Concentric Cable: Design, Applications, and Key Benefits in Power Systems
1. What is a Concentric Cable?
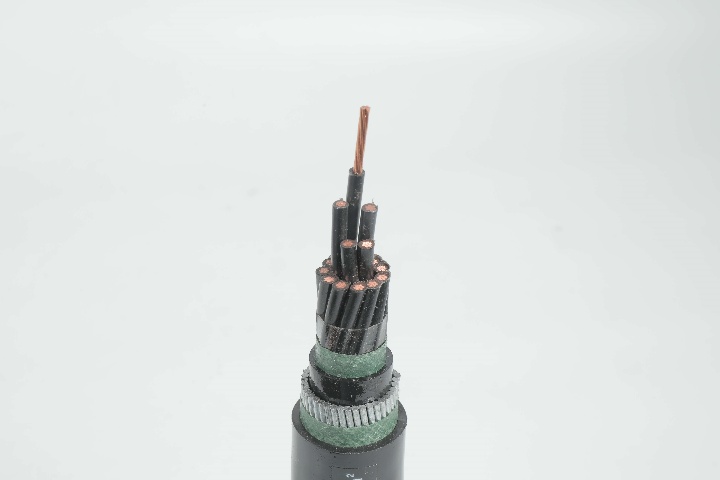
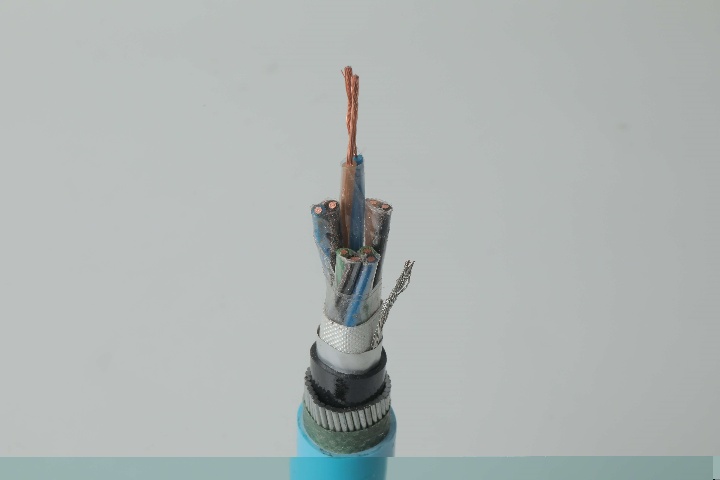
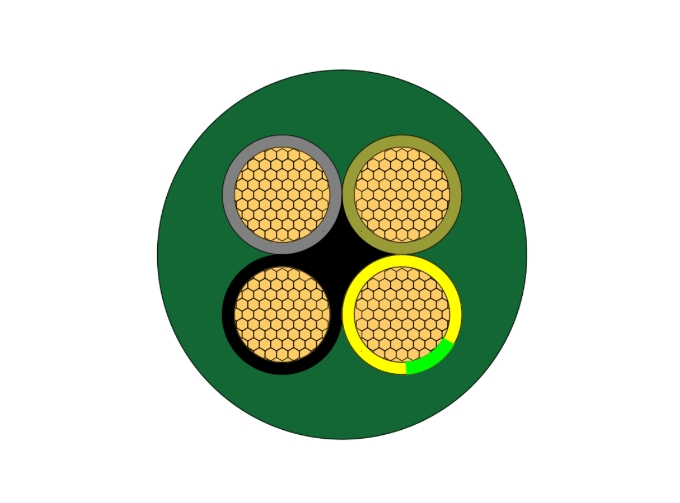
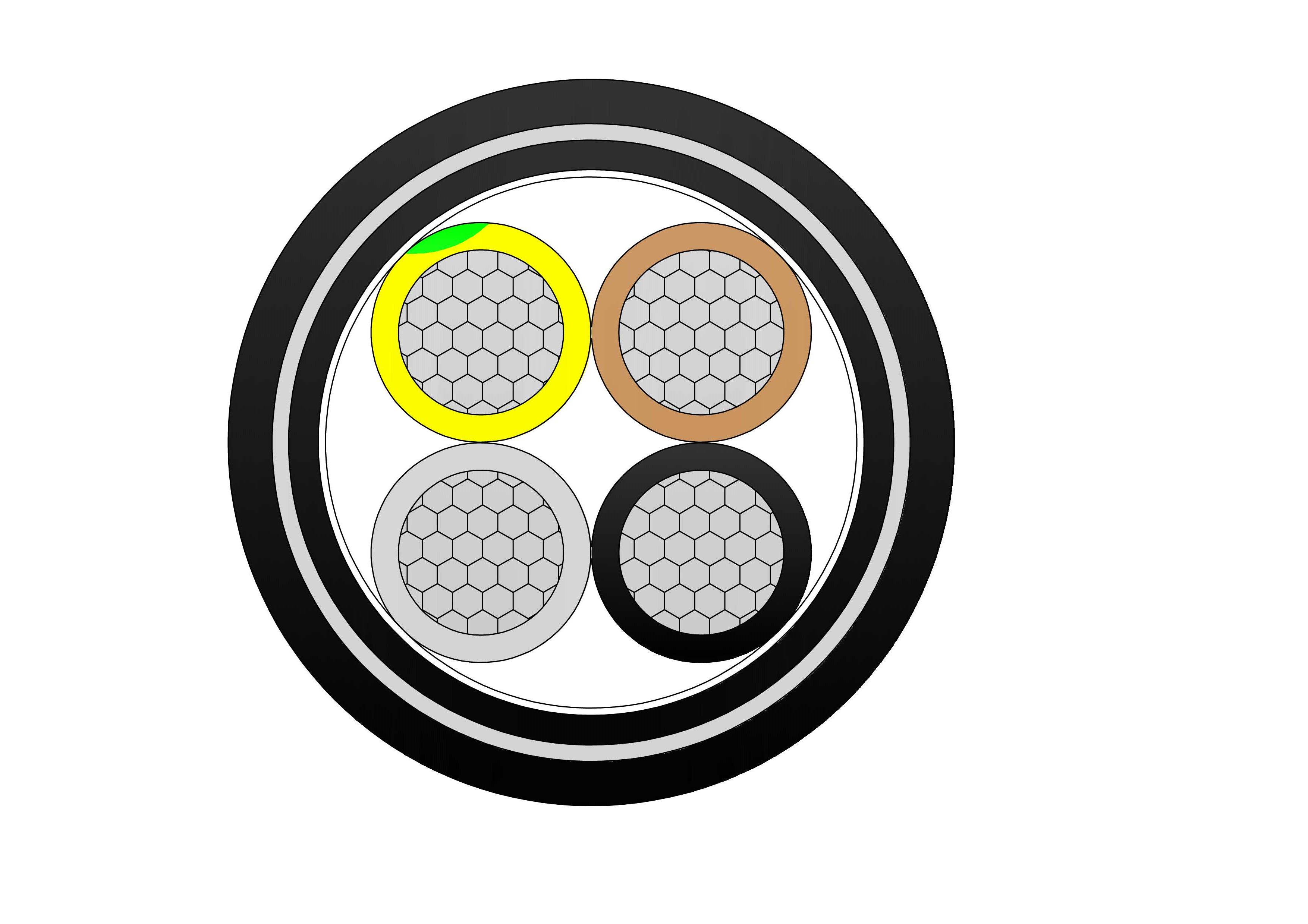
Concentric cables are specialized cables widely used in power distribution systems. They have a unique structure with a central main conductor surrounded by one or more concentric conductors. These outer conductors, typically used as neutral or grounding wires, are evenly wound in a spiral around the central conductor. This design not only ensures excellent electrical continuity and a safe current loop but also enhances the cable's mechanical strength and interference resistance. Concentric cables are commonly used in urban power distribution, industrial power supply, and underground power grids, offering high reliability and convenient installation and maintenance.
