What is Concentric Cable? Understanding its Structure and Applications
In today's modern power infrastructure, the need for reliable and efficient power distribution systems is more urgent than ever. With accelerated urbanization and industrial development, electricity demand is constantly increasing, making the stable operation of the power system a top priority. Against this backdrop, concentric cables, as a highly efficient power transmission method, are increasingly being used in various power projects. Whether in residential communities, industrial parks, or commercial facilities, concentric cables effectively guarantee reliable power transmission. Their unique design not only improves power transmission efficiency but also reduces electromagnetic interference, providing higher security and lower maintenance costs for power facilities. In modern power grids, concentric cables play a crucial role and are one of the core technologies for achieving a stable power supply.
What is Concentric Cable?
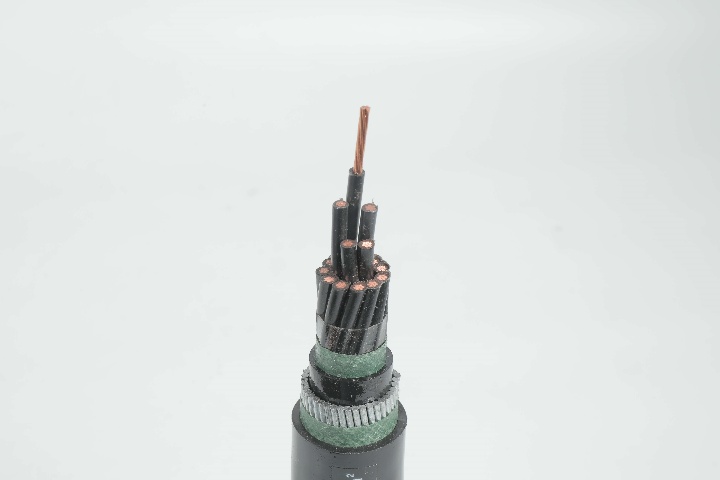
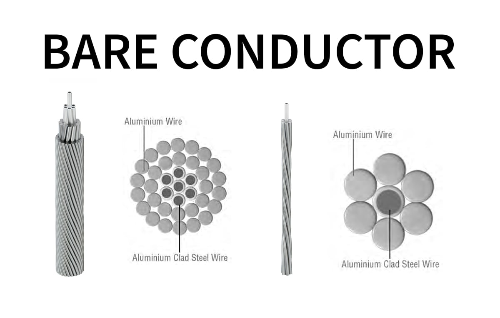
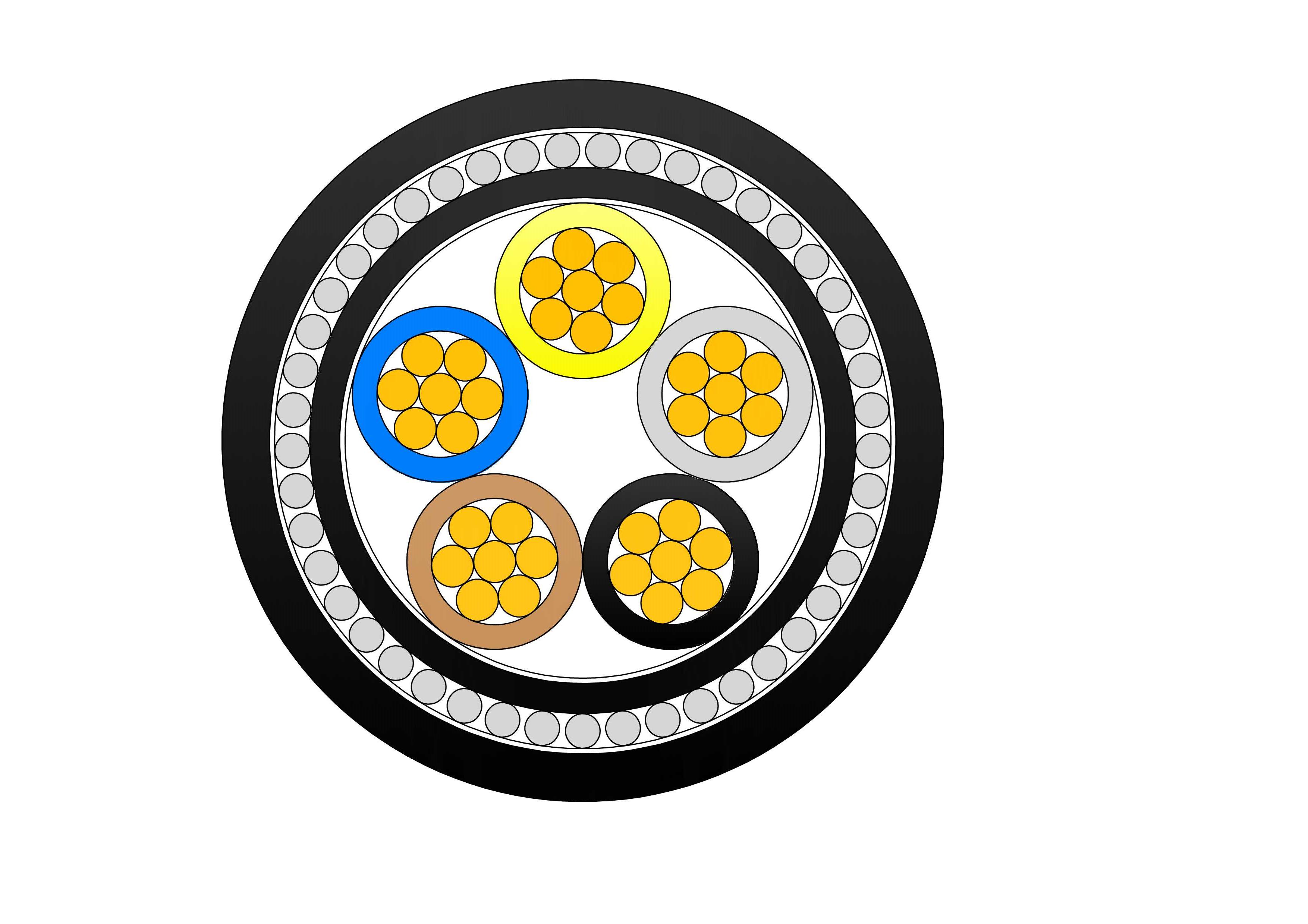
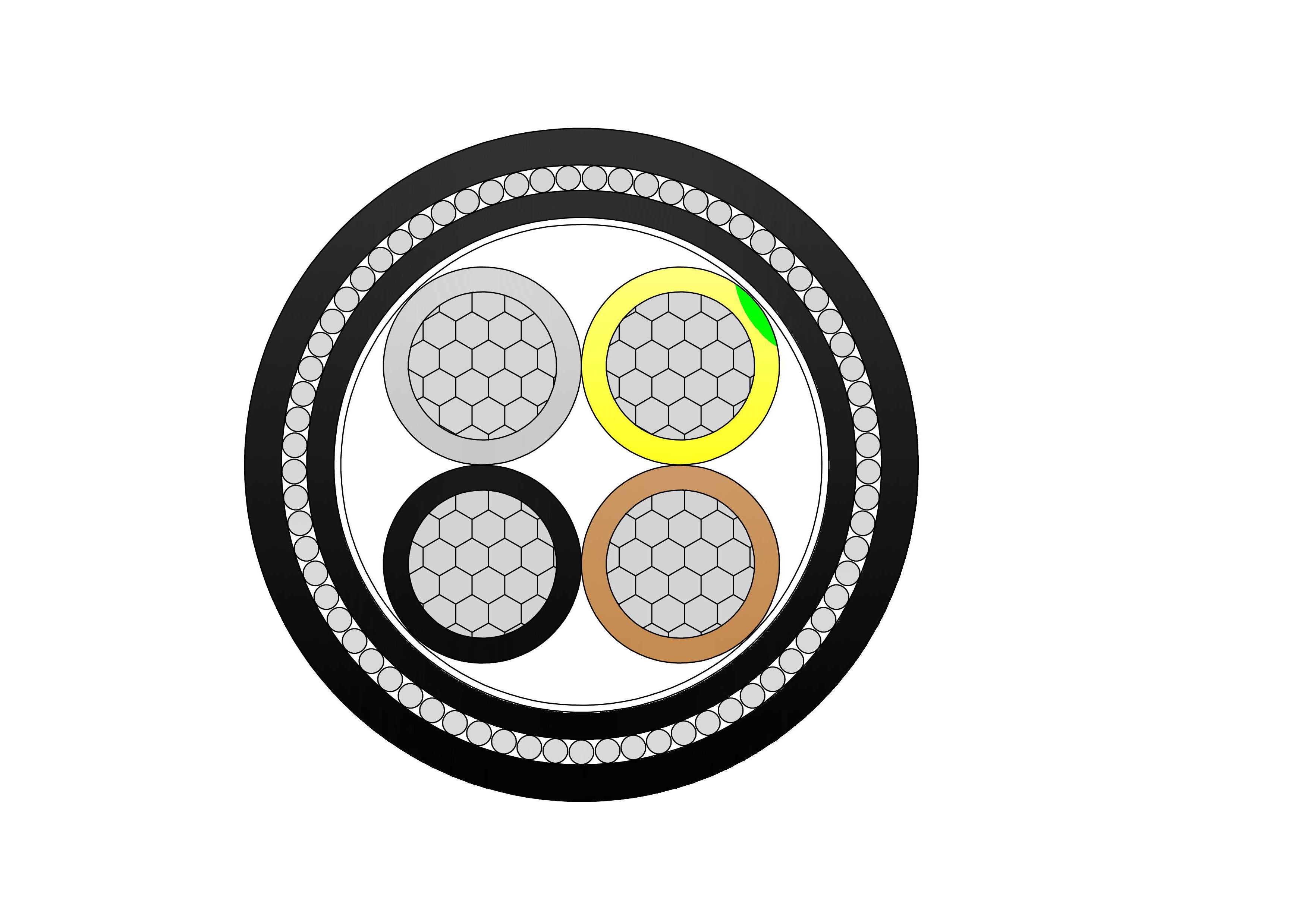
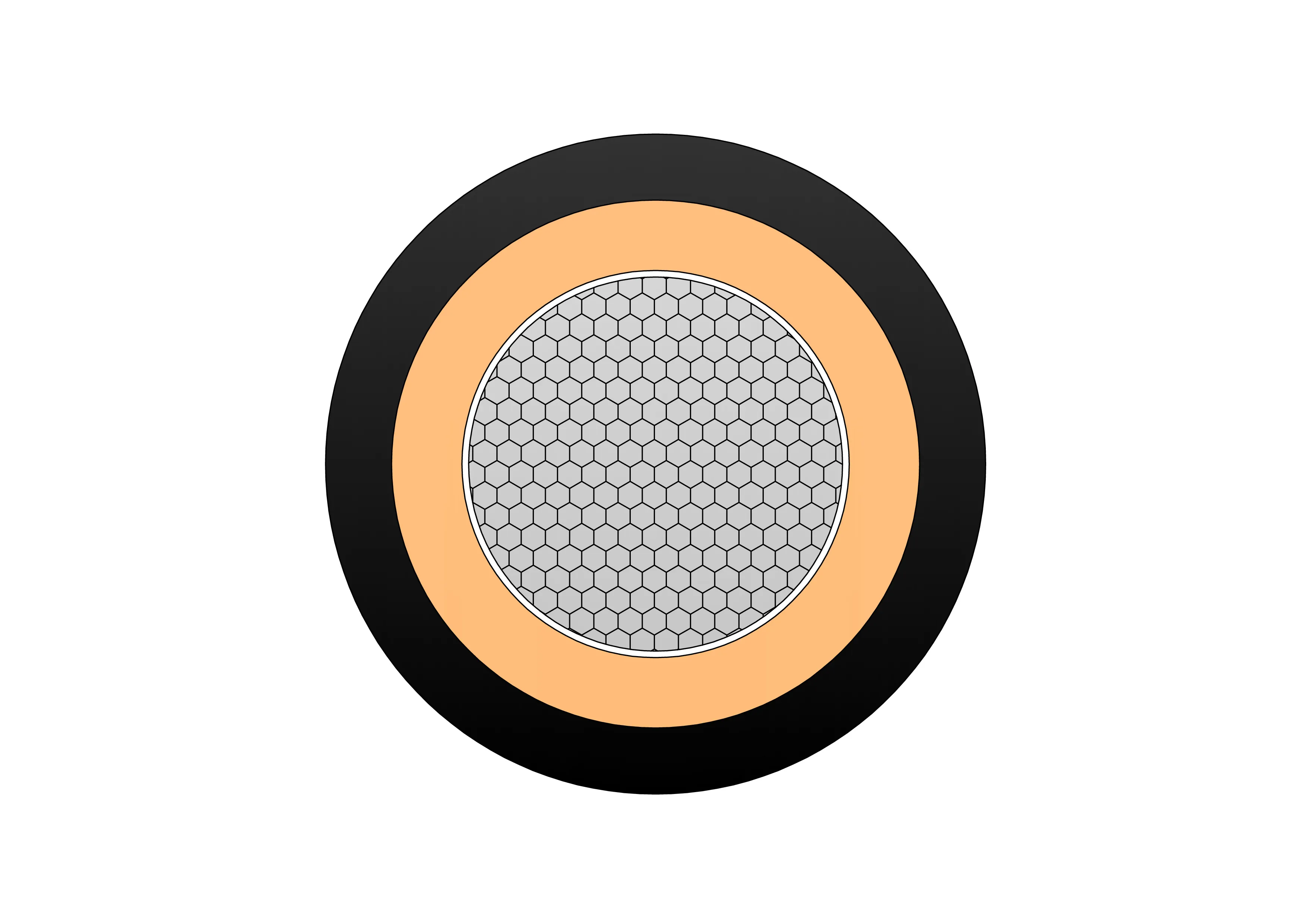
