How to Choose the Right High Voltage Switchgear for Your Power System
High voltage switchgear plays a critical role in protecting, controlling, and isolating electrical equipment in modern power systems. As grids become more complex—integrating renewable energy, data centers, and long-distance power transmission—choosing the right HV switchgear is no longer just a compliance issue, but a strategic engineering decision.
1. What Is High Voltage Switchgear?
High voltage switchgear refers to a combination of electrical equipment, including circuit breakers, disconnect switches, protection relays, and control devices, designed to operate typically above 35 kV.
Its core functions include:
- Switching power transmission circuits
- Protecting electrical systems from short circuits and overloads
- Isolating faulty sections safely
- Ensuring the reliability of power distribution networks
In ANSI/IEEE systems, HV switchgear is widely used in substations, power plants, renewable energy integration points, and data centers.

2. Typical Voltage Levels and Standards (ANSI/IEEE)
Different voltage levels require different switchgear designs and insulation strategies.
Table 1: Common Voltage Levels for HV Switchgear
|
Voltage Class |
Nominal Voltage |
Typical Applications |
|
Medium Voltage |
5–35 kV |
Industrial plants, data centers |
|
High Voltage |
69–230 kV |
Transmission substations |
|
Extra High Voltage |
345–800 kV |
Long-distance power transmission |
Key ANSI/IEEE Standards include:
- IEEE C37 series (switchgear & breakers)
- ANSI C84.1 (voltage ratings)
- IEEE C37.04 / C37.06 (HV circuit breaker ratings)
3. Main Types of High Voltage Switchgear
Selecting the correct type of switchgear depends on space, safety, maintenance philosophy, and environmental constraints.
Table 2: Types of High Voltage Switchgear Comparison
|
Type |
Insulation Medium |
Key Advantages |
Typical Use |
|
Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS) |
Air |
Lower cost, simple design |
Outdoor substations |
|
Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS) |
SF₆ / eco-gas |
Compact, high reliability |
Urban & data centers |
|
High Voltage Hybrid Switchgear |
Air + Gas |
Balance of cost & footprint |
Modern substations |
|
Modular Switchgear |
Varies |
Flexible expansion |
Renewable & smart grids |
High voltage hybrid switchgear is increasingly popular due to its reduced footprint and improved safety without the full cost of GIS.
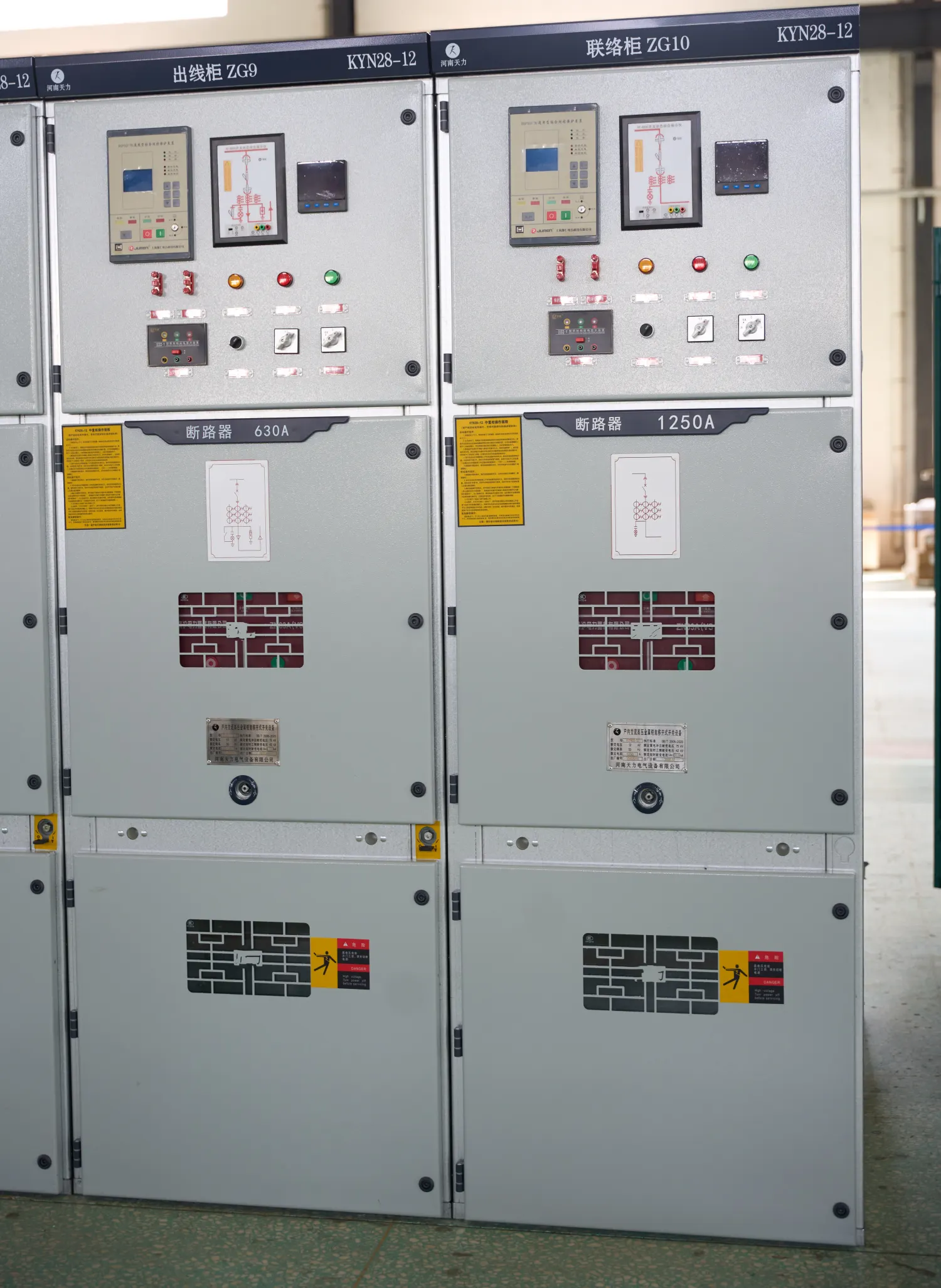

4. Role of HV Circuit Breakers
At the heart of every HV switchgear lineup is the HV circuit breaker, which interrupts fault currents and protects the power system.
Common HV Circuit Breaker Types
- SF₆ Circuit Breakers – High dielectric strength, compact
