25kV XLPE-HDPE Tree Wire: High-Durability Solution for Modern Power Networks
Power companies face numerous challenges, including extreme weather, vegetation contact, wildlife disturbance, and increasing demands for power reliability. To address these issues, 25kV XLPE-HDPE insulated tree conductors have become one of the most widely used solutions for overhead distribution networks. Tree conductors combine advanced insulation materials with robust mechanical strength, significantly reducing electrical faults, improving system safety, and extending service life.
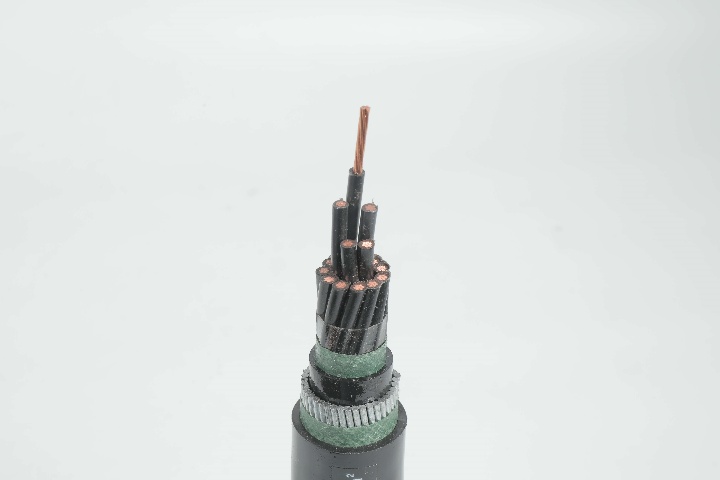
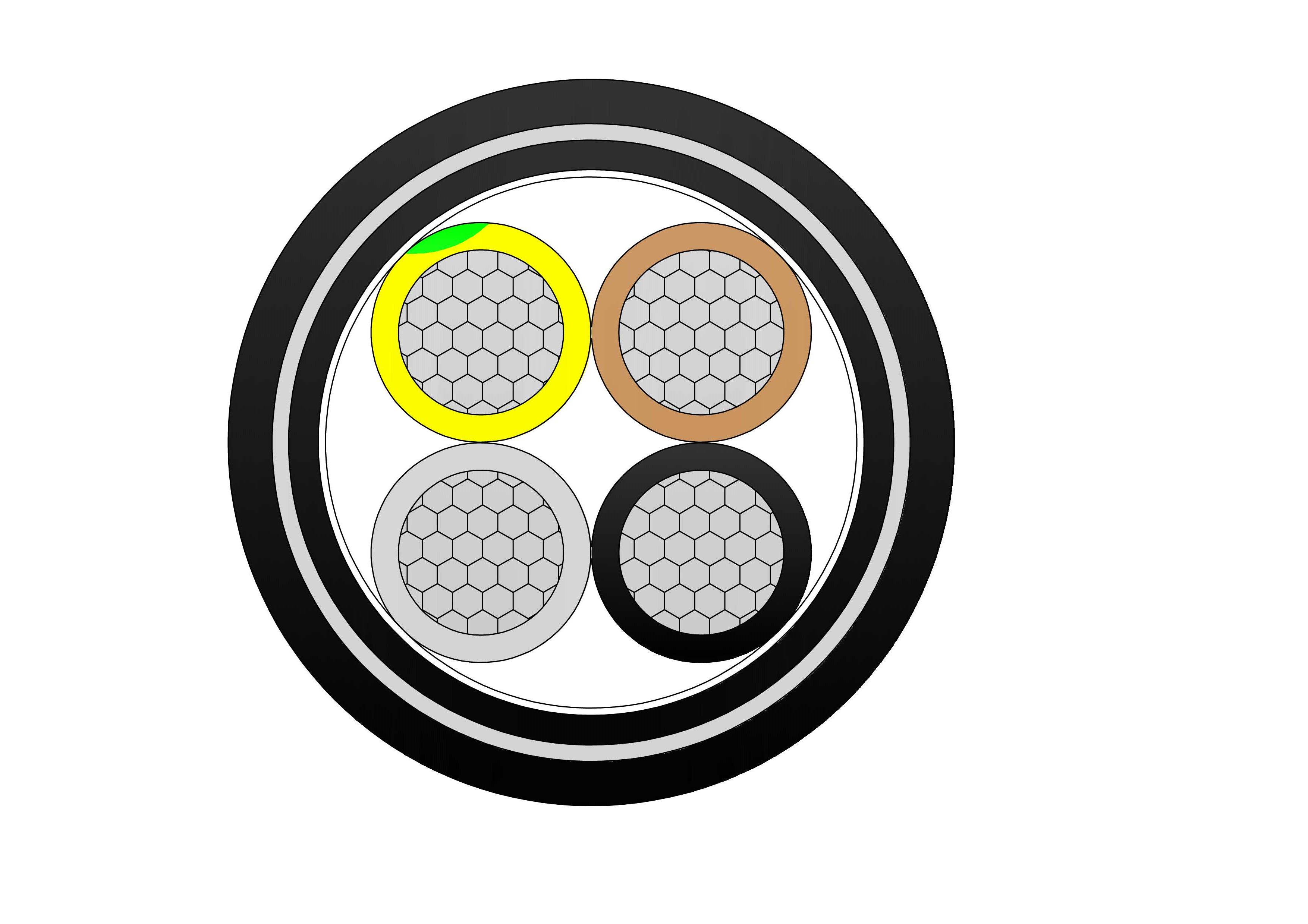
Tree conductors (sometimes also called tree cables) are coated conductors specifically designed for overhead applications where contact with vegetation is unavoidable. Unlike bare conductors, tree conductors feature a double-insulation structure, typically an inner XLPE insulation layer and an outer HDPE protective layer, offering properties such as abrasion