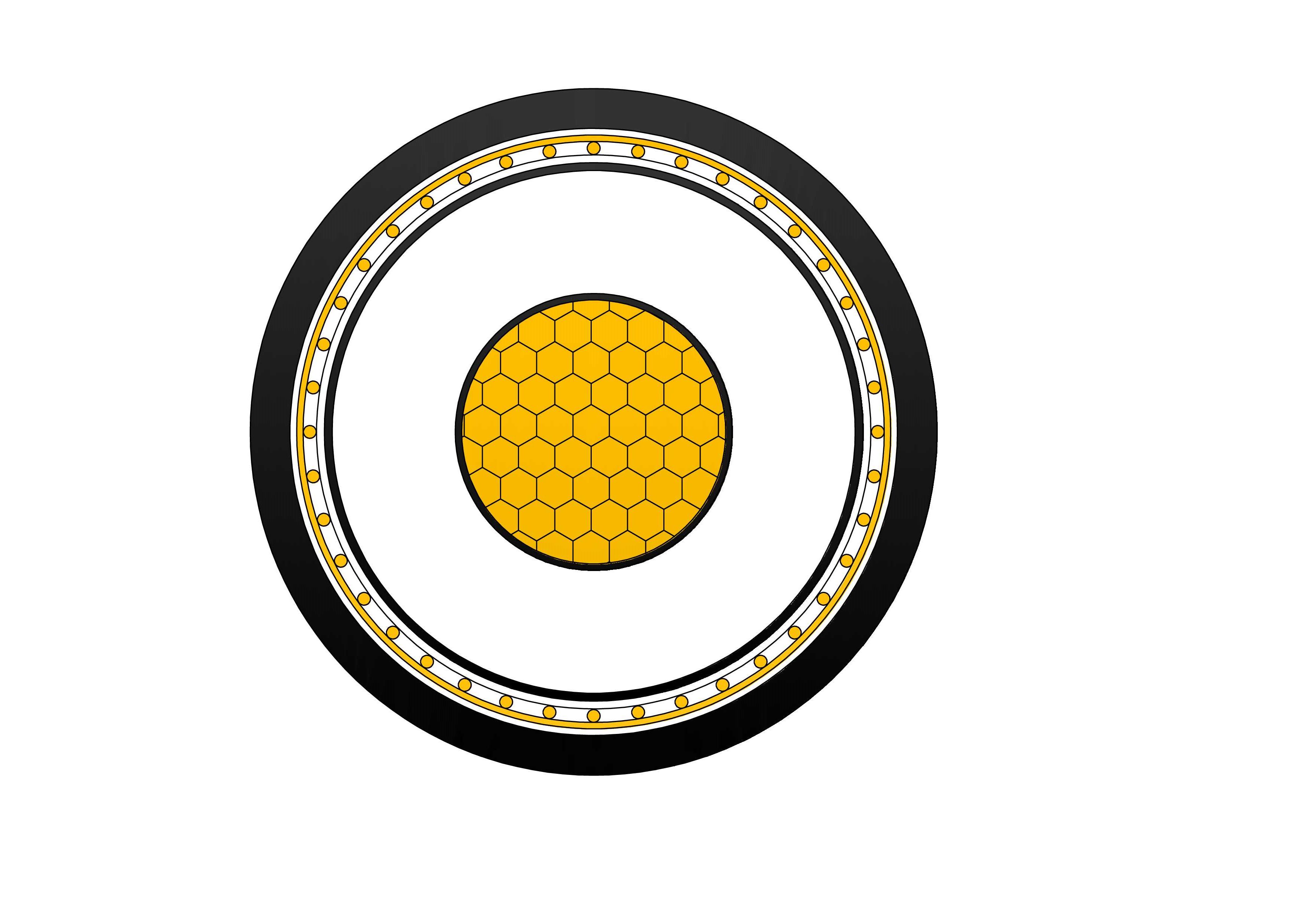
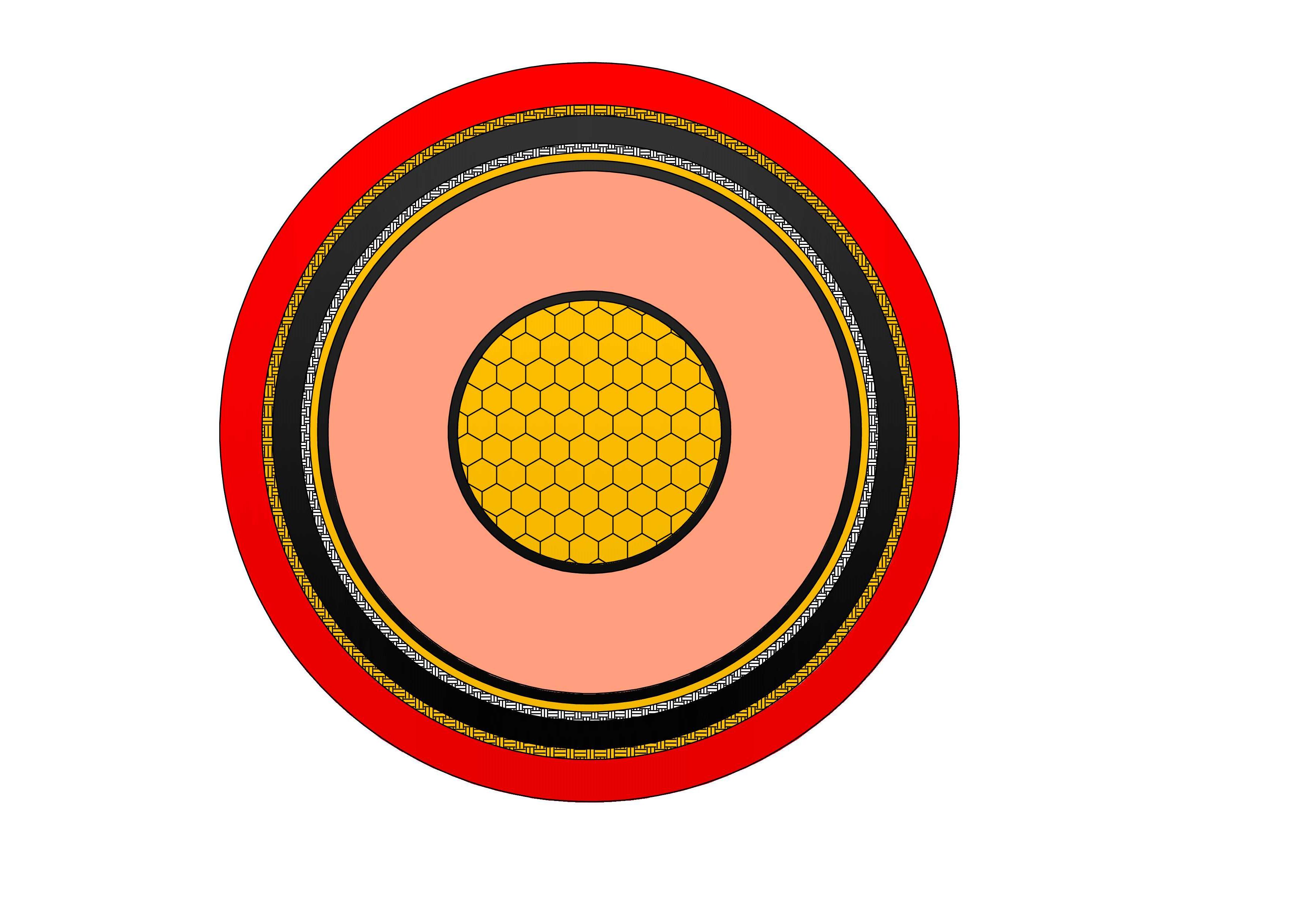
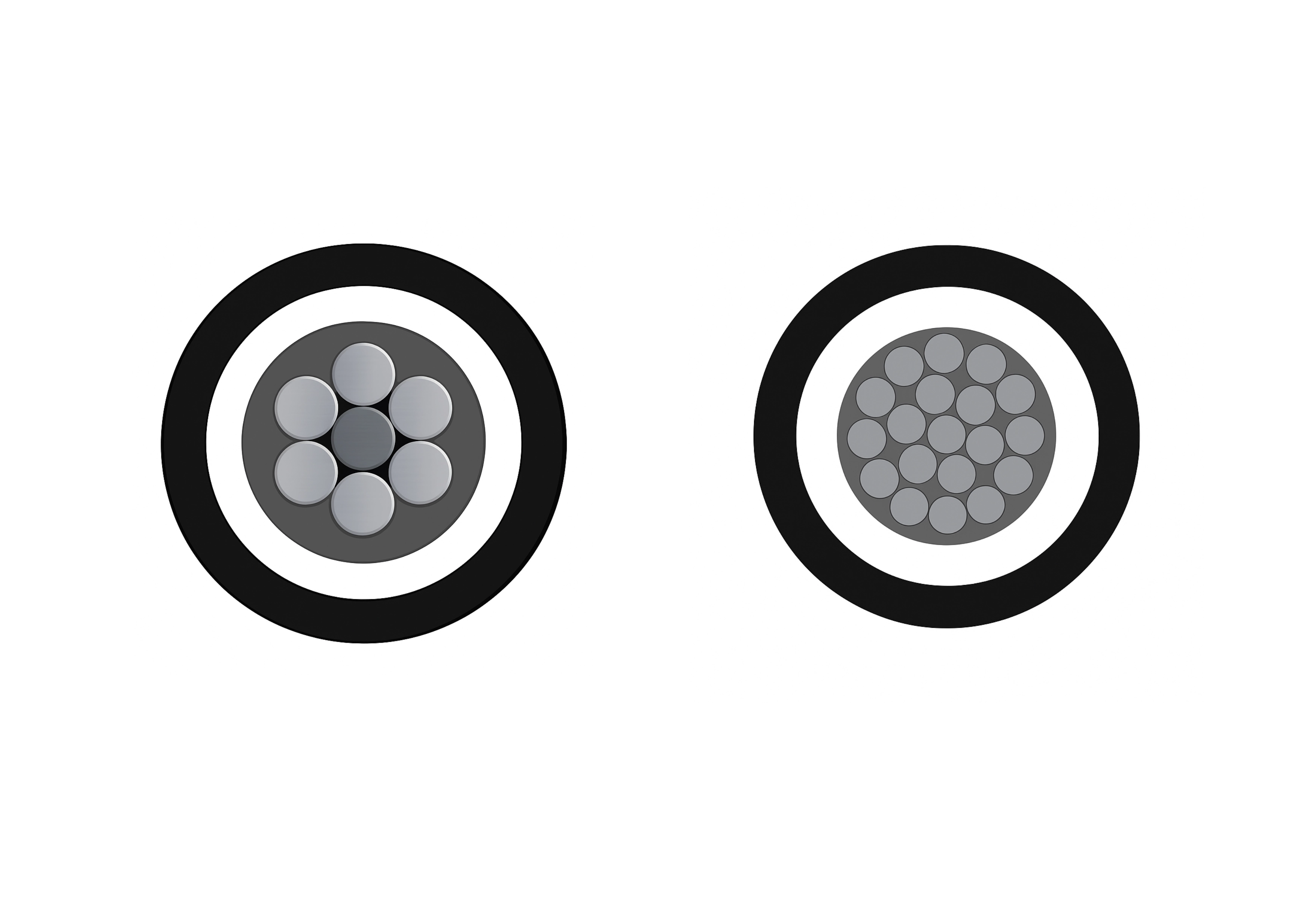
Underground cables are designed to function similarly to overhead cables, but with additional protections and considerations for their underground environment. The basic structure of an underground power cable consists of several layers:
-
Conductor: The inner core, usually made of copper or aluminum, carries the electrical current.
-
Insulation: Surrounding the conductor, insulation materials like XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) or PVC protect the cable and prevent short circuits.
-
Shielding: A layer of shielding, such as copper tape or metallic wires, protects the cable from external electrical interference and offers additional safety.
-
Outer Sheath: The final layer, often made of polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride, provides physical protection against moisture, mechanical stress, and external elements.
In underground installations, the cables are buried in trenches or ducts, and the installation is carefully planned to avoid damage during future construction projects. Additionally, some systems use direct-buried cables, while others employ duct systems, which protect the cables and allow for easier maintenance or replacement.
4. Challenges of Installing Underground Power Cables
