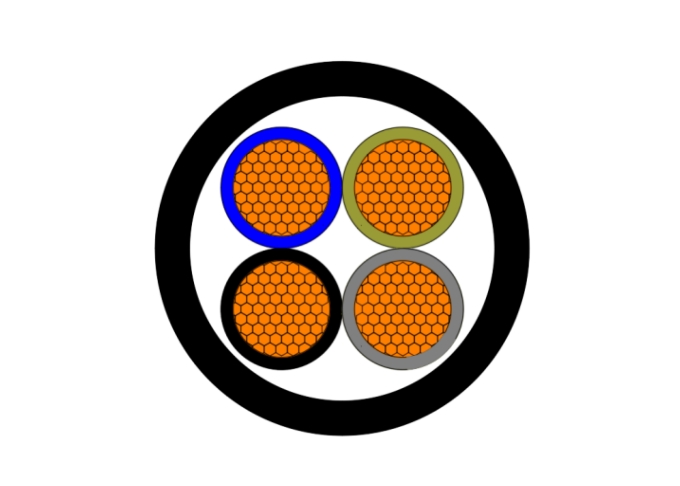
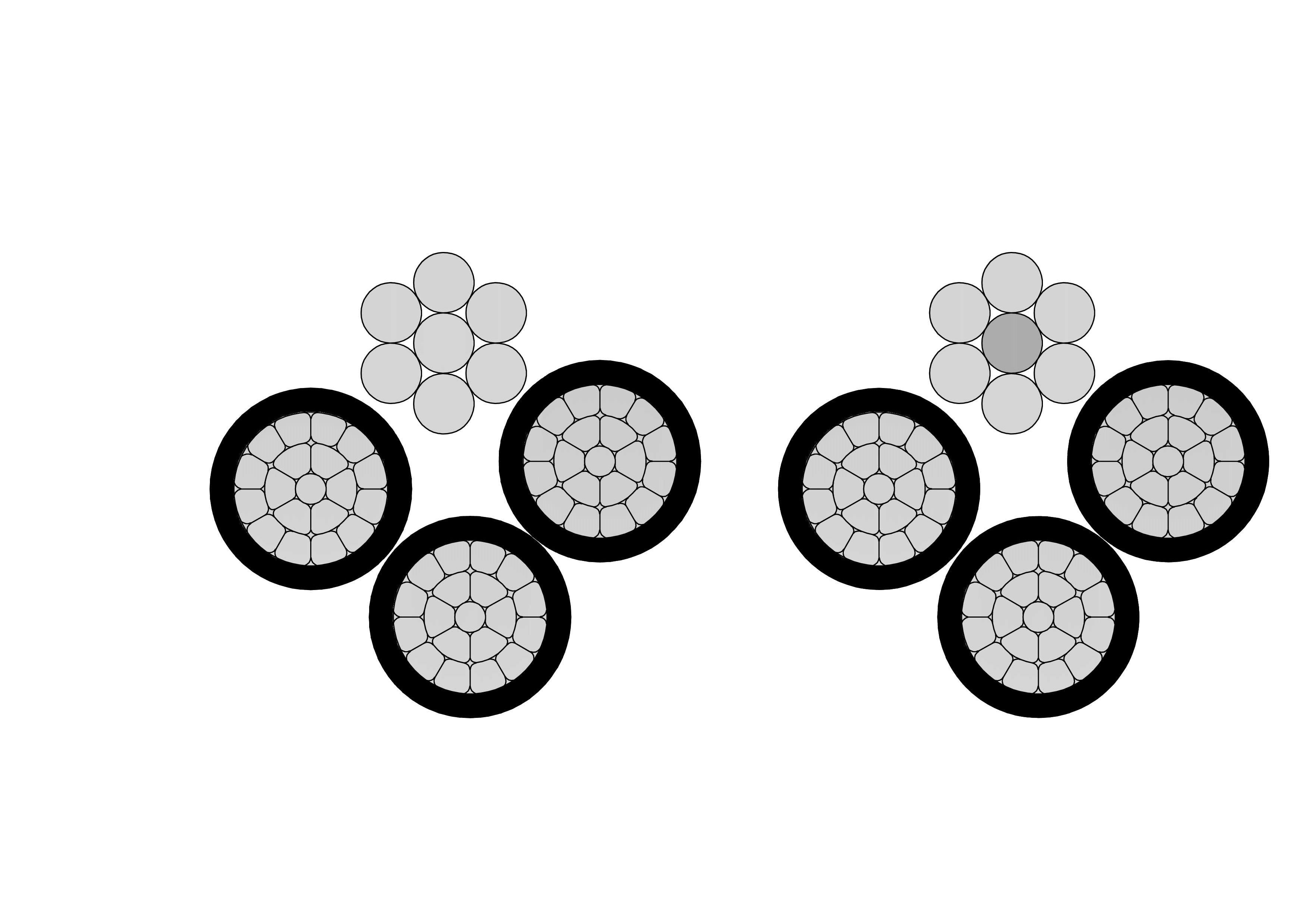
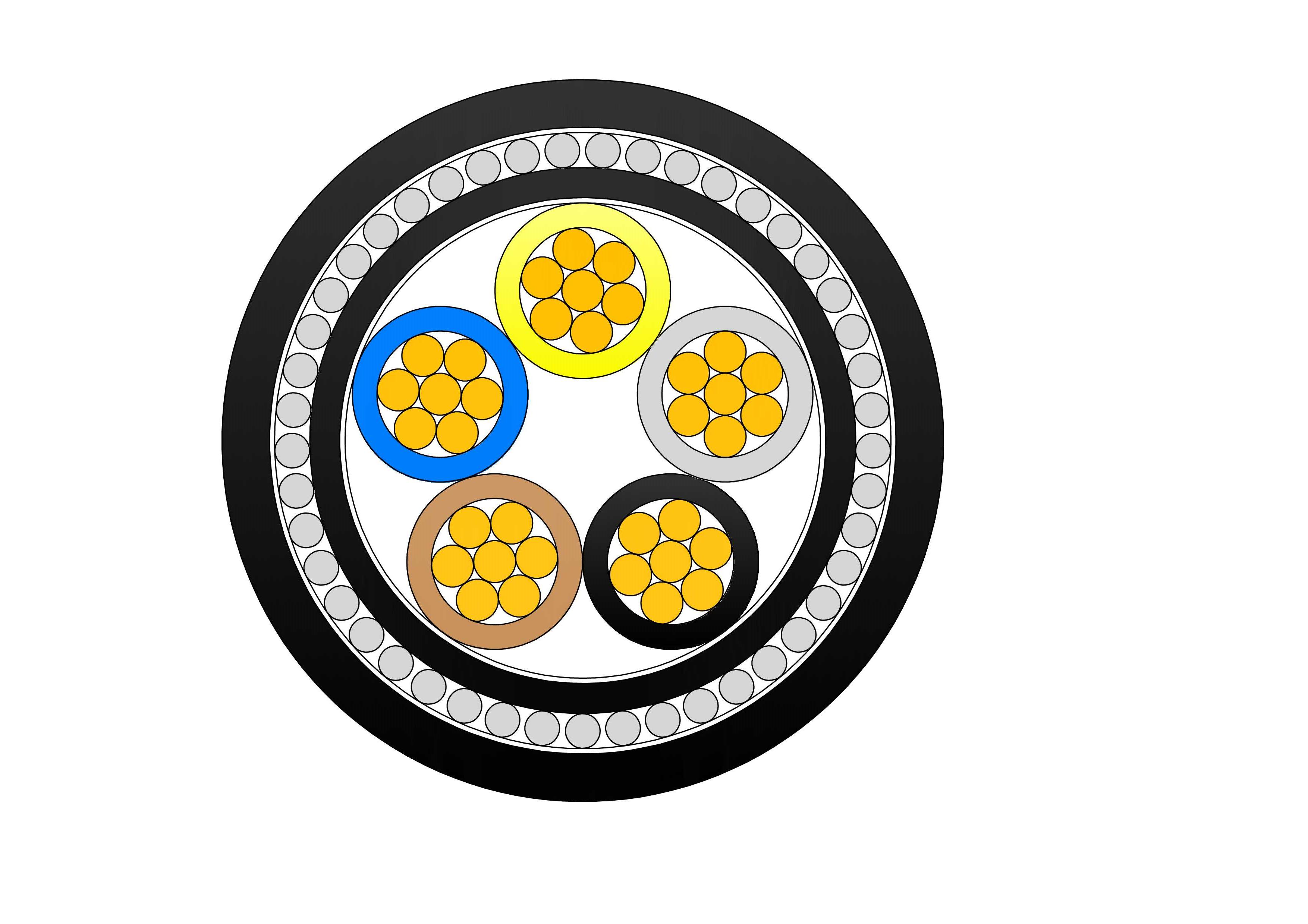
High-Voltage Transmission Lines: The Backbone of the Electric Power Grid
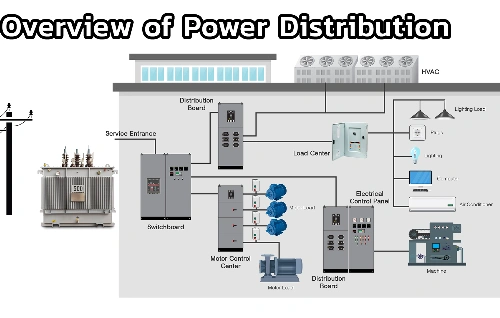
High-voltage transmission lines form the backbone of the power distribution network, ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of electricity to homes, industries, and businesses. These lines, carrying high-voltage power, enable long-distance, high-capacity energy transmission, reducing energy losses caused by long distances. High-voltage transmission lines play a crucial role in the power system, especially in cross-regional and cross-border power transmission scenarios, ensuring stable and efficient power flow. As the world's reliance on renewable energy gradually increases, widely distributed new energy sources such as wind and solar power also require high-voltage transmission lines to efficiently transmit them to the grid center, further enhancing the flexibility and reliability of the power system.
Furthermore, with the growth in electricity demand and the increasing focus on clean energy, high-voltage transmission lines are not only key to solving energy shortages and power supply bottlenecks, but also essential for ensuring stable grid operation, responding to load fluctuations, and providing higher energy efficiency. With continuous technological innovation, high-voltage transmission lines will continue to play an increasingly important role in future power systems.
