Understanding High-Voltage Power Lines: Importance, Safety, and Technology Behind Efficient Power Transmission
High-voltage transmission lines are the core infrastructure for modern long-distance power transmission. They are responsible for efficiently delivering electricity from power plants to homes, businesses, and industrial areas. Without these lines, power distribution would be limited by transmission distance and significantly less efficient. Understanding the technology behind high-voltage transmission lines, their crucial role in power transmission, and related safety measures is essential to ensuring the reliability and continuity of power supply.
1. What Are High-Voltage Power Lines?
High-voltage power lines are electrical conductors used to transport electricity at high voltage from power generation stations (like power plants) to substations or directly to end-users. These power lines operate at voltages typically above 35 kV, and in many cases, they can reach voltages as high as 765 kV in ultra-high voltage systems.
The primary role of high-voltage transmission lines is to move large quantities of electricity over long distances. The advantage of transmitting power at higher voltages is that it reduces energy loss due to resistance in the wires.
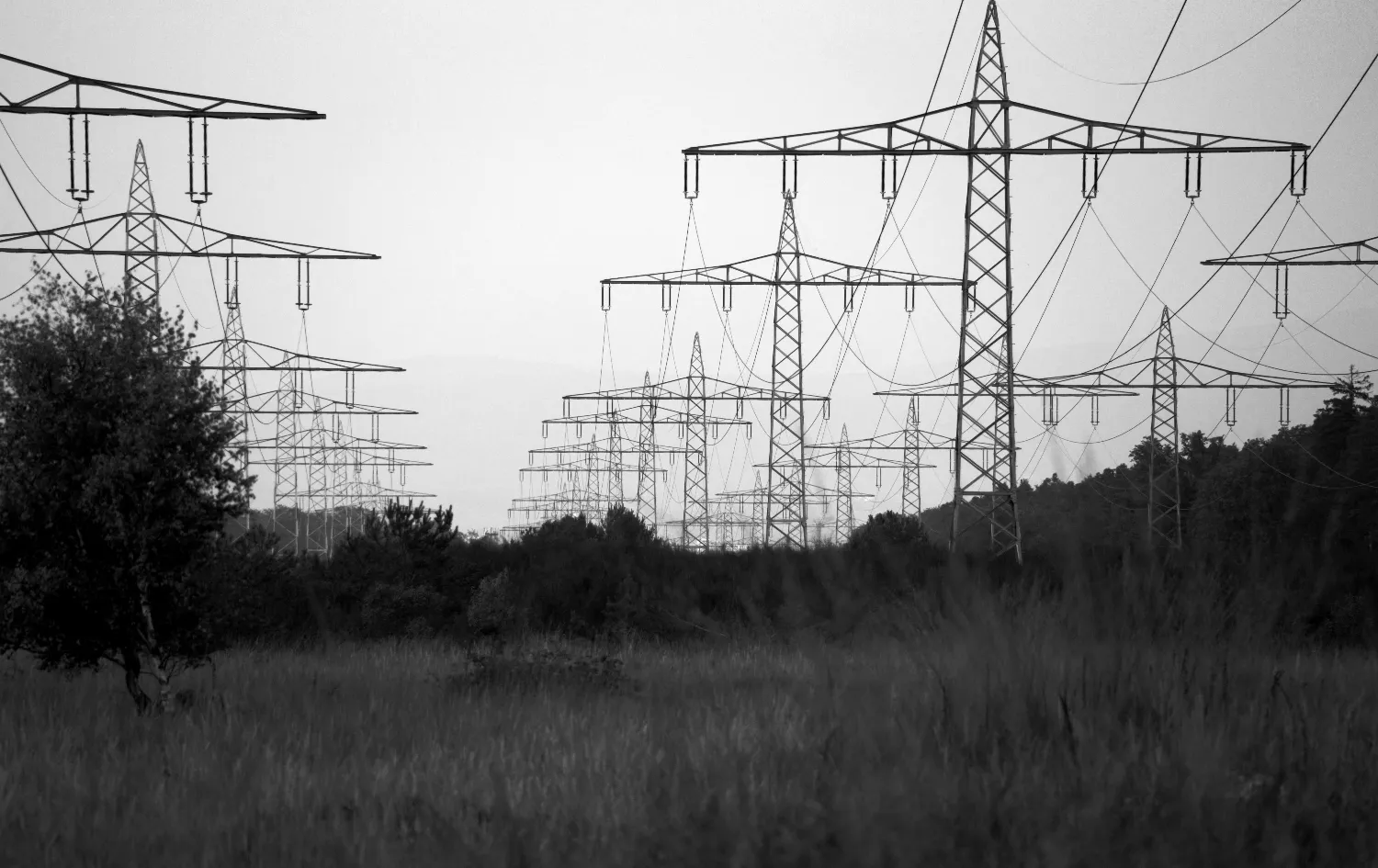

2. How Do High-Voltage Power Lines Work?
The working principle behind high-voltage power lines lies in the concept of electrical voltage and current. Voltage is the electrical force that pushes electric current through conductors (wires), and current is the flow of electrical charge.
