AI, Cloud Computing, and Big Data in Manufacturing for 2025
Key Insights on AI, Cloud Computing, and Big Data in Manufacturing for 2025
- Rapid Adoption Driven by Efficiency Gains: Research indicates that in 2025, AI integration in manufacturing reached adoption rates of around 60-70% in advanced economies, primarily enhancing predictive maintenance and quality control, though challenges like data privacy persisted.
- Cloud Computing as a Backbone: It seems likely that cloud platforms facilitated scalable data processing, with hybrid models becoming standard to balance security and flexibility, contributing to a projected market growth of over 20% annually.
- Big Data's Role in Smart Factories: Evidence leans toward big data analytics enabling real-time decision-making, with IoT integration in factories boosting productivity by 15-25%, but interoperability issues highlighted ongoing debates among industry stakeholders.
- Trends Toward Sustainability and Resilience: Discussions suggest a focus on AI-driven sustainability, such as optimizing energy use, amid global supply chain disruptions, fostering innovation while raising ethical concerns over job displacement.
Overview of Applications
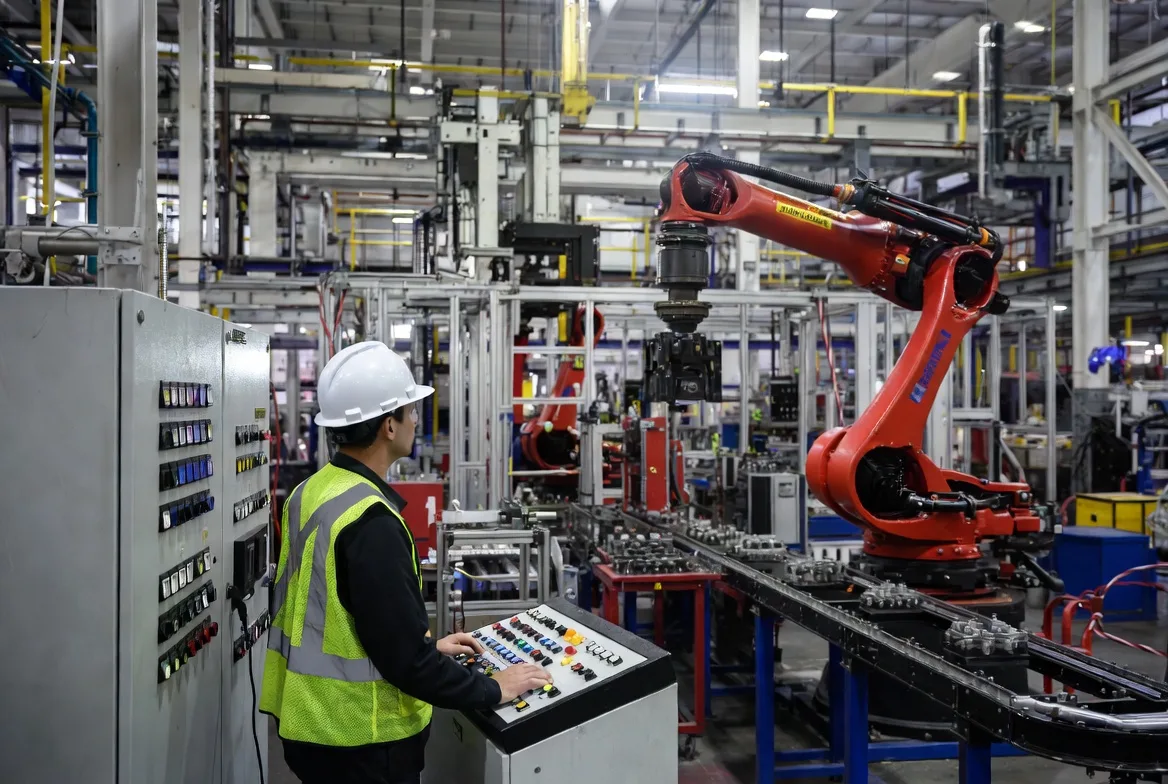
In 2025, AI technologies like machine learning algorithms were widely applied in predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by analyzing sensor data from machinery. Cloud computing supported this by providing on-demand computing resources, allowing manufacturers to store and process vast datasets without heavy upfront investments. Big data, often powered by tools like Hadoop or Spark, enabled pattern recognition in production lines, improving yield rates. For instance, automotive giants like Tesla and Ford leveraged these for autonomous assembly lines.