resistance, moisture resistance, UV resistance, and electrical stress resistance. This structure makes them suitable for operation at 15kV, 25kV, and 35kV distribution levels.
1. Engineering Purpose of Tree Wire in Distribution Networks
From an engineering perspective, tree wire plays a crucial role in medium-voltage rural and suburban networks where maintaining clearances between conductors and vegetation is challenging. Because outages caused by falling branches are one of the leading causes of feeder interruptions, utilities increasingly rely on tree wire to mitigate contact-related faults.
Key engineering objectives include:
-
Reducing line faults caused by vegetation, animals, and severe weather
-
Increasing line reliability in forested or windy regions
-
Enhancing safety for field personnel and the public
-
Extending the maintenance cycle by reducing the frequency of tree trimming
-
Improving resistance to moisture, sunlight, and mechanical stress
Tree wire is not an insulated power cable; it is a covered conductor. The covering provides dielectric protection but is not intended for continuous grounded contact. It significantly delays flashovers, giving distribution protection systems more time to react.
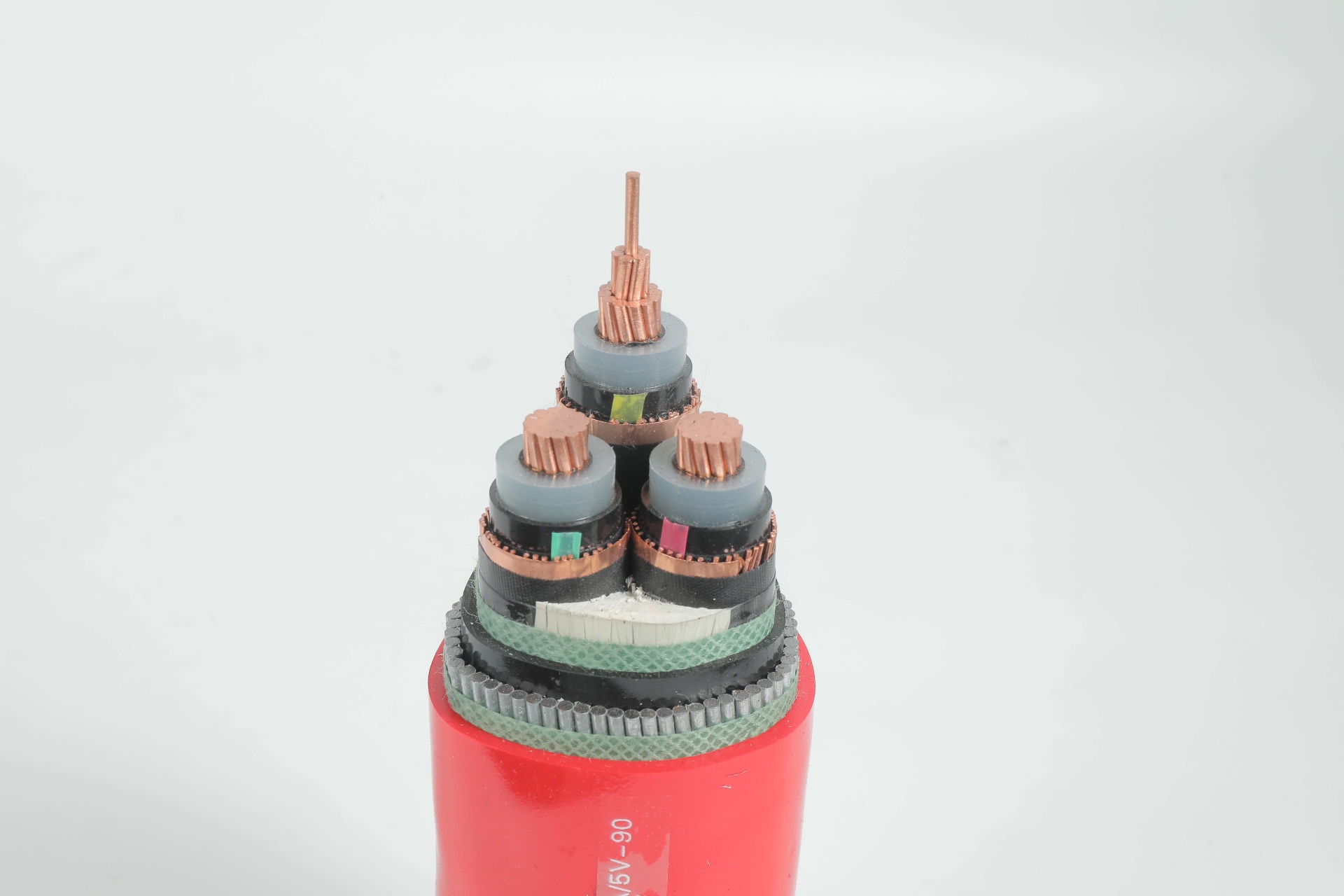
2. Material Composition: XLPE + HDPE Dual-Layer System
The typical 25kV tree wire structure includes:
-
Conductor
Usually, aluminum or AAAC is selected for conductivity and weight balance.
-
XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) Inner Layer
-
Provides primary electrical insulation
-
Excellent dielectric strength
-
Low dielectric loss
-
Strong resistance to electrical treeing
-
-
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Outer Jacket
-
provides mechanical protection
-
High wear, moisture, and UV resistance
-
Prevents damage from branches and wildlife
-
High surface hardness for environmental durability
-
The synergy between XLPE and HDPE ensures that 25kV XLPE-HDPE tree wire performs reliably in harsh field conditions.