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers – Mostly MV but expanding upward
- Oil Circuit Breakers – Largely phased out due to maintenance
- Hybrid Breakers – Used in HVDC and advanced grids
Table 3: HV Circuit Breaker Selection Factors
|
Parameter |
Importance |
|
Short-circuit rating |
Must exceed system fault level |
|
Operating duty cycle |
Frequent vs infrequent switching |
|
Insulation coordination |
Based on voltage level |
|
Maintenance interval |
Critical for remote substations |
5. MV and HV Breaker Coordination in Power Systems
Modern electrical systems often include both medium voltage and high voltage breakers working together.
- MV breakers protect feeders and loads
- HV breakers isolate transmission-level faults
- Coordination ensures selective tripping, minimizing outages
This coordination is essential in data centers, where uptime is mission-critical.
6. Application-Specific Switchgear Selection
Power Transmission & Distribution
- Requires high short-circuit withstand capability
- AIS or hybrid switchgear commonly used
- Designed for outdoor, harsh environments
Data Centers
- Preference for GIS or compact modular designs
- High reliability and low maintenance
- Enhanced arc-flash protection
Renewable Energy Integration
- Rapid switching and grid protection
- Modular and expandable switchgear
- Compatibility with fluctuating generation sources
7、HV Switchgear Selection Flowchart for Engineers
Choosing the right high voltage switchgear requires a structured decision process that balances voltage level, application environment, protection requirements, and lifecycle cost.
The following HV switchgear selection flowchart provides a practical step-by-step guide used by power system engineers.
HV Switchgear Selection Flowchart (Text-Based)
START
│
├─► Step 1: Determine System Voltage Level
│ ├─ 5–35 kV → Medium Voltage Switchgear
│ └─ > 35 kV → High Voltage Switchgear
│
├─► Step 2: Identify Application Scenario
│ ├─ Power Transmission Substation
│ ├─ Power Distribution Network
│ ├─ Data Center / Critical Load
│ └─ Renewable Energy Integration
│
├─► Step 3: Assess Installation Environment
│ ├─ Outdoor, Space Available → AIS
│ ├─ Indoor / Urban, Limited Space → GIS
│ └─ Mixed Conditions → Hybrid Switchgear
│
├─► Step 4: Evaluate Short Circuit & Fault Level
│ ├─ High Fault Current → High-rated HV Circuit Breaker
│ └─ Moderate Fault Current → Standard HV Breaker
│
├─► Step 5: Select Circuit Breaker Technology
│ ├─ SF₆ Circuit Breaker
│ ├─ Vacuum (mainly MV, limited HV)
│ └─ Hybrid / Eco-Gas Breaker
│
├─► Step 6: Consider Operation & Maintenance Strategy
│ ├─ Low Maintenance Priority → GIS / Hybrid
│ └─ Cost-Sensitive → AIS
│
├─► Step 7: Future Expansion & Modular Needs?