A concentric cable is an electrical power cable that consists of an inner conductor, an insulating layer, a neutral conductor, and an outer metallic sheath. The outer conductor is generally composed of a series of wires that are spiraled around the insulation, with the purpose of forming a complete return path for the current. The neutral conductor is usually made from copper or aluminum, providing a continuous loop for the current to travel back to its source.
Concentric cables are widely used in power distribution systems due to their reliability and ability to transmit electricity efficiently over long distances. The structure of the cable helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensures the safe transmission of power, making it a crucial part of both urban and rural electrical networks.
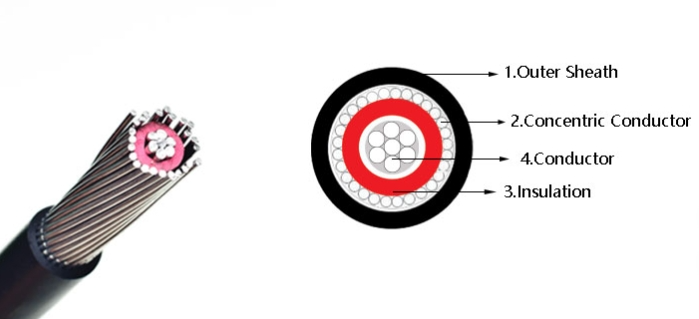
Concentric Cable Construction and Components
A typical concentric cable is composed of the following key components:
-
Inner Conductor: The central conductor, usually made of copper or aluminum, carries the electrical current from the source to the load. It’s often a solid or stranded wire, depending on the application.