What Are High-Voltage Transmission Lines?
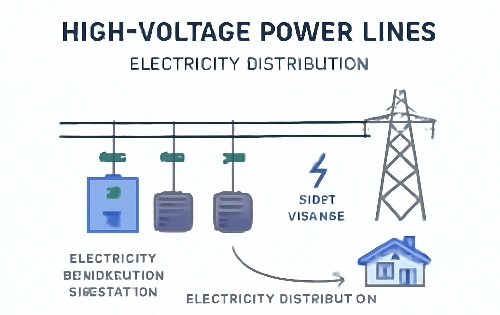
High-voltage transmission lines are a key component of electric power systems. They are designed to carry electricity at very high voltage levels from power plants to local substations, where it is then distributed to homes and businesses. These transmission lines are typically used to transport electricity over long distances, which is why long-distance transmission is one of their key functions.
The high voltage allows the electricity to travel with minimal energy loss, a vital aspect of efficiency in modern electrical infrastructure. High voltage reduces the current flowing through the lines, which in turn minimizes the heat and energy lost due to resistance in the conductors. High-voltage transmission is thus essential for maintaining efficient power flow across vast networks, ensuring that power lines can deliver electricity reliably over vast distances.

High-Voltage Transmission Lines in the Power Grid
In the context of the power grid, high-voltage transmission lines serve several key purposes:
-
Efficient Power Transfer: High voltage allows for efficient power transfer with less energy loss. Transmission lines carrying high-voltage power reduce the energy dissipated as heat, making the system more efficient.
-
Connecting Power Plants to Distribution Networks: High-voltage lines transport electricity from large power plants, whether coal, natural gas, or renewable energy sources, to substations for local distribution.
-
Voltage Level Management: Voltage levels are carefully regulated at each stage of the transmission process, using transformers to step up the voltage for long-distance transmission and step it down again for use in homes and businesses.
-
Reliable Long-Distance Transmission: High-voltage power lines enable the transport of electricity across long distances without significant loss of power, which is crucial for urban and rural energy supply.
Types of High-Voltage Transmission Lines
There are several types of high-voltage transmission lines, each serving different purposes based on the specific needs of the power grid:
1. High Voltage AC Transmission Lines
The most common type of transmission line used for electric power transfer is alternating current (AC) high-voltage transmission. These lines carry electricity over long distances from the power generation source to substations where it can be distributed. AC is preferred because it is easier and cheaper to generate and distribute than DC (Direct Current).
