Solar PV Power for Homes and Industries: Cost, Efficiency, and System Setup Guide
Solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation has become one of the most promising renewable energy technologies for both residential and industrial applications. PV systems directly convert solar radiation into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cell modules, and "PV" refers to this process of generating electricity from sunlight. With the accelerating global energy transition, rising electricity prices, stricter carbon emission controls, and continued government subsidies, installing solar PV systems has become an important way to reduce energy costs and enhance energy independence. Whether it's a residential rooftop system or a large-scale industrial and commercial distributed power station, solar PV provides stable, clean, and sustainable electricity. At the same time, the efficiency of modern PV technology is constantly improving, and system installation costs are continuously decreasing, making it more economical in the long run. For users seeking green energy and reduced operating costs, solar PV power generation is gradually becoming one of the most worthwhile energy solutions to invest in.
1. What Is Solar PV Power and How Does It Work?
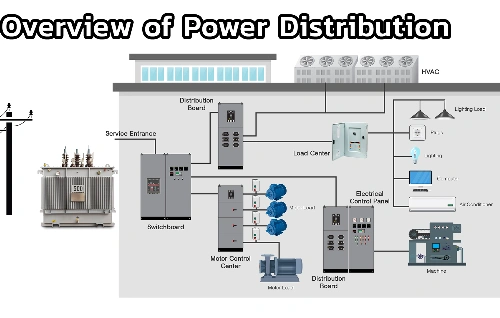
A solar PV power system consists of several key components:
- Solar panels (PV modules)
- Inverters for DC–AC conversion
- Mounting structures
- Cables and protection devices
- Energy meters
- Optional battery storage
Solar PV cells convert sunlight into DC electricity, which is then converted into AC power through inverters, enabling it to be used by household appliances, industrial machinery, and grid-connected systems.
According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), modern PV modules have significantly improved efficiency, offering longer service life and lower degradation rates, making them suitable for large solar PV power plant installations.
2. Solar PV Power for Homes: Reducing Electricity Bills
Homeowners choose PV solar power systems for one main reason—lowering electricity bills. When the system generates power during the day, household loads are supplied directly, reducing grid consumption. In many regions, excess energy can be exported to the grid through net metering programs, offsetting future bills.
Benefits for homeowners include:
- Long-term reduction in electricity costs
- Increased home value
- Low maintenance operation
- Quiet, safe, and non-polluting energy
- 25+ year expected lifespan
The Department of Energy notes that homes with solar power can save thousands of dollars over the system’s lifetime, depending on sunlight conditions and local electricity rates.

3. Solar PV Power for Industries: High Efficiency and Energy Stability
Industries with high energy demand—such as manufacturing, logistics centers, mining, textiles, and data centers—gain significant benefits from solar PV power generation:
- Reduced peak-hour demand charges
- Improved energy cost predictability
- Enhanced power reliability
- Lower carbon emissions for ESG compliance
- Opportunities for government incentives
Many factories install ground-mounted or rooftop PV solar power systems to offset large daytime loads. For even greater efficiency, solar systems may integrate with energy storage and smart energy management platforms.
4. Solar Panel Efficiency: What Impacts Actual Performance?
Solar panel efficiency is expressed as a percentage, showing how much sunlight is converted to usable electricity. Actual efficiency depends on:
- PV cell technology (mono, poly, thin-film)
- Temperature (hot surfaces reduce efficiency)
- Installation angle and orientation
- Shading from trees or buildings
- Maintenance and cleaning
- Inverter efficiency
Modern systems installed by professional solar installers often achieve real-world efficiencies between 18%–23% for monocrystalline modules.
5. Solar PV Power System Costs: What to Expect
The cost of a solar power system varies by region, installation size, and equipment. Homeowners typically evaluate:
- Solar panel cost
- Installation costs
- Inverter and mounting hardware
- Optional battery system
- Electrical upgrades
Industrial solar projects additionally consider:
- Transformer upgrades
- Medium-voltage interconnection
- Power quality systems
- Structural engineering for large rooftops
Below is a simplified comparison:
6. Cost & Performance Comparison Table
|
System Type |
Typical Capacity |
Estimated Cost Range |
Expected Annual Savings |
Best For |
|
Home Rooftop System |
3–10 kW |
$3,000 – $12,000 |
30–70% bill reduction |
Homes, small offices |
|
Commercial Rooftop System |
50–500 kW |
$40,000 – $400,000 |
20–50% load offset |
Office buildings, malls |
|
Industrial Ground-Mount PV Plant |
1–10 MW |
$900,000 – $8 million |
Significant peak demand reduction |
Factories, logistics parks |
|
Solar + Battery Storage System |
5 kW + 10 kWh |
$7,000 – $15,000 |
Backup power + peak shaving |
Homes & industries |
7. Steps for Installing a Solar PV Power System
- Site assessment – Determine available sunlight, shading, roof structure, or land area.
- Load analysis – Evaluate electricity bills and usage patterns.
- System design – Select panel type, inverter size, and installation method.
- Quotation & permits – Solar installers prepare documents for approval.
- Installation – Mounting, cabling, inverter setup, and commissioning.
- Grid connection – Energy meter configuration and local utility approval.
- Monitoring & maintenance – Track performance and clean panels regularly.

Solar PV power systems are reshaping how homes and industries manage energy. Whether for reducing electricity bills, improving energy independence, or supporting sustainable development, PV solar power systems offer long-term, reliable, and cost-effective solutions. As technology continues to evolve, solar PV power generation will become even more efficient and accessible, driving the expansion of renewable energy worldwide.

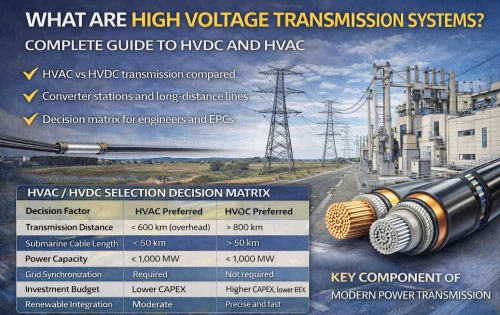










2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)