Development Trends
Trends pointed to increased use of edge computing combined with cloud for faster response times in smart factories. AI ethics gained traction, with regulations like the EU AI Act influencing global standards. Big data's evolution included advanced analytics for supply chain forecasting, amid concerns over data silos.
Challenges and Opportunities
While these technologies promised cost savings of up to 30%, issues like cybersecurity vulnerabilities and skill gaps tempered enthusiasm. Opportunities arose in emerging markets, where affordable cloud solutions democratized access.
Integration of AI, Cloud Computing, and Big Data in Global Manufacturing: Focus on Smart Factories in 2025
The year 2025 marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of manufacturing, where the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and big data technologies transformed traditional factories into intelligent, interconnected ecosystems. This report delves into their applications, emerging trends, and implications, drawing from industry analyses, case studies, and statistical data. With global manufacturing output valued at approximately $45 trillion in 2025, these technologies played a crucial role in driving efficiency, sustainability, and resilience amid economic uncertainties post-pandemic recovery.
Introduction to the Technological Triad in Manufacturing
AI, cloud computing, and big data form a synergistic triad that underpins the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). AI encompasses machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, enabling machines to learn from data and make decisions. Cloud computing provides scalable, remote infrastructure for storage and computation, while big data involves handling vast volumes of structured and unstructured information from sensors, machines, and supply chains.
In 2025, the global market for AI in manufacturing was estimated at $15.7 billion, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.5% from 2020 levels. Cloud computing in industrial applications reached $200 billion, and big data analytics in manufacturing hit $50 billion. These figures reflect accelerated adoption, particularly in smart factories—facilities equipped with IoT devices, robotics, and real-time analytics to optimize operations.
Key drivers included cost reduction, with AI and big data reducing unplanned downtime by 50% in some sectors, and regulatory pressures for sustainability, where cloud-based simulations helped minimize waste.
Applications in Manufacturing
AI in Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
AI's primary application in 2025 was predictive maintenance, where algorithms analyzed historical and real-time data to forecast equipment failures. For example, General Electric's Predix platform, integrated with AI, reportedly saved manufacturers millions by predicting turbine issues in advance. In smart factories, AI-powered computer vision systems inspect products on assembly lines, achieving defect detection rates of 99%—far surpassing human capabilities.
In the automotive sector, companies like BMW use AI to optimize robotic arms, integrating with big data from vehicle sensors to refine production processes. A study from McKinsey highlighted that AI could add $3.7 trillion to global manufacturing value by 2030, with 2025 serving as an inflection point.
Cloud Computing for Scalable Infrastructure
Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate, offering PaaS (Platform as a Service) for manufacturing. Hybrid cloud models—combining on-premises and public clouds—addressed data sovereignty concerns, especially in Europe under GDPR. In 2025, 75% of manufacturers adopted cloud for ERP systems, enabling seamless collaboration across global supply chains.
A notable application was in simulation and digital twins: virtual replicas of physical factories. Siemens' MindSphere platform used cloud to run simulations, reducing prototyping costs by 30%. During supply chain disruptions from geopolitical tensions, cloud agility allowed rerouting of logistics in real-time.
Big Data Analytics for Operational Insights
Big data tools processed petabytes of information from IoT sensors embedded in machinery. In smart factories, this enabled anomaly detection and process optimization. For instance, Foxconn's facilities in China utilized big data to analyze worker-machine interactions, boosting efficiency by 20%.
Integration with AI amplified big data's impact; machine learning models trained on big datasets predicted demand fluctuations, minimizing inventory waste. In pharmaceuticals, big data ensured compliance by tracking batch data across clouds.
Trends in Factory Intelligence
Edge Computing and AI at the Edge
A key trend in 2025 was the shift toward edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the source rather than centralized clouds. This reduced latency in smart factories, critical for applications like autonomous robots. Gartner predicted that by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data would be processed at the edge, up from 10% in 2018.