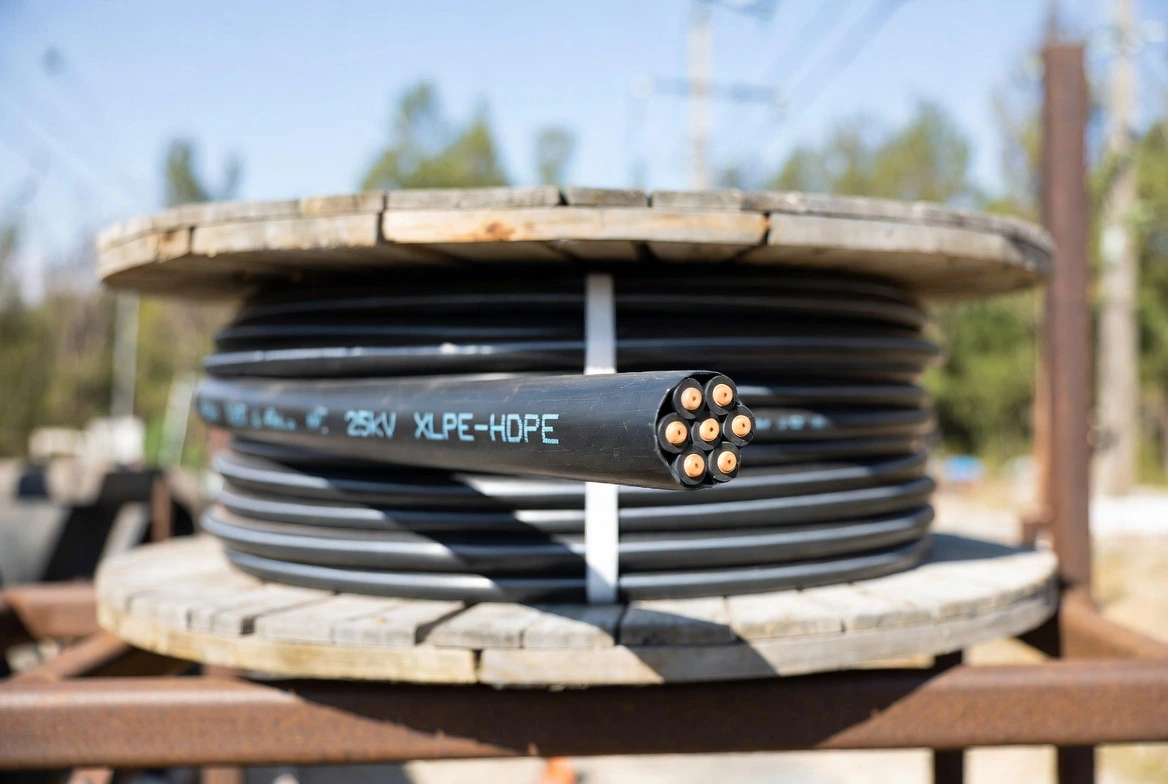

3. Performance Advantages in Real Utility Applications
From field engineering to long-term operations, tree wire provides measurable performance benefits:
3.1 Enhanced Reliability
Tree wire significantly reduces transient faults caused by momentary tree contact. Unlike bare conductors, the insulated design prevents immediate flashover, which is essential for:
-
Rural overhead networks
-
Mountainous or forested areas
-
High-wind regions
3.2 Lower Maintenance Costs
Because vegetation contact does not immediately result in outages, utilities can reduce tree-trimming cycles, saving significant O&M costs over the lifetime of the feeder.
3.3 Improved Safety and Reduced Outage Frequency
The covered structure minimizes:
-
Phase-to-ground faults
-
Fire risks
-
Wildlife-induced outages
-
Weather-related failures
3.4 Long-Term Durability
XLPE and HDPE materials provide strong resistance to:
-
UV degradation
-
Moisture and rain
-
Abrasion from branches
-
Salt spray in coastal zones
As a result, tree wire installations typically achieve service lives of 30–40 years, depending on environmental conditions.
4. Typical Applications of 15kV, 25kV, and 35kV Tree Wire
Tree wire can be deployed in the following medium-voltage systems:
-
Overhead distribution feeders (primary)
-
Rural electrification networks
-
Coastal and tropical climates require corrosion resistance
-
Mountainous and forested areas
-
Utility grid modernization projects
-
Areas with frequent storms or falling branches
For 15kV and 25kV networks, three-wire is the most common solution. For long spans or high mechanical loads, 35kV tree wire offers additional insulation and strength.
5. Technical Specification Table (Typical)
| Item | Specification |
| Rated Voltage | 25 kV (also available in 15 kV, 35 kV) |
| Conductor Material | AAC / AAAC / ACSR |
| Inner Insulation | XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) |
| Outer Jacket | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
| Temperature Rating | 90°C normal operation |
| UV Resistance | Excellent |
| Water Resistance | High |
| Typical Application | Overhead distribution lines, forested areas |
| Fault Reduction Capability | High for vegetation contact |
| Expected Service Life | 30–40 years |
Utilities may request customized conductor sizes or jacket thicknesses depending on mechanical load requirements.
6. Installation Considerations in Real Utility Projects
Practical engineering considerations when deploying 25kV tree wire include:
6.1 Proper Clearance and Sag
Although tree wire resists vegetation contact, utilities still maintain minimum clearances for operational safety and to prevent long-term abrasion.