2. High Voltage DC Transmission Lines (HVDC)
High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines are used for long-distance power transmission when AC lines become inefficient or impractical. HVDC lines are particularly effective for transmitting power across large distances, especially undersea cables or international borders. HVDC technology helps minimize energy losses and allows for the integration of renewable energy sources that require efficient power transfer.
3. High Voltage Power Lines Map and Routes for Power
The configuration of the high-voltage power lines and the routes for power are vital to the layout of the power grid. These routes are often mapped to optimize transmission efficiency and reliability. Urban areas might use underground high-voltage transmission lines, while rural areas rely more heavily on overhead power lines. The paths of these lines are planned to minimize disruptions, environmental impact, and energy loss.
4. Three-Phase Transmission Lines
Three-phase power is commonly used in high-voltage transmission lines to improve the efficiency of electrical power delivery. The three-phase system uses three separate conductors carrying alternating currents that are phased 120 degrees apart, which enables more efficient power distribution and power flow compared to single-phase systems.
|
Transmission Line Type |
Description |
Key Features |
Typical Applications |
|
High-Voltage AC Transmission |
AC transmission lines used for long-distance power transfer. |
Most common, uses alternating current; typically overhead or underground. |
Power distribution in urban and rural areas, high-voltage substations. |
|
High-Voltage DC Transmission (HVDC) |
DC transmission lines used for long-distance or undersea transmission. |
Reduces energy loss over very long distances, often used for international connections. |
Offshore wind farms, undersea cables, cross-border power transmission. |
|
Three-Phase Transmission Lines |
Uses three-phase electrical power to improve power transfer efficiency. |
Reduces loss, provides a stable and continuous power flow. |
High power applications, industrial facilities, and power grids. |
|
High Voltage Power Lines |
Overhead or underground lines carrying high-voltage electricity. |
Designed for long-distance electricity transport with minimal losses. |
Electric grid connections, long-distance transmission. |
|
High-Voltage Power Lines Map |
Mapping of high-voltage transmission routes to optimize power flow. |
Visualization of transmission routes for optimal energy distribution. |
Planning and monitoring electrical grid infrastructure. |
|
High-Voltage DC Transmission Lines |
Specific to DC lines for optimal energy transfer across vast distances. |
Efficient for long-distance energy transport with minimal losses. |
Renewable energy integration, remote solar and wind power transmission. |
High-Voltage Transmission Lines for Renewable Energy
As the world increasingly shifts towards renewable energy, high-voltage transmission lines have become even more critical for integrating solar, wind, and other renewable power sources into the existing grid. These sources are often located in remote areas far from major population centers, requiring long-distance transmission capabilities.
For example, high-voltage transmission lines are essential for transmitting wind power from offshore wind farms or remote land-based turbines to major urban areas. Similarly, solar farms in sunny regions require robust transmission networks to transport electricity to cities and industrial areas.
Moreover, HVDC transmission lines are increasingly being used to connect regions with high renewable energy potential to national or international grids, facilitating the efficient transport of electricity across borders.

Challenges and Innovations in High-Voltage Transmission Lines
While high-voltage transmission lines are integral to modern power grids, they face several challenges:
-
Aging Infrastructure: Much of the high-voltage transmission infrastructure is aging and in need of upgrades to handle modern demands, including renewable energy integration.
-
Environmental Impact: The construction and maintenance of high-voltage transmission lines can have significant environmental impacts, especially when located in sensitive areas. Innovations such as underground lines and less invasive materials are helping to mitigate these issues.
-
Technological Advancements: Advancements in high-voltage power lines technology, such as superconducting transmission lines and advanced HVDC systems, promise to increase efficiency and reduce power losses further.
High-voltage transmission lines are the backbone of the electric power grid, facilitating the efficient and reliable delivery of power across long distances. As the world transitions towards renewable energy, these lines will play an even more vital role in ensuring that energy from solar, wind, and other sustainable sources reaches consumers efficiently. By understanding how high voltage power lines work, their types, and their importance in power transmission, we can better appreciate their role in shaping the future of global energy systems.
As technology evolves and demand for energy grows, innovations in high-voltage transmission lines will continue to enhance the efficiency of the grid, reduce energy losses, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.