Here’s a breakdown of the working principles:
a. Voltage Step-Up and Step-Down
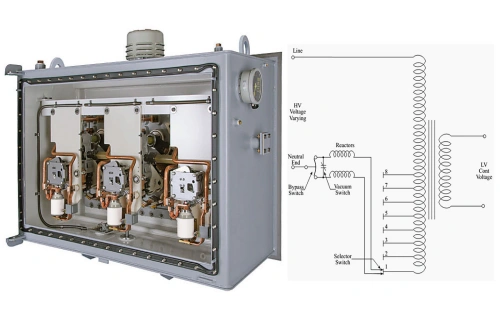
To ensure efficient transmission, electricity is stepped up to high voltage at the power plant using step-up transformers. The increase in voltage significantly reduces the current in the transmission lines, which in turn reduces the energy loss caused by resistance (known as I²R losses).
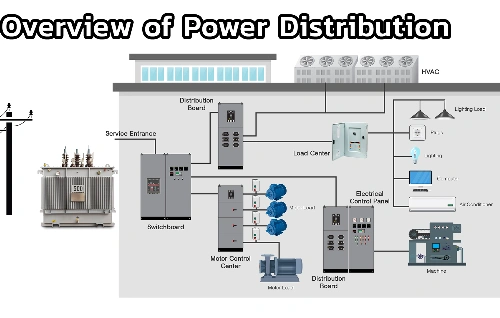
When electricity reaches a substation closer to the end-user, it is stepped down to lower, safer voltages using step-down transformers. These voltage levels are now suitable for local distribution to homes and businesses.
b. Electrical Conduction Through Wires
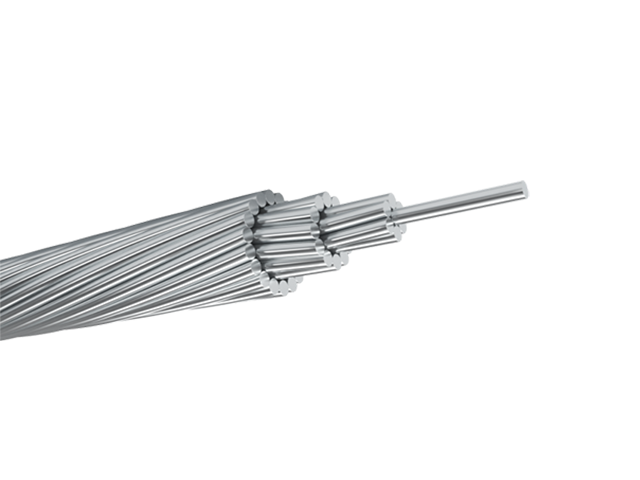
Electricity flows through the conductors of the high-voltage power lines. Most commonly, aluminum or copper conductors are used because of their excellent conductivity and relatively low cost. Aluminum is often preferred for overhead lines due to its lightweight nature, but in some cases, steel is used as a reinforcement material in ACSR (aluminum conductor steel reinforced) cables for better mechanical strength.
c. Insulation and Safety
To ensure safety and prevent short circuits, high-voltage power lines are insulated using special materials that protect both the lines and the surrounding environment. Porcelain insulators and polymer insulators are commonly used to prevent the high-voltage lines from touching other structures or the ground, ensuring that the electricity is safely transmitted without leakage.
3. Importance of High-Voltage Power Lines in the Electrical Grid
High-voltage power lines are crucial for long-distance electricity transmission. Without them, the electrical power system would be inefficient, and the distance over which electricity could be effectively delivered would be extremely limited. Some key benefits of high-voltage power lines include:
a. Reduced Energy Losses
As mentioned earlier, transmitting power at higher voltages significantly reduces energy losses. When electricity is transmitted at lower voltages over long distances, the resistance of the conductors causes heat loss, resulting in inefficient power transmission. High-voltage lines mitigate this issue by reducing the current and minimizing losses.
b. Support for the National Grid
High-voltage power lines help connect regional and national power grids, allowing electricity to flow seamlessly from generation sources to areas with high demand. They form the backbone of the electricity transmission system, supporting national economies and industries by ensuring an uninterrupted supply of power.
c. Increased Power Capacity
High-voltage transmission lines enable the efficient transfer of large quantities of electricity over vast distances, providing a higher power capacity. This is essential for industrial regions that require significant energy and for remote areas that are far from power plants.
4. Advanced Technologies Used in High-Voltage Power Lines
To ensure the reliability, efficiency, and safety of high-voltage power lines, several advanced technologies are integrated into the transmission system. Some key innovations include:
a. Smart Grid Technology
Smart grids are modernized power grids that incorporate digital sensors, communication networks, and automated control systems to optimize electricity distribution. By using real-time data, smart grids allow for more efficient load balancing and fault detection, improving the overall reliability of the electrical grid. Smart grids are also capable of integrating renewable energy sources into the transmission network.
b. High-Temperature Low-Sag (HTLS) Conductors
HTLS conductors are newer materials used in high-voltage power lines that offer higher current-carrying capacity while minimizing sag in the transmission wires. This allows power companies to increase the power capacity of existing lines without the need for full infrastructure replacement.
c. High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
HVDC transmission is an emerging technology that uses direct current (DC) rather than alternating current (AC) for long-distance transmission. HVDC lines are particularly effective for transmitting power over very long distances and across undersea cables. They can also interconnect power grids that operate at different frequencies.