In practical applications, concentric cables are widely used in low- and medium-voltage networks, underground distribution systems, and service entrances. The design enhances electrical performance and allows for simplified grounding, which is essential for safety in modern installations.
2. Structural Design and Components
The typical structure of a concentric cable includes:
- Central Conductor: Made of copper or aluminum, serving as the main current-carrying core.
- Insulation Layer: High-grade polyethylene (XLPE or PVC) that provides electrical insulation and thermal protection.
- Concentric Neutral Layer: Multiple strands of smaller conductors wrapped around the insulation, functioning as both neutral and grounding path.
- Outer Sheath: A protective jacket designed to resist moisture, abrasion, and UV radiation.
This layered configuration provides not only electrical reliability but also mechanical durability, making the cable ideal for both indoor and outdoor use.
3. Types of Concentric Cables
Concentric cables come in several variations based on system requirements:
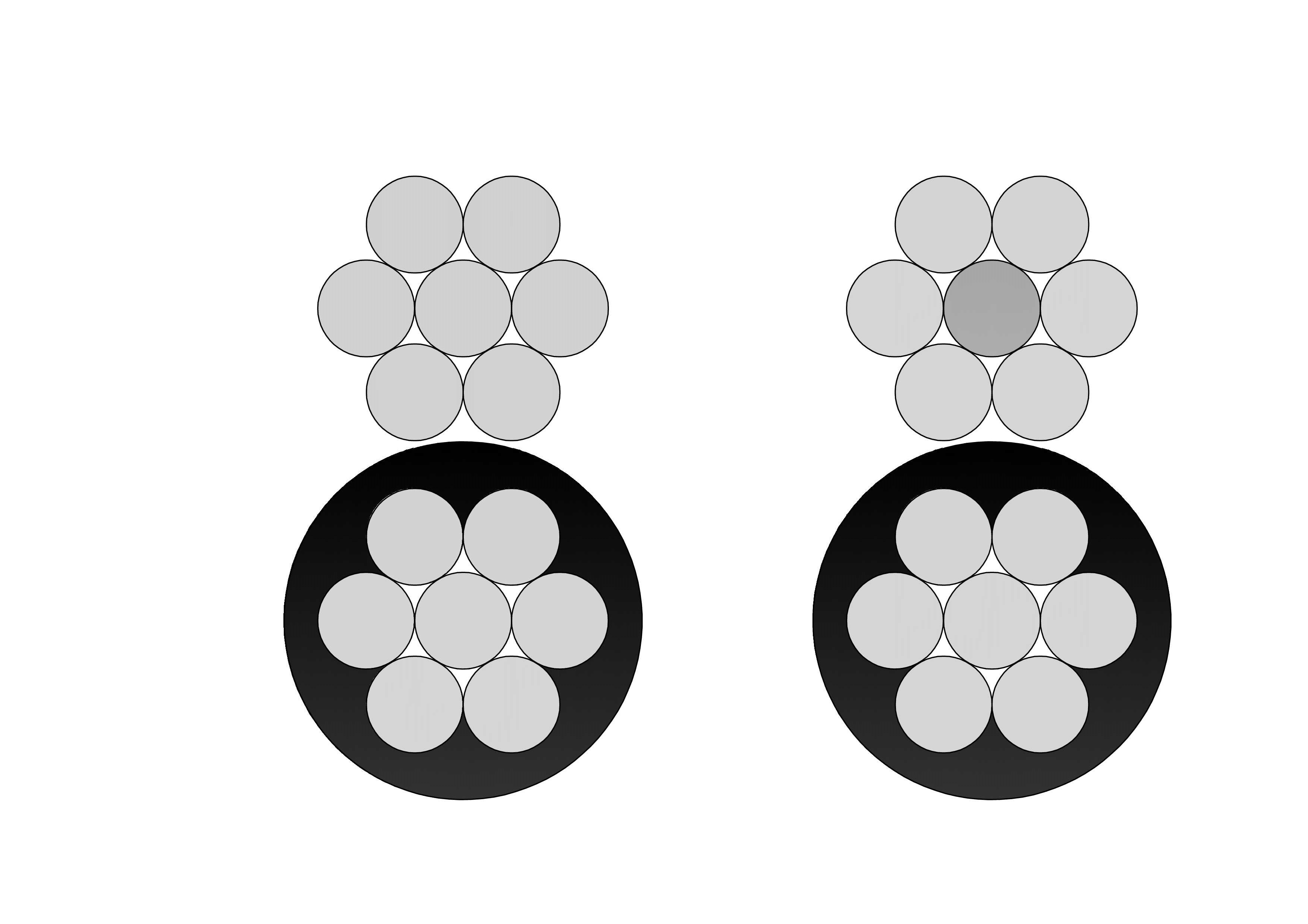
- Concentric Neutral Cable: Common in distribution networks, where the outer neutral conductors maintain consistent electrical potential, ensuring balanced current flow.