While underground power cables offer significant advantages, their installation presents unique challenges. These challenges must be carefully addressed to ensure the effectiveness of the system:
a. High Installation Costs
Underground cables typically cost more to install than overhead cables due to the labor-intensive process of digging trenches, laying cables, and ensuring the proper installation of duct systems. However, these upfront costs are often offset by the long-term benefits, including lower maintenance and fewer power outages.
b. Maintenance and Repairs
One of the main drawbacks of underground power cables is that, unlike overhead systems, which are easily accessible, underground cables require more effort and equipment for repairs. If an issue occurs, locating the fault and performing repairs can be time-consuming and costly. This is why regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term performance of underground power systems.
c. Environmental Impact and Considerations
While underground power cables are more resilient to environmental conditions, their installation can disrupt local ecosystems, particularly in areas where underground systems require significant digging. Additionally, environmental conditions such as water tables or soil conditions can affect the choice of cable types and installation methods.
5. Applications of Underground Power Cables
Underground power cables are used in a variety of applications in urban areas:
-
Residential Areas: Providing a safer, more reliable power supply while maintaining aesthetics in suburban and metropolitan neighborhoods.
-
Commercial Buildings: Ensuring uninterrupted power supply for office complexes, shopping malls, and retail businesses.
-
Critical Infrastructure: Powering hospitals, emergency services, and industrial facilities that require a constant and stable electricity supply.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: In systems where solar farms, wind turbines, or hydropower plants are connected to the grid, underground cables are used to transport power to the utility network.
In urban areas where safety, reliability, and efficiency are paramount, underground power cables provide an ideal solution for modern power distribution systems. By enhancing electrical safety, reducing maintenance costs, and improving reliability in the face of severe weather conditions, underground systems are becoming an increasingly popular choice for power delivery. While installation costs can be higher, the long-term benefits of underground cables—including fewer power outages, improved urban aesthetics, and greater environmental resilience—make them a crucial element in the future of power infrastructure.
As cities continue to grow and evolve, underground power cables will remain at the forefront of ensuring safe, efficient, and sustainable electrical systems that meet the demands of modern life.