6.2 Conductor Strength and Span Length
AAAC conductors are preferred for long spans due to better tensile strength-to-weight ratios.
6.3 Accessories Compatibility
All clamps, connectors, dead-ends, and spacers must be certified for covered conductor applications to avoid insulation damage.
6.4 Environmental Conditions
In areas with heavy ice loading, larger conductor sizes or reinforced designs may be required.
6.5 Inspection and Condition Monitoring
Periodic visual inspections are recommended to detect jacket damage, wildlife activity, or mechanical wear.
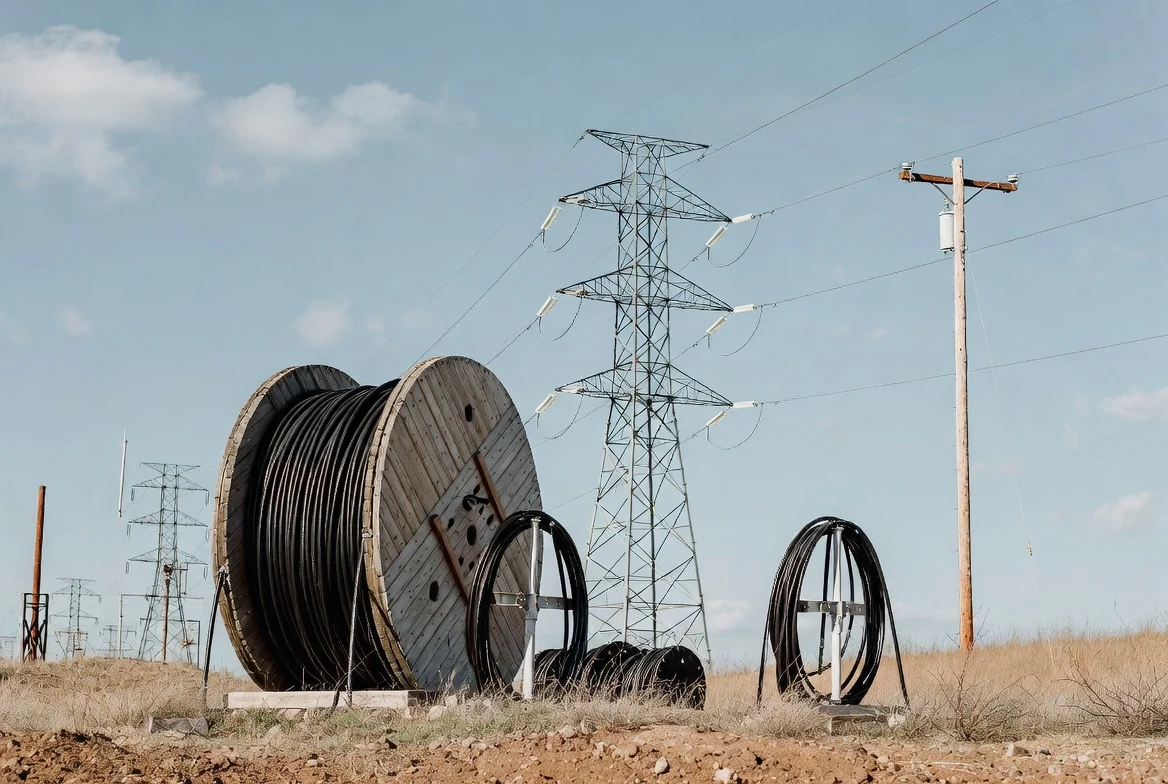

25kV XLPE-HDPE tree wire delivers a robust, reliable, and cost-effective solution for medium-voltage overhead distribution grids. With its dual-layer insulation, high dielectric performance, and exceptional durability, it meets the increasing demands of modern utilities seeking to reduce outages, improve public safety, and extend asset life. As grid modernization accelerates, tree wire—together with smart grid equipment and advanced monitoring—is playing an increasingly important role in building resilient, long-term, and low-maintenance distribution networks.














2Y-high-voltage-power-cable-2.webp)