-
Insulation Layer: Surrounding the inner conductor is an insulating material, typically made from cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which prevents short circuits and protects the wire from external elements.
-
Concentric Neutral Conductor: This is the crucial feature that distinguishes concentric cables. A series of small wires is wound around the insulation layer in a concentric manner to form the neutral conductor. This neutral wire helps to complete the electrical circuit and provides a return path for the current.
-
Outer Sheath: The final layer is a protective outer sheath, often made from materials such as PVC or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which shields the cable from physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors.
What is Split Concentric Cable?
A split concentric cable is a variant of the standard concentric cable. In this type of cable, the neutral conductor is split into two halves to form a more efficient and balanced return path for the current. The split design increases the current-carrying capacity and improves the cable’s performance in high-power applications.
Split concentric cables are commonly used in high-voltage power systems, particularly for the distribution of electricity in urban areas where high capacity and reliability are essential. The design allows for better control of the flow of electricity and ensures minimal losses during transmission, making it ideal for modern power networks.
Applications of Concentric Cables
Concentric cables are used in a wide range of applications, with their most common use being in electrical power distribution systems. Here are some of the primary applications:
-
Power Distribution Networks: Concentric cables are the backbone of many electrical grids, delivering power from substations to consumers. They are especially suitable for underground installations in residential, commercial, and industrial areas due to their robust construction and space-saving features.
-
Residential and Commercial Installations: Many residential and commercial buildings use concentric neutral cables to connect to the main power supply. Their compact design makes them ideal for confined spaces and minimizes the risk of electrical faults, especially when installed underground.
-
Industrial Facilities: In industrial applications, split concentric cables are often used to distribute high amounts of power efficiently. The additional neutral conductor helps manage the power load, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems in factories, processing plants, and large facilities.
-
Renewable Energy Integration: Concentric cables are also used in renewable energy applications, such as connecting solar panels and wind turbines to the main electrical grid. Their ability to handle varying load conditions makes them a practical choice for clean energy systems.
-
Transportation and Rail Systems: Concentric cables are frequently used in railway electrification systems, where the need for efficient and safe transmission of power is paramount. The robust construction of concentric cables ensures that they can withstand the high mechanical stresses typically found in transportation infrastructure.
Benefits of Concentric Cables
-
Space Efficiency: The compact design of concentric cables makes them ideal for installations where space is limited. For example, in underground or confined environments, concentric cables reduce the amount of space needed for wiring and improve overall efficiency.
-
Safety: The concentric neutral conductor ensures a continuous return path for current, reducing the risk of electric shock or fault in case of damage to the cable. Additionally, the protective outer sheath adds another layer of safety by preventing physical damage to the wire.
-
Reduced Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): The design of concentric cables helps minimize electromagnetic interference, which is critical in sensitive industrial and commercial applications where electronic equipment needs to function without disruption.
-
Durability and Longevity: The outer sheath and insulation material of concentric cables are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Whether exposed to moisture, heat, or physical stress, these cables maintain their performance over long periods, offering superior durability compared to traditional cables.
-
Flexibility and Reliability: Concentric cables are particularly effective in situations where high reliability is required, such as in power distribution networks. The additional neutral conductor in split concentric cables provides an enhanced level of flexibility and ensures reliable power distribution even under fluctuating loads.
In conclusion, concentric cables are an essential component of modern electrical power distribution systems. Their unique construction, which includes a concentric neutral conductor and protective outer sheath, ensures that they can handle high power loads while minimizing the risk of electrical faults. Whether used in residential, commercial, or industrial applications, concentric cables provide safe, efficient, and reliable power delivery.
With increasing demand for high-efficiency and sustainable power systems, split concentric cables are becoming an increasingly popular choice in areas with high power requirements, such as urban environments and industrial facilities. Understanding the structure, benefits, and applications of concentric cables helps engineers, contractors, and utilities make informed decisions about their use in both new and retrofit installations.