5. Safety of High-Voltage Power Lines
Working with high-voltage power lines requires strict safety standards. These lines carry extremely high voltages that could be deadly if proper precautions aren’t taken. Key safety features include:
a. Grounding and Insulation
Grounding systems help prevent electrical shocks by ensuring that any unintended electrical surges are safely dissipated into the ground. Insulated cables and protective equipment such as arc flash barriers are used to keep workers safe while working near or on transmission lines.
b. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
To ensure that power lines operate efficiently and safely, regular maintenance and monitoring are necessary. This includes inspections, cleaning of insulators, and testing for wear and tear on cables and transformers. Sensors placed along the lines provide real-time data to monitor the health of the transmission network.
c. Emergency Shut-off Systems
In the case of power surges, storm damage, or accidental faults, modern high-voltage lines are equipped with emergency shut-off systems that can immediately disconnect parts of the grid to prevent cascading failures and equipment damage.
6. Future of High-Voltage Power Lines in Smart Grids and Renewable Energy Integration
As the world moves toward more sustainable energy solutions, high-voltage power lines are playing an increasingly crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power into existing power grids. This transition requires significant upgrades to both transmission infrastructure and grid management technologies. Here’s how high-voltage transmission lines are evolving in the context of smart grids and renewable energy integration:
a. Smart Grids and Dynamic Voltage Regulation
The integration of smart grids with high-voltage power lines allows for real-time monitoring, automated voltage regulation, and intelligent load balancing across the grid. Smart sensors embedded in the transmission network can track fluctuations in voltage, current, and load as well as renewable energy generation levels. This enables the grid to make real-time adjustments, ensuring that electricity is distributed efficiently even when solar or wind generation fluctuates.
For example, when a solar farm generates more electricity during peak sunlight hours, the smart grid can use high-voltage power lines to efficiently transmit this energy to areas with higher demand while maintaining voltage stability.
b. Facilitating Long-Distance Renewable Energy Transmission
Renewable energy sources such as offshore wind farms or large-scale solar installations are often located far from areas with high energy demand. High-voltage power lines, particularly High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission, are crucial in overcoming this challenge. HVDC lines allow for efficient long-distance energy transmission with minimal losses and are becoming a popular solution for connecting remote renewable energy sources to urban areas.
The ability of high-voltage power lines to handle intermittent renewable energy is essential in smart grid systems, which rely on data and automation to manage fluctuating power generation and ensure grid stability.
c. Energy Storage and High-Voltage Power Lines
Another significant development is the integration of energy storage systems such as battery storage or pumped hydro storage. These systems are being linked with high-voltage power lines to store excess energy generated during low-demand periods, which can be released during peak demand. Smart tap changers and smart grids can dynamically adjust voltage to efficiently charge and discharge these storage systems, ensuring that power is available when it’s needed most.

7. Challenges and Solutions in High-Voltage Power Lines
Despite the advancements in high-voltage transmission technologies, there are still several challenges faced by power grids, especially as renewable energy integration accelerates and demand for electricity grows.
a. Environmental Factors
High-voltage transmission lines are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions such as extreme weather, lightning, and flooding. These external factors can cause damage to the infrastructure, leading to power outages. To address this issue, engineers are developing weather-resistant transmission systems, including insulated cables and advanced conductor materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and physical stress.
b. Aging Infrastructure
Many existing high-voltage power lines were built decades ago, and the infrastructure is beginning to show signs of wear and tear. Aging infrastructure is prone to breakdowns, and upgrading these systems can be costly and time-consuming. Smart grid technologies can help monitor the health of these systems and provide predictive maintenance data, allowing for proactive upgrades and repairs before major failures occur.
c. Power Loss and Efficiency
Even with modern high-voltage transmission lines, there is always some energy loss due to resistance in the wires. However, recent innovations like High-Temperature Low-Sag (HTLS) conductors and superconducting cables are being used to reduce losses and increase the power-carrying capacity of existing lines without the need for full infrastructure replacements. These solutions are crucial in improving the efficiency of long-distance power transmission.
8. Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Power Transmission
As the global demand for electricity increases and the shift toward renewable energy continues, high-voltage power lines will remain a critical component in the evolution of modern power systems. The development of smart grids, energy storage systems, and HVDC transmission technologies will help optimize the efficiency and reliability of high-voltage transmission networks.
With the integration of smart tap changers, advanced conductor materials, and real-time monitoring systems, the future of high-voltage power lines is set to be more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly than ever before. The role of high-voltage power lines will continue to evolve as they support the transition to a more sustainable, smarter energy future.











3GHSSYCY-mining-cable-2.webp)