│ ├─ Yes → Modular / Hybrid Switchgear
│ └─ No → Conventional Configuration
│
└─► FINAL SELECTION: Optimized HV Switchgear Solution8.How to Use This HV Switchgear Selection Flowchart
Step 1: Voltage Level Defines the Foundation
The voltage level immediately determines whether the system falls under medium voltage or high voltage switchgear, influencing insulation design, breaker type, and standard compliance (ANSI/IEEE).
Step 2: Application Drives Reliability Requirements
Different applications demand different priorities:
- Power transmission → high short-circuit withstand, outdoor durability
- Power distribution → operational flexibility
- Data centers → compact design, high reliability, low downtime
- Renewable energy → modular design, fast switching, grid compatibility
Step 3: Installation Environment Determines Switchgear Type
- AIS (Air-Insulated Switchgear)
Best for outdoor substations with ample space and cost sensitivity. - GIS (Gas-Insulated Switchgear)
Ideal for urban areas and data centers where space is limited. - High voltage hybrid switchgear
A balanced solution combining footprint reduction with cost efficiency.
Step 4: Short Circuit Level Is a Critical Safety Factor
HV switchgear must protect electrical systems from short circuit events.
The circuit breaker’s interrupting rating must always exceed the system’s calculated fault current.
Step 5: Circuit Breaker Technology Selection
Modern HV circuit breakers are chosen based on:
- Interrupting capacity
- Environmental considerations
- Maintenance cycles
SF₆ breakers remain common, while eco-gas and hybrid breakers are gaining adoption under sustainability goals.
Step 6: Maintenance Philosophy Impacts Lifecycle Cost
- GIS and hybrid switchgear reduce maintenance frequency
- AIS offers easier inspection but higher long-term labor costs
This step is critical for remote substations and power transmission lines.
Step 7: Future-Proofing Through Modular Designs
If system expansion is expected:
- Choose modular switchgear
- Enable digital monitoring and protection upgrades
This is especially important in energy transition projects and smart grids
9. Why This Flowchart Matters in Modern Power Systems
Using a structured HV switchgear selection flowchart helps engineers:
- Reduce design errors
- Improve system reliability
- Optimize capital and operating cost
- Ensure compliance with ANSI/IEEE standards
In today’s evolving power transmission and power distribution networks, systematic selection is no longer optional—it is essential.
10. How to Choose the Right Switchgear: Decision Matrix
Table 4: HV Switchgear Selection Matrix
|
Criteria |
AIS |
GIS |
Hybrid |
|
Space availability |
High |
Low |
Medium |
|
Initial cost |
Low |
High |
Medium |
|
Maintenance |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
|
Environmental sensitivity |
Low |
High |
Medium |
|
Future expansion |
Limited |
Moderate |
High |
This matrix helps engineers choose the right switchgear based on technical and economic priorities.
11. Short Circuit and Protection Considerations
HV switchgear protects electrical systems against:
- Short circuit faults
- Ground faults
- Switching surges
Proper protection design includes:
- Correct breaker interrupting capacity
- Relay coordination
- Insulation coordination
Failing to size switchgear correctly can lead to catastrophic equipment damage.
12. Modular Designs and Future-Proof Power Systems
Modern power systems demand flexibility. Modular switchgear designs allow:
- Faster installation
- Easier upgrades
- Integration with digital monitoring
This is particularly important for:
- Energy transition projects
- Smart grids
- Expanding industrial facilities
13. Building a Safe and Efficient Power System
Choosing the right high voltage switchgear is a balance between:
- Voltage levels
- System fault requirements
- Application environment
- Long-term operational cost
By understanding types of switchgear, HV circuit breakers, modular designs, and ANSI/IEEE standards, engineers can design reliable, safe, and future-ready power systems.
As power transmission networks expand and data centers and renewables grow, well-selected HV switchgear remains the backbone of modern electrical infrastructure