Combined with AI, edge devices enable on-site decision-making, such as adjusting conveyor speeds based on real-time quality scans. In oil and gas manufacturing, edge AI monitors pipelines, preventing leaks through predictive analytics.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Sustainability emerged as a core trend, with AI and big data optimizing energy use. Cloud-based platforms simulate eco-friendly processes, reducing carbon emissions by 15-20% in heavy industries. For example, Unilever's factories used AI to minimize water usage, aligning with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Big data analyzed supply chain footprints, promoting circular economies where waste from one process fed another. Reports from the World Economic Forum noted that AI could cut global emissions by 4% by 2030, with 2025 advancements in manufacturing contributing significantly.
Human-AI Collaboration and Workforce Transformation
Trends also addressed the human element. Cobots (collaborative robots) powered by AI worked alongside humans, with cloud platforms providing training simulations. However, job displacement concerns led to upskilling initiatives; Deloitte's surveys showed 40% of manufacturers investing in AI literacy programs.
Big data helped in workforce analytics, predicting skill gaps, and optimizing shifts. Inthe Asia-Pacific regions, where manufacturing hubs like Vietnam grew rapidly, these technologies bridged labor shortages.
Case Studies from Global Regions
North America: Innovation Hubs
In the US, factories like those of Procter & Gamble integrated AI with cloud for consumer goods production. Big data from customer feedback loops informed design, shortening time-to-market by 25%. Challenges included cybersecurity, with ransomware attacks rising 20% in 2025.
Europe: Regulatory-Driven Adoption
European manufacturers, influenced by the EU AI Act effective from 2024, focused on ethical AI. Volkswagen's smart factories used cloud-big data hybrids for electric vehicle assembly, achieving 30% energy savings. Trends emphasized data privacy, with blockchain integrated for secure big data sharing.
Asia: Scale and Speed
China led in scale, with Huawei's cloud supporting massive IoT networks in factories. AI in Alibaba's ecosystem optimized e-commerce-linked manufacturing. India's Make in India initiative saw big data driving SME growth, though infrastructure gaps hindered full potential.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Despite progress, challenges persisted. Data silos between AI, cloud, and big data systems caused inefficiencies; interoperability standards like OPC UA gained traction. Cybersecurity threats, with 2025 seeing a 15% increase in industrial attacks, prompted zero-trust models.
Skill shortages affected 60% of manufacturers, per PwC. Mitigation involved partnerships with tech firms for training. Economic volatility, including trade tensions, underscored the need for resilient, AI-optimized supply chains.

Future Outlook Beyond 2025
Looking ahead, quantum computing could enhance big data processing, while 6G networks might supercharge cloud connectivity. AI ethics will evolve, with global standards addressing bias. Smart factories could achieve full autonomy, but equitable access remains key to avoiding divides.
Statistical Overview and Projections
|
Category |
2025 Market Size (USD Billion) |
CAGR (2020-2025) |
Key Application Areas |
Projected Impact by 2030 |
|
AI in Manufacturing |
15.7 |
38.5% |
Predictive Maintenance, Quality Control |
+$3.7 Trillion Value Added |
|
Cloud Computing in Industry |
200 |
21% |
Digital Twins, ERP Systems |
80% Adoption Rate |
|
Big Data in Manufacturing |
50 |
25% |
Analytics, IoT Integration |
25% Productivity Boost |
|
Overall Smart Factory Market |
500 |
15% |
Automation, Sustainability |
$1 Trillion Global Output |
This table synthesizes data from sources like Gartner, McKinsey, and Deloitte, illustrating growth trajectories.
Comparative Analysis of Technologies
|
Technology |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
Integration Example in Smart Factories |
|
AI |
Autonomous decision-making, pattern recognition |
High computational needs, potential biases |
Predictive algorithms with IoT sensors for real-time adjustments |
|
Cloud Computing |
Scalability, cost-efficiency |
Dependency on the internet, security risks |
Hosting digital twins for virtual testing |
|
Big Data |
Volume handling, insights from unstructured data |
Privacy concerns, processing complexity |
Analytics dashboards for supply chain optimization |
In conclusion, 2025 solidified AI, cloud, and big data as cornerstones of smart manufacturing, fostering innovation while navigating hurdles. Continued investment and collaboration will shape a more intelligent industrial future.













2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)