- Split Concentric Cable: Features separate neutral and earth conductors in the outer layer, offering better fault detection and improved grounding in domestic or commercial installations.
- Armored Concentric Cable: Includes an additional steel tape or wire armor layer for protection against physical damage in industrial or buried environments.
Each type is designed to meet specific IEC and UL standards, ensuring compliance and safety in various regions.
4. Working Principle and Electrical Performance
In operation, the central conductor carries the load current, while the outer concentric neutral conductors act as the return path for current flow. This design minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI), reduces voltage drop, and enhances system efficiency.
From a practical engineering perspective, the concentric configuration ensures:
- Equal potential distribution around the cable.
- Enhanced fault current return in case of insulation failure.
- Improved shielding against external electrical noise.
This makes concentric cables particularly valuable in smart grid systems, urban distribution networks, and renewable energy projects.

5. Applications in Power Systems
Concentric cables are used across a wide range of power applications:
- Utility Service Drops: For connecting power from overhead lines to residential or commercial premises.
- Underground Distribution Networks: Their robust insulation and grounding system make them suitable for buried installations.
- Renewable Energy Systems: In solar and wind installations, concentric cables ensure stable current return paths and safety under variable load conditions.
- Industrial Power Distribution: Providing reliable grounding and reduced electromagnetic interference in control and automation systems.
In many cases, aluminum concentric neutral cables are chosen for their lightweight and cost-effective properties, while copper concentric cables are preferred for high-conductivity applications.
6. Key Benefits of Concentric Cables
|
Feature |
Technical Benefit |
Practical Advantage |
|
Integrated Neutral Path |
Simplifies circuit design |
Reduces installation time |
|
Enhanced Safety |
Improved grounding and fault management |
Prevents electric shock and fire |
|
Durability |
Resistant to corrosion, moisture, and mechanical damage |
Long service life |
|
Low Electromagnetic Interference |
Balanced current return path |
Stable signal quality |
|
Versatility |
Suitable for indoor, outdoor, and underground use |
Broad application range |
These benefits explain why we use concentric cable in modern electrical networks — reliability, safety, and reduced operational cost make them a standard choice for utilities and contractors alike.
7. Future Trends and Technological Advancements
With the growth of smart grids and distributed energy systems, the role of concentric cables is expanding. Future innovations focus on:
- Improved insulation materials (e.g., cross-linked polymers for higher temperature resistance).
- Enhanced corrosion-resistant sheathing for marine and offshore use.
- Integration with smart monitoring systems that can detect temperature and load variations in real time.
As the demand for renewable and decentralized power grows, concentric cables will continue to evolve, supporting a more efficient and sustainable energy infrastructure.
In conclusion, concentric cables play an essential role in ensuring safe, reliable, and efficient power transmission. Their unique design, combining conductor, insulation, and grounding in a single structure, makes them indispensable in both traditional and modern electrical systems.
Whether it’s for urban power distribution, renewable energy integration, or utility service connections, the concentric cable offers a balanced solution that meets the technical, economic, and safety demands of today